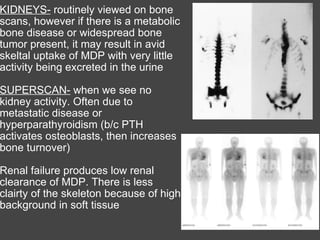
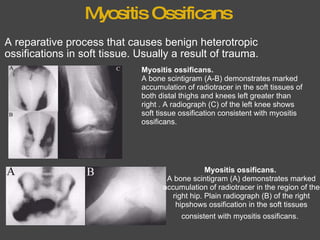
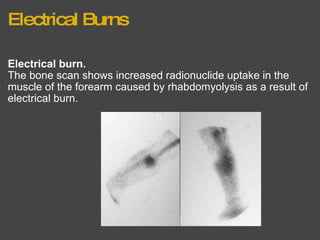
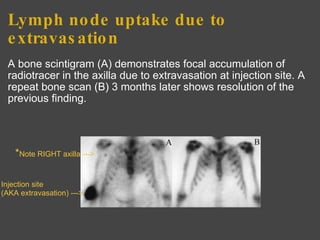
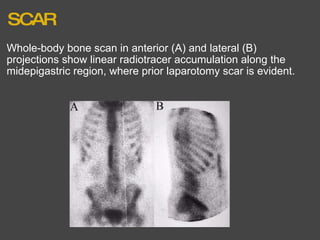
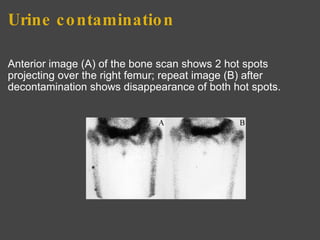
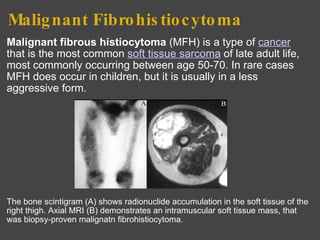
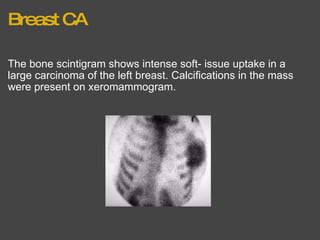
The bone scan shows normal uptake in kidneys, joints, and growing bones in children. Increased uptake elsewhere can indicate metastatic bone disease, hyperparathyroidism, or renal failure. Soft tissue uptake may be seen in tumors, necrosis, breast tissue in young women, and radiotracer impurities collecting in other organs. While bone scans can detect abnormalities, further testing is needed to differentiate between benign and malignant causes. Interpretation requires correlating scan findings with clinical history and other imaging results.