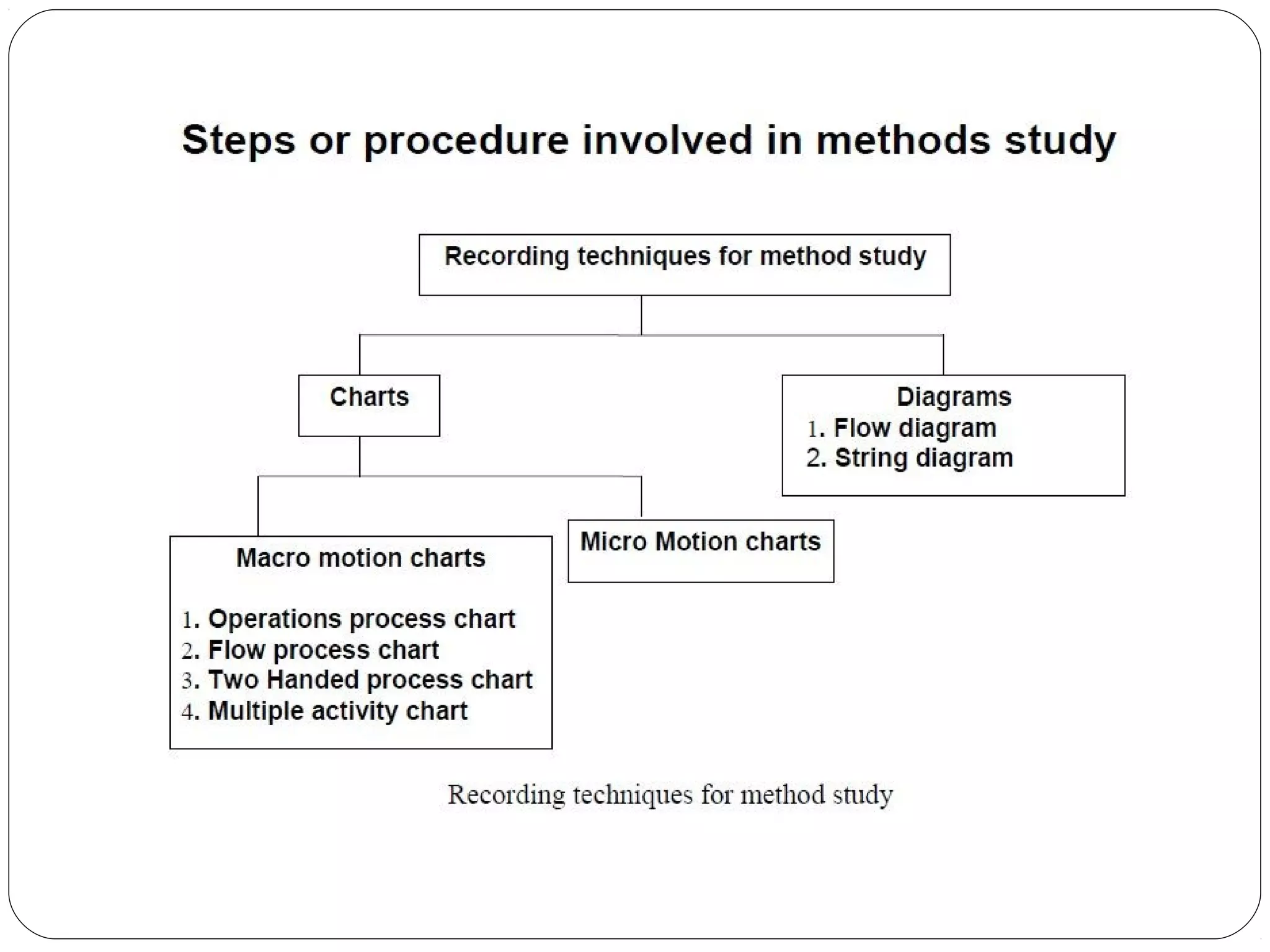
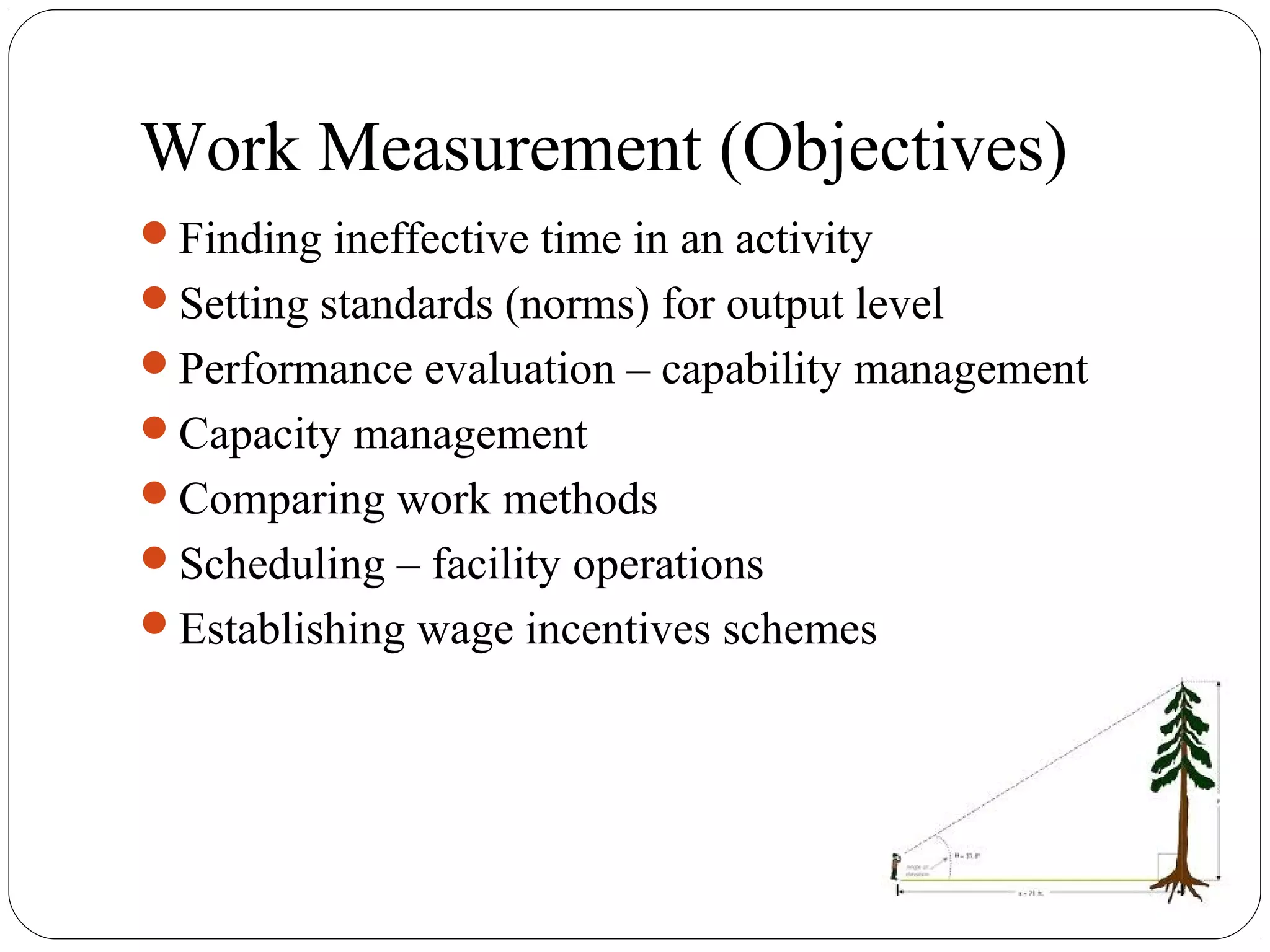
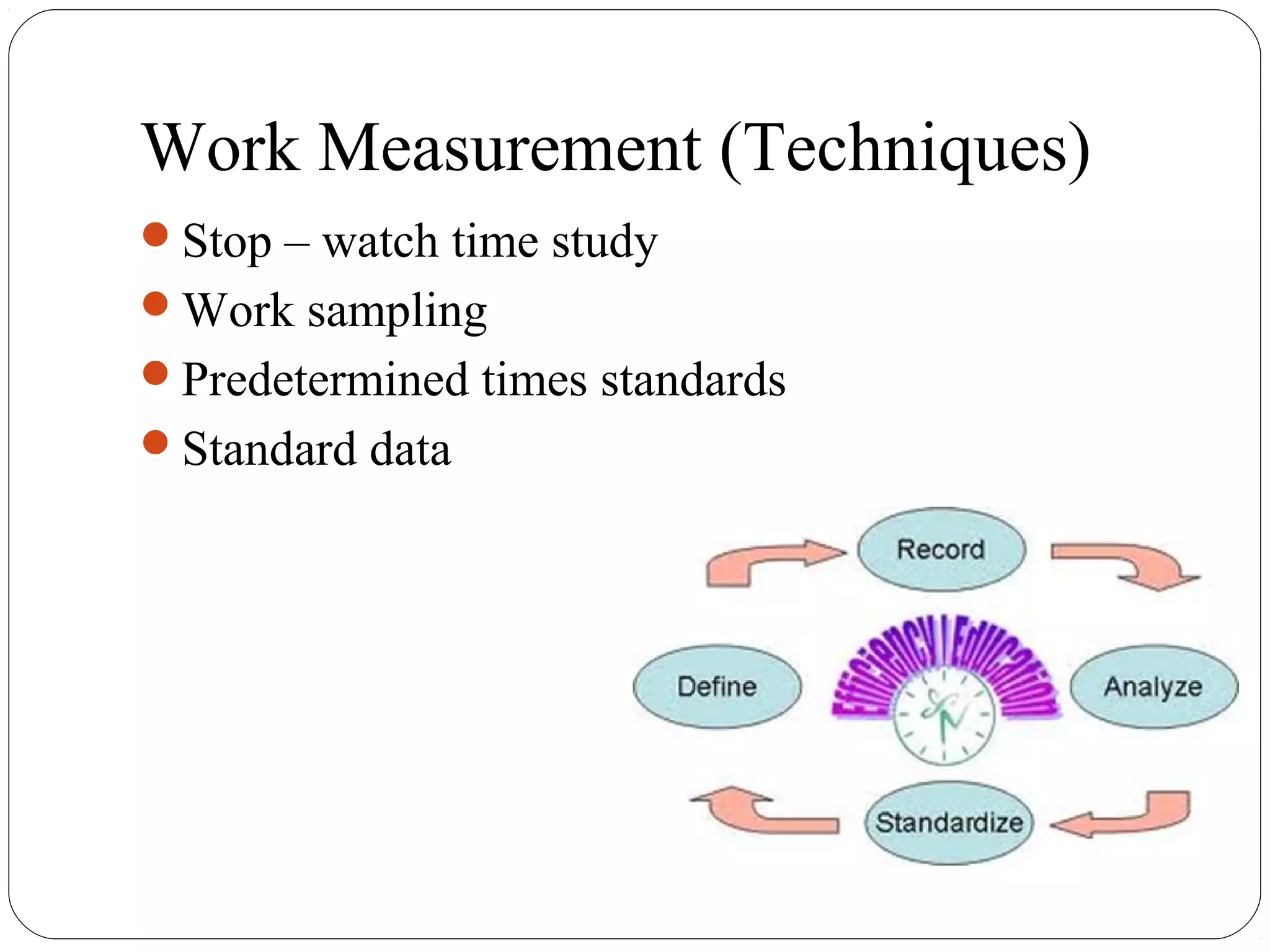
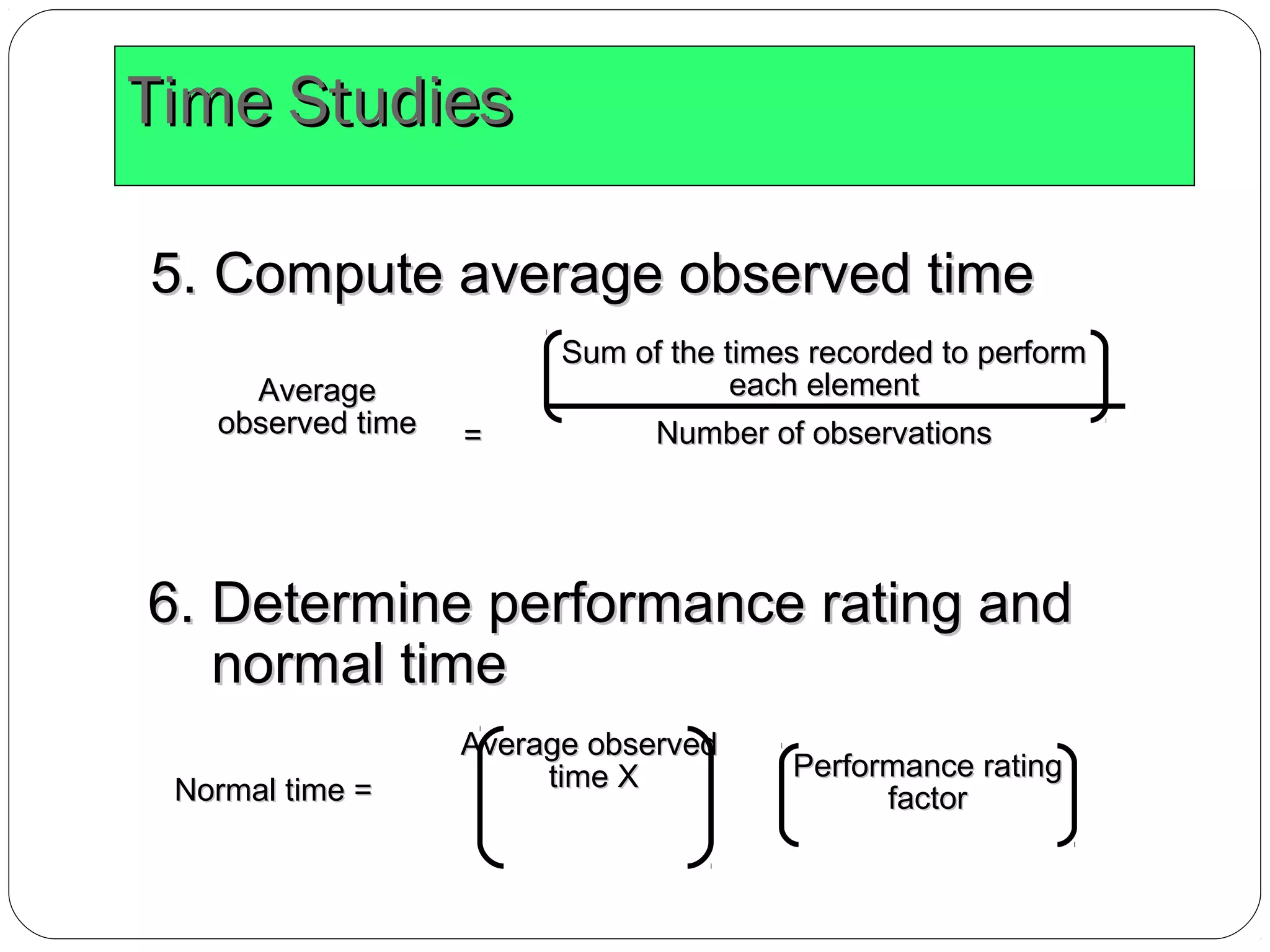
