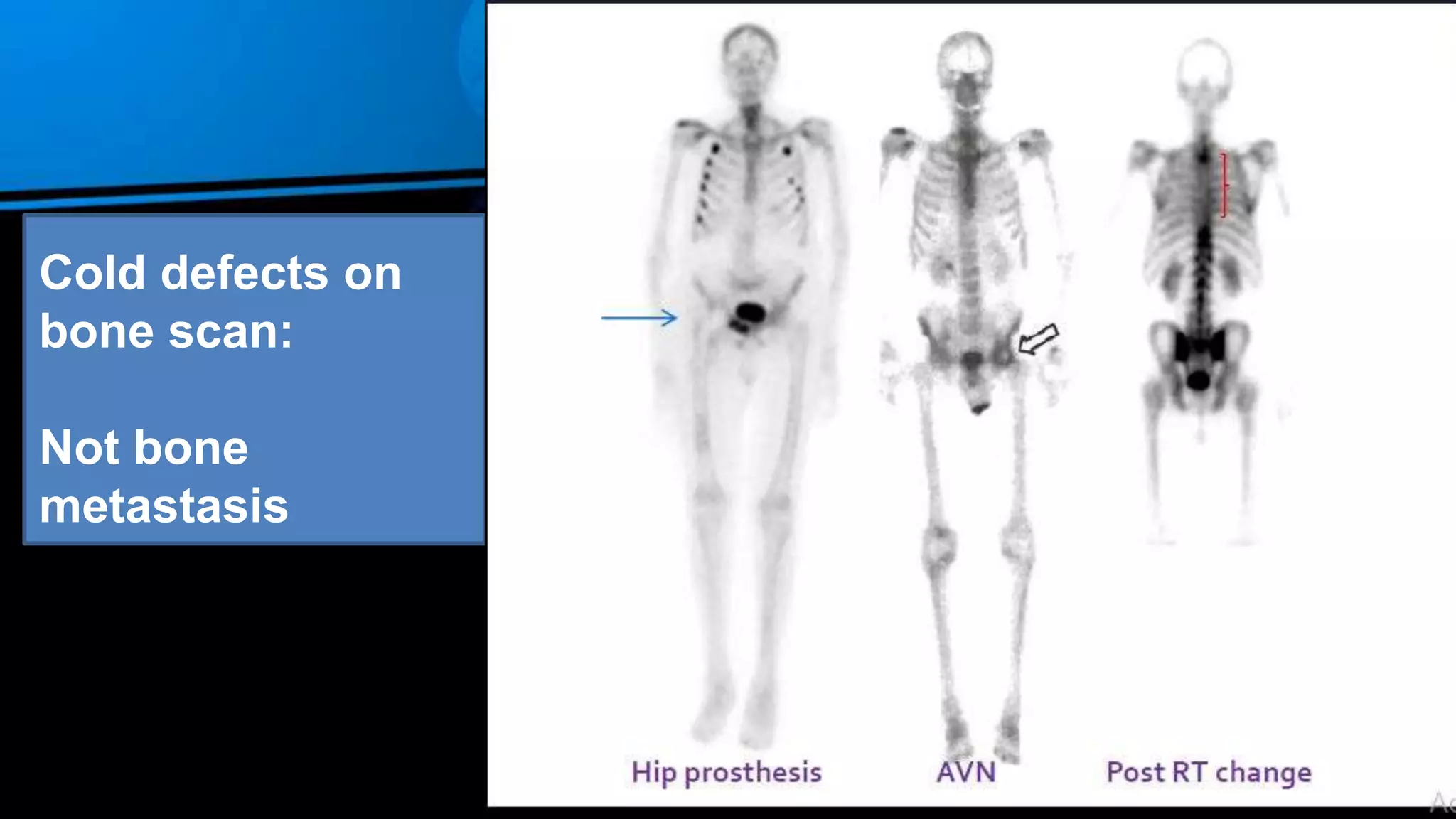
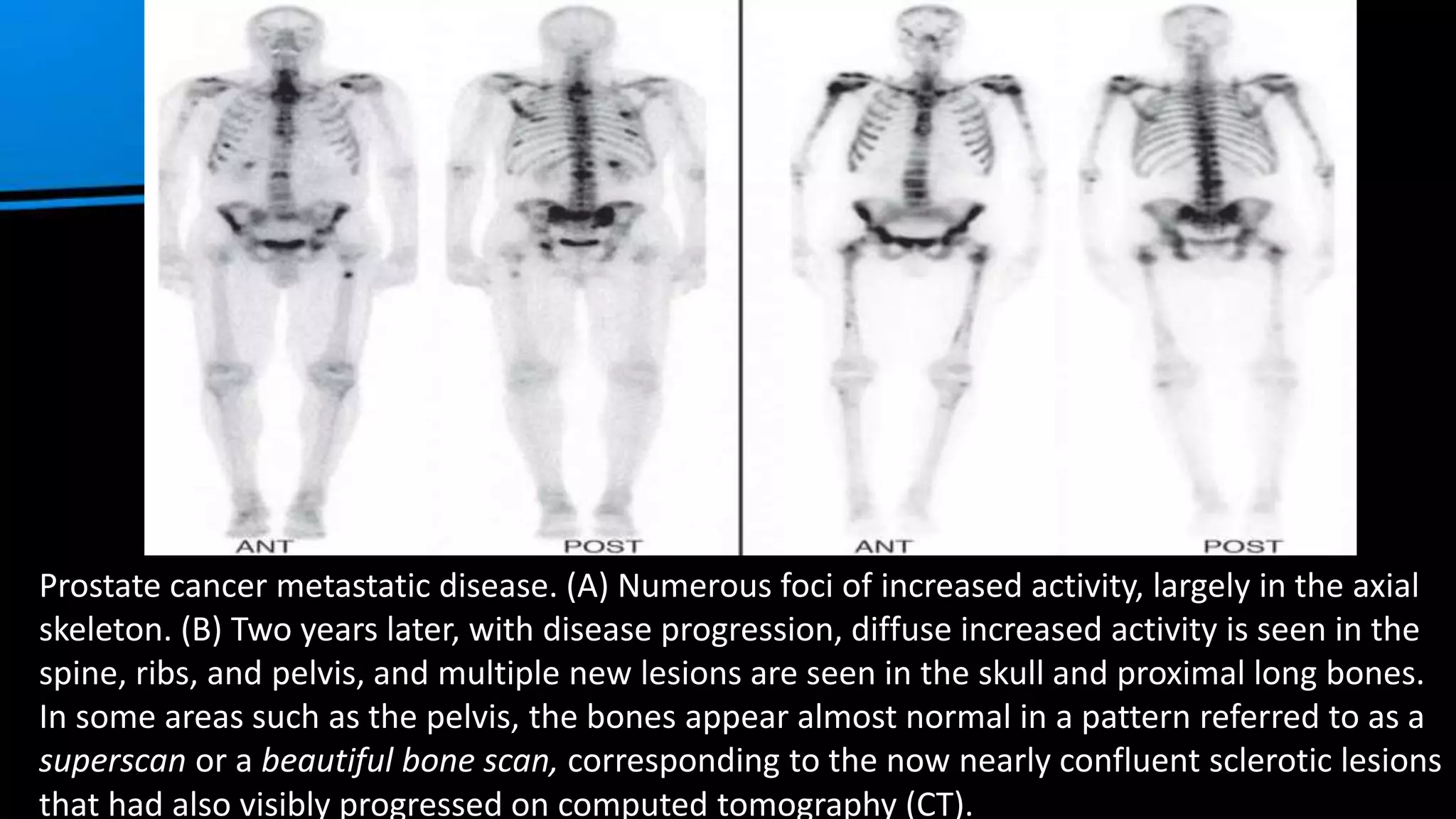
1. The document discusses bone scintigraphy (bone scan), providing information on its uses, procedures, interpretations, and applications.
2. A bone scan uses radiopharmaceuticals like technetium-99m MDP to detect areas of abnormal bone metabolism that could indicate conditions like fractures, infections, tumors and metastases.
3. It is a sensitive test but not specific, so findings must be interpreted in the full clinical context. The document outlines patterns for various bone diseases and cancers.