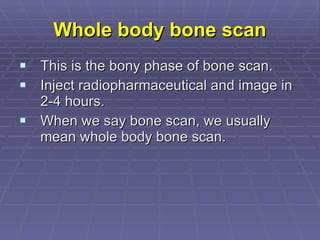
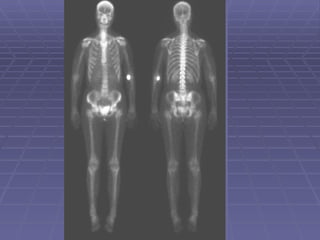
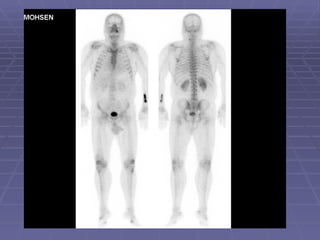
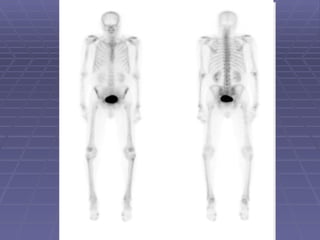
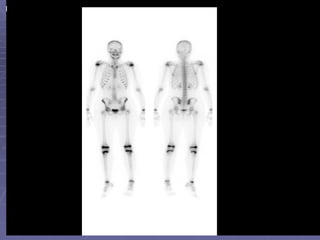
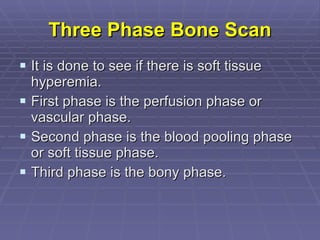
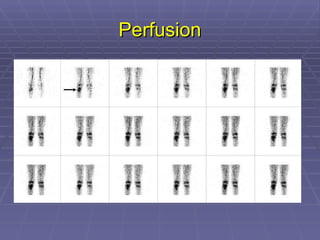
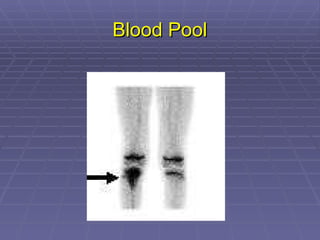
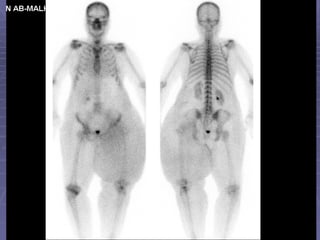
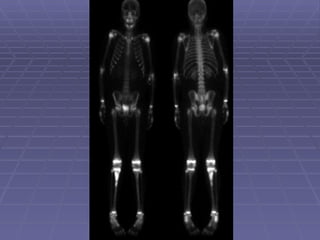
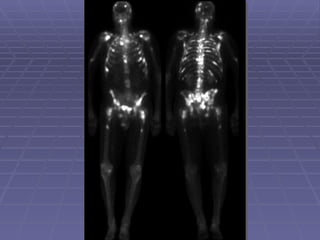
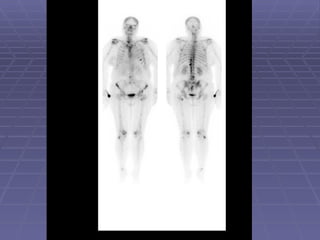
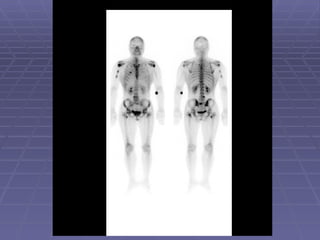
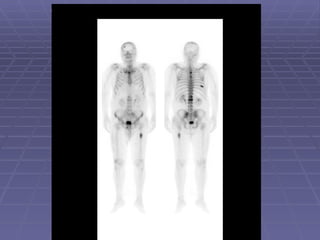
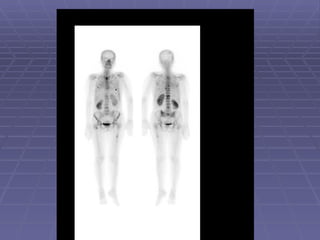
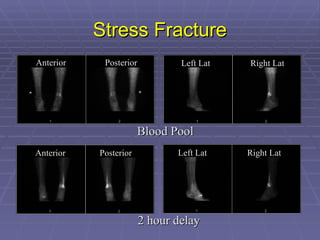
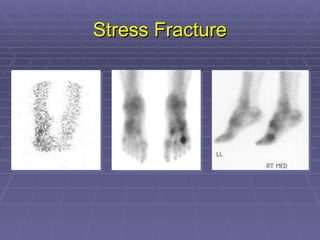
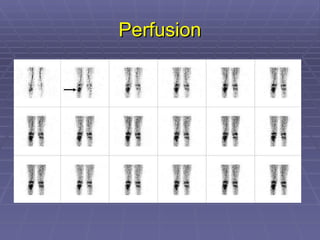
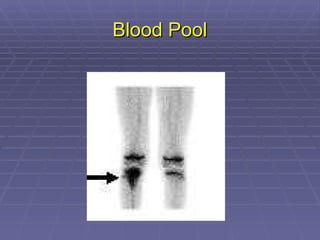
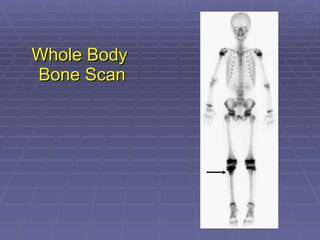
Bone isotope scans are a sensitive method for detecting bone abnormalities. They involve injecting radioactive tracers that are drawn to bone tissue, allowing areas of abnormal bone metabolism to be visualized. Common clinical uses include detecting bone cancer metastases, stress fractures, and infections like osteomyelitis. The scan may reveal single or multiple problematic areas and provides diagnostic information beyond plain X-rays.




![Mechanism of Localization Phosphate groups bind to the hydroxyapatite [Ca3(Po4)2] structure of bone tissue by a mechanism called chemisorption. The hydroxyapatite structure of the bone is exposed during bone remodeling. So, more radiopharmaceutical will deposit in that region giving “hot” area. 50-60% of injected dose localized on bone, remain dose is cleared by kidneys.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-bonescan2010-120202131218-phpapp02/85/2-bone-scan-2010-5-320.jpg)