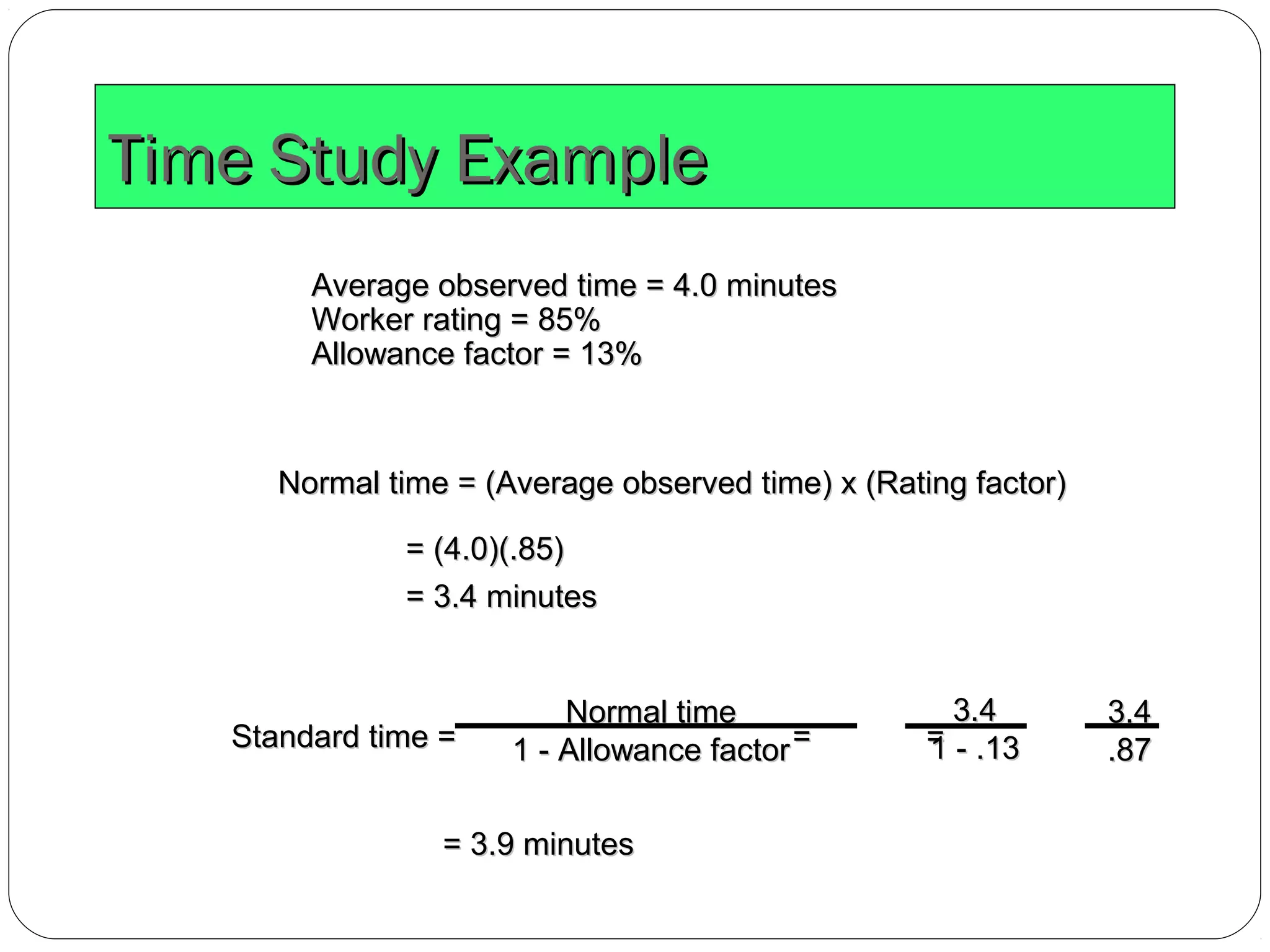
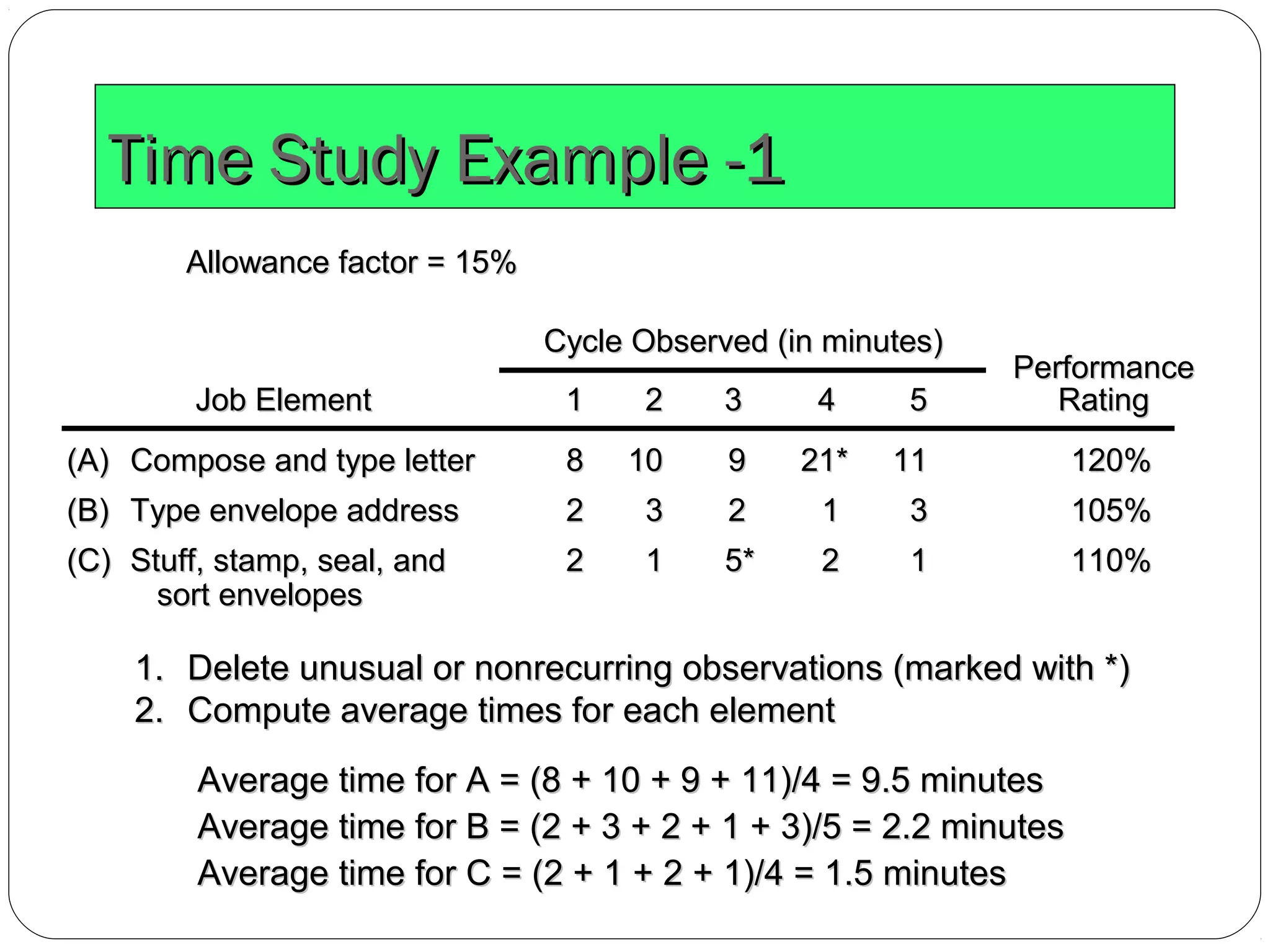
The document discusses work study and time study methods. It defines work study as the systematic examination of work methods to improve efficiency. The main objectives of work study are productivity enhancement and human comfort/safety. Method study involves critically examining work processes to develop more effective methods. Time study is a work measurement technique that involves observing and timing workers to set performance standards. The document provides examples of conducting a time study, including defining the task, timing elements, calculating average and normal times, and setting the standard time.