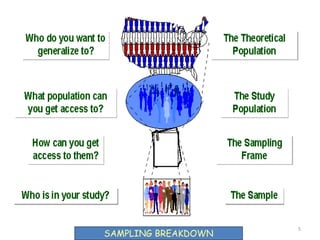
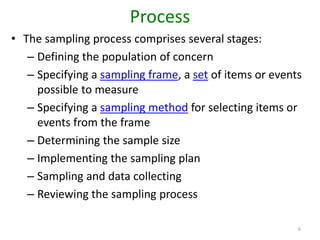
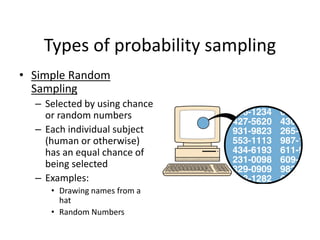
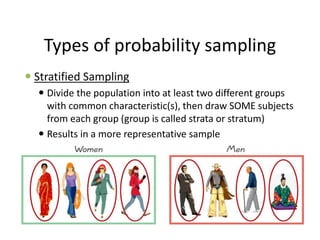
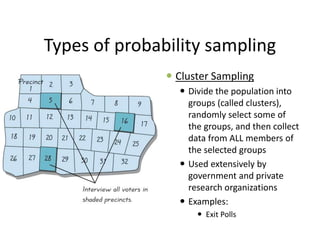
This document discusses different sampling techniques used in research. It explains that sampling involves selecting a subset of a population to gather information about the whole population in a more efficient manner than a complete census. The key types of sampling discussed are probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling which aim to select representative samples, as well as non-probability methods like convenience sampling and snowball sampling which rely on availability and referrals. Factors that influence sample representativeness and potential sources of error in sampling are also outlined.