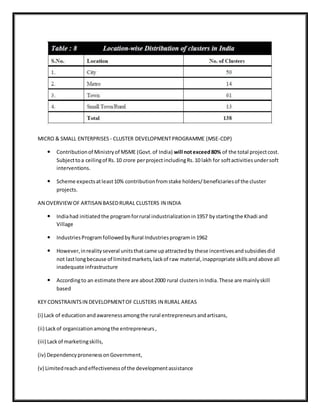
This document discusses cluster development in India. It defines a cluster as a group of enterprises located within an identifiable and contiguous area that produce similar products or services. The objectives of cluster development programs are to enhance productivity and competitiveness of small and medium enterprises. India has many documented industrial clusters across various industries that contribute significantly to the economy and employment. Cluster development requires state intervention due to its long-term nature and need for common facilities and programs.