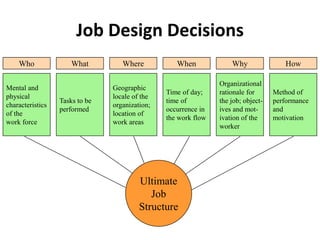
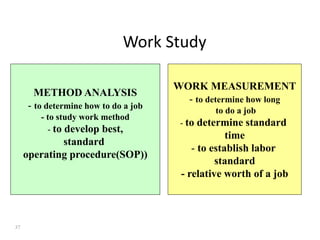
1. The document discusses job design, work measurement, and time studies. It defines job design as determining the contents and structure of a job and discusses key decisions involved.
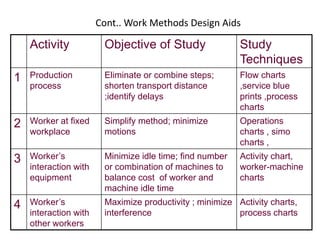
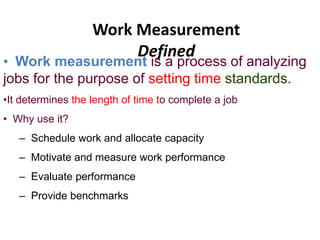
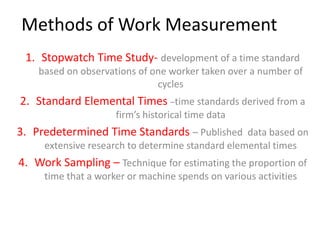
2. Work measurement is defined as analyzing jobs to set time standards and involves methods like stopwatch time studies, predetermined time standards, and work sampling. Important terms in work measurement like observed time, normal time, and standard time are explained.
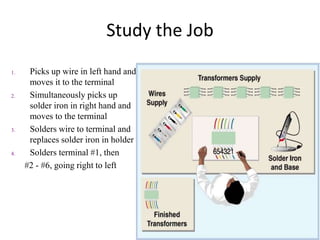
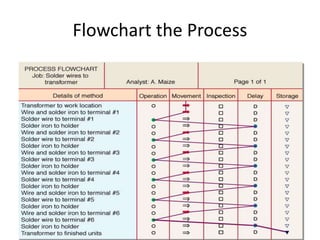
