This document discusses work study and related techniques such as method study and work measurement. It defines work study as the systematic analysis of work processes and factors that affect efficiency. The goal is to improve efficiency through optimizing utilization of resources. Key aspects covered include:
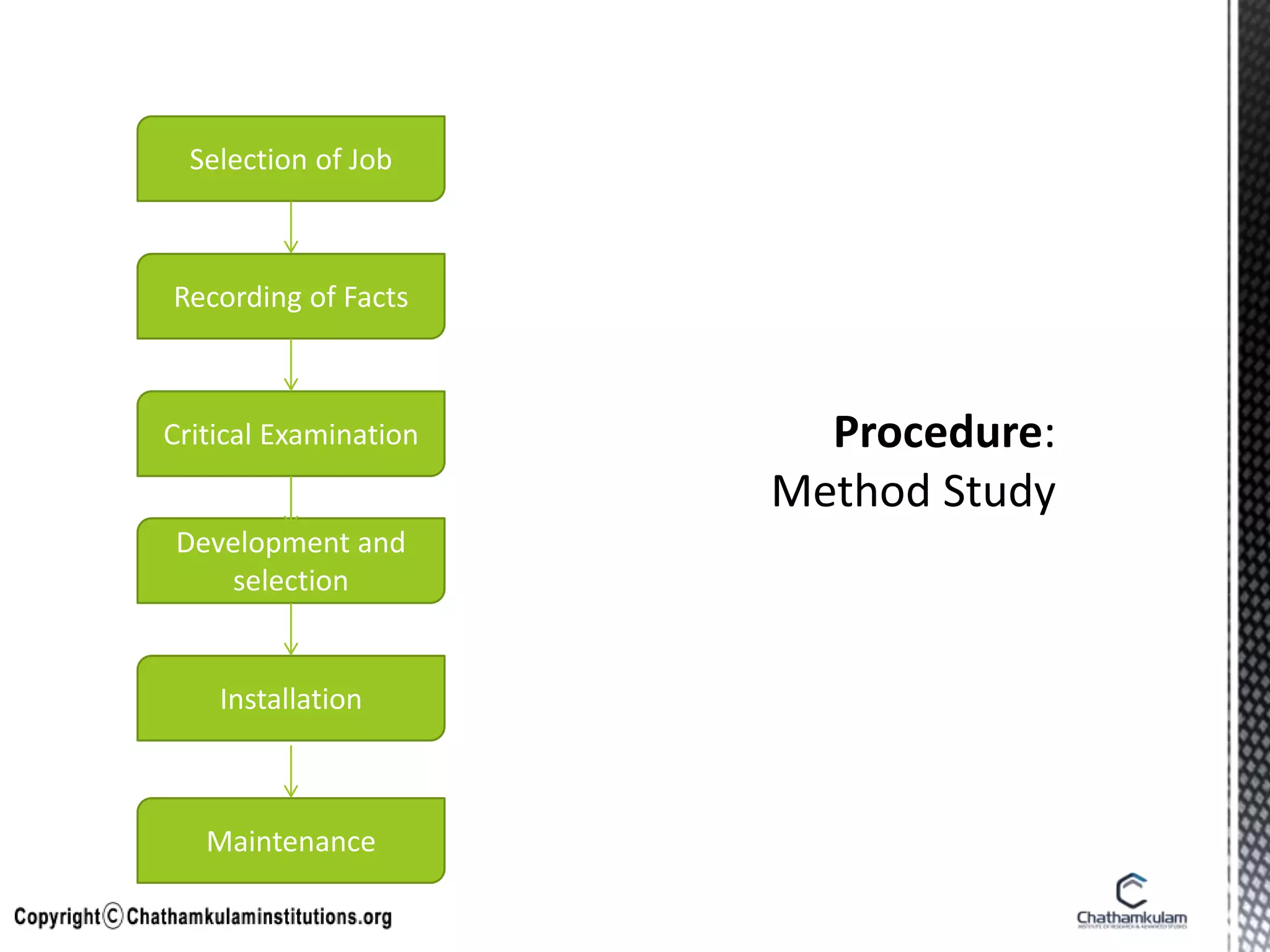
- Method study examines existing work methods and proposes improvements by accurately recording facts about operations, developing and selecting new plans, installing and maintaining changes.
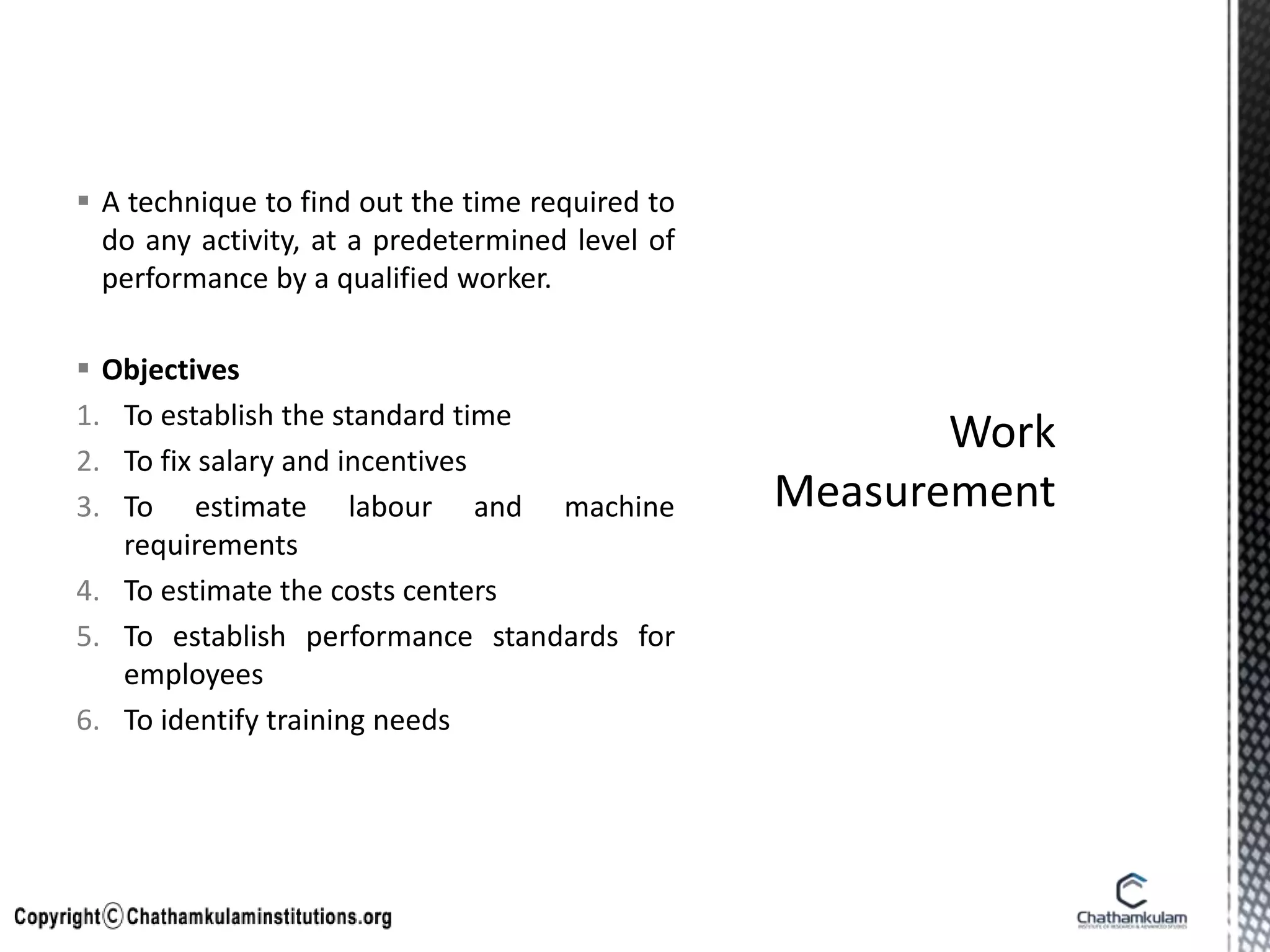
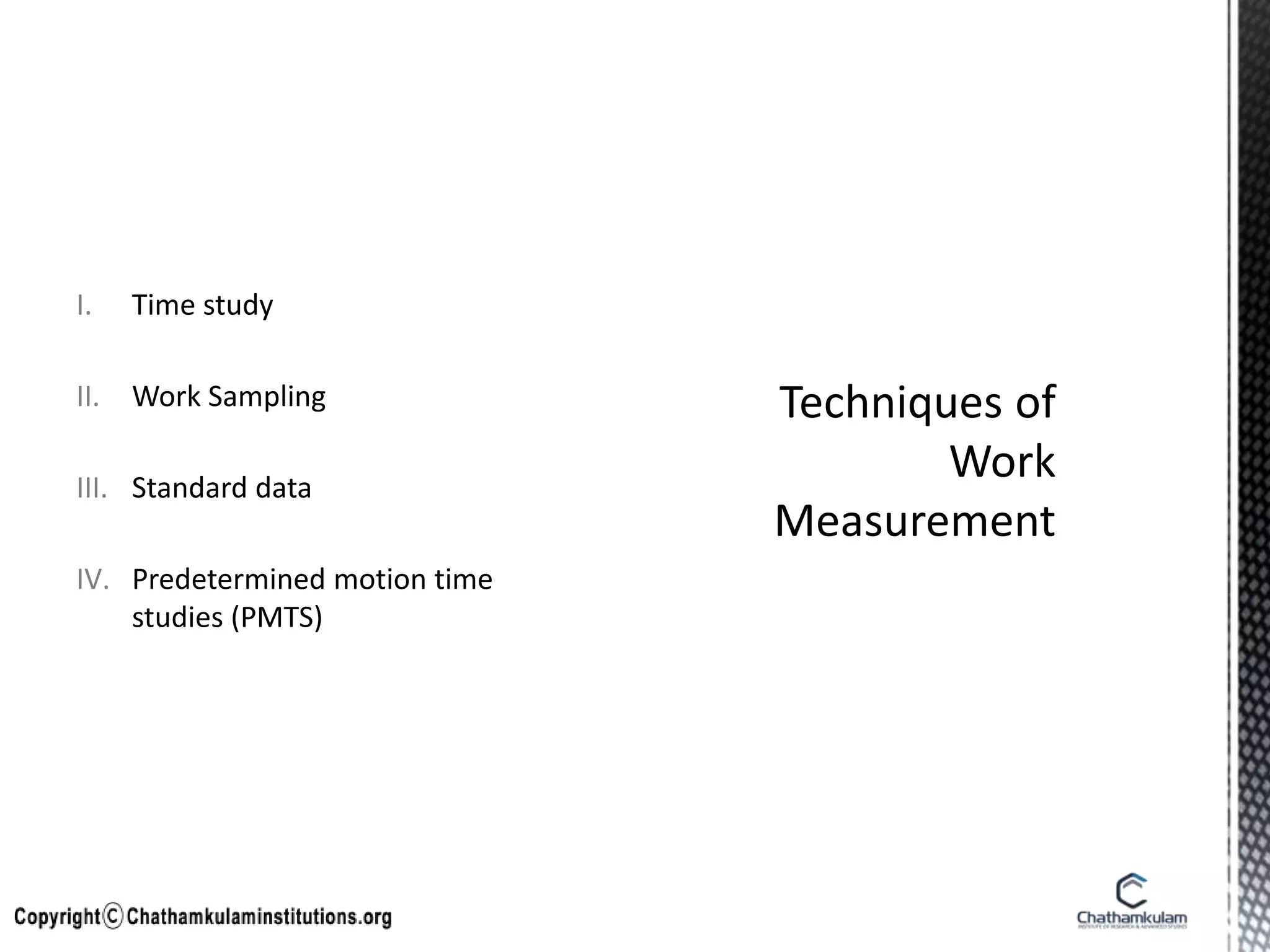
- Work measurement techniques like time study and work sampling are used to set performance standards and determine time required for tasks.
- Predetermined motion time studies and standard data help estimate times for new jobs based on previously studied similar operations.