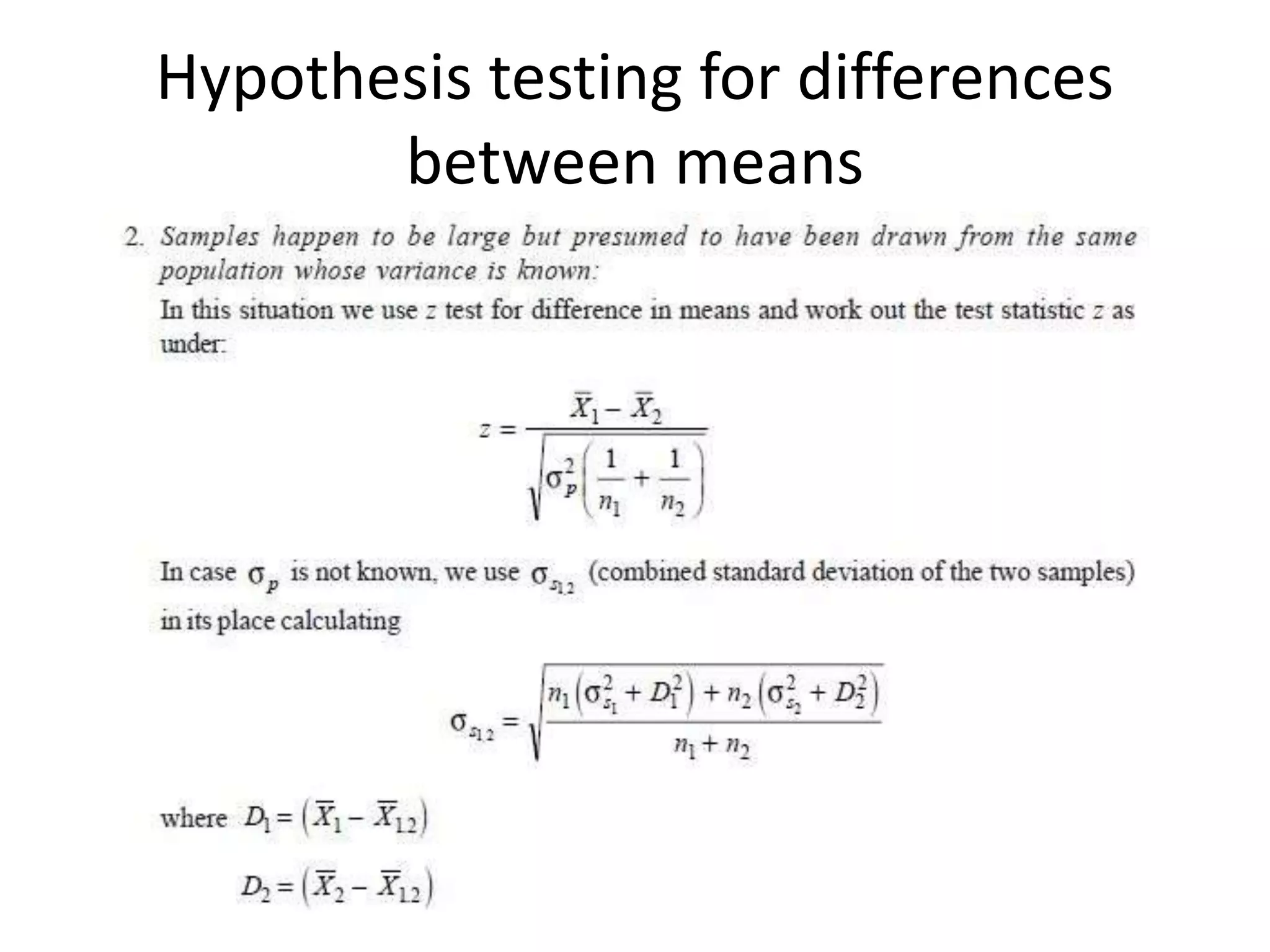
The document discusses hypothesis, which is a conjectural statement about the relationship between two or more variables that is tested through data collection and analysis. A hypothesis must be specific, testable, and consistent with existing facts. The null hypothesis states there is no significant difference or relationship, while the alternative hypothesis claims the null is false. Type I and II errors occur when the null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected or accepted. Confidence intervals indicate the probability the true population value falls within a certain range. Hypothesis testing of means and differences between means depends on factors like population distribution and sample size.