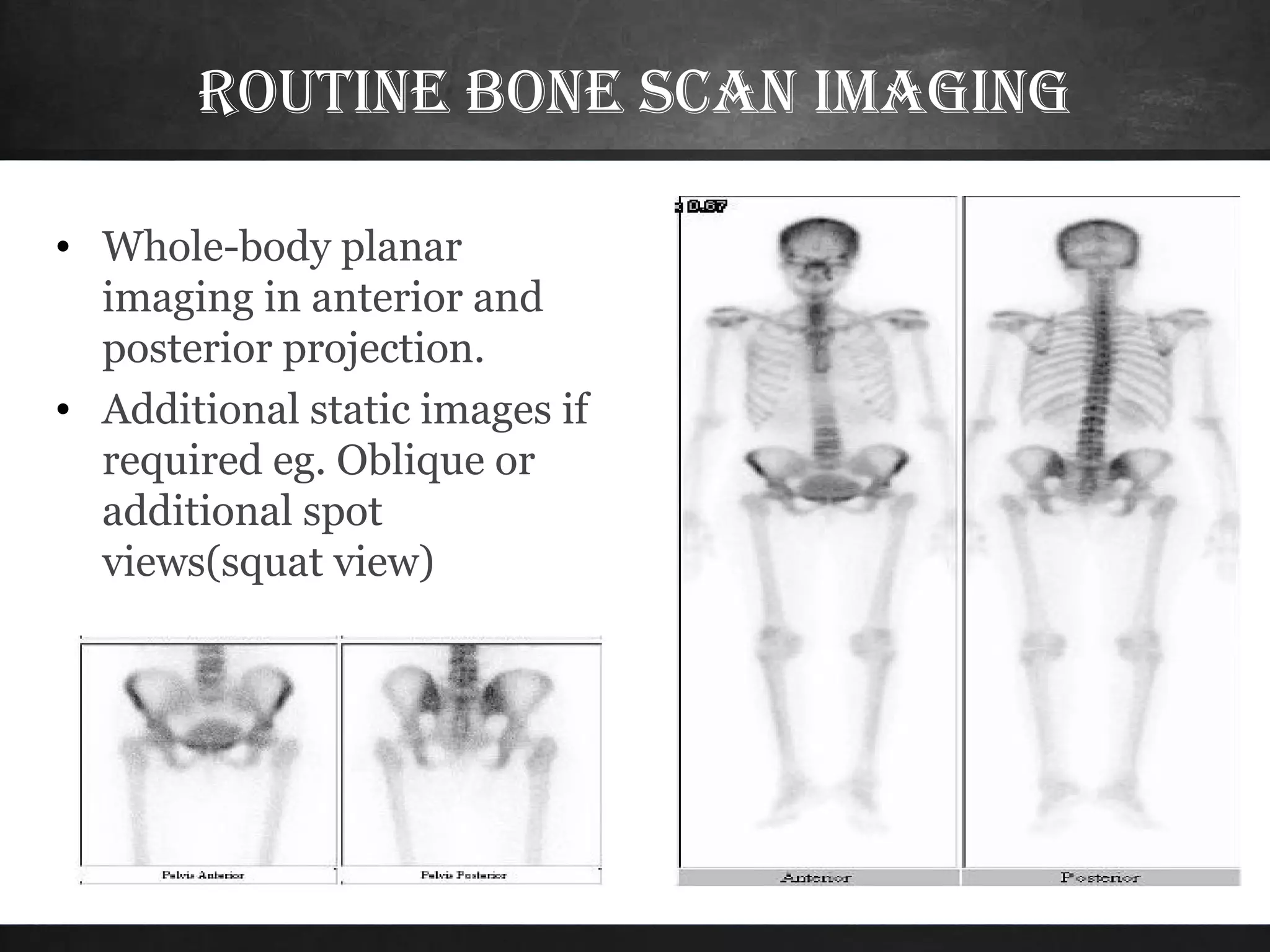
A bone scan is a sensitive imaging test that uses radiopharmaceuticals like Tc-99m MDP to detect areas of bone activity, indicating possible injury or disease. While it's valuable for diagnosing various conditions such as tumors, fractures, and infections, it has limitations including low specificity and high costs. The procedure typically includes whole-body planar imaging, with multiple phases to assess vascular, soft tissue, and bone activity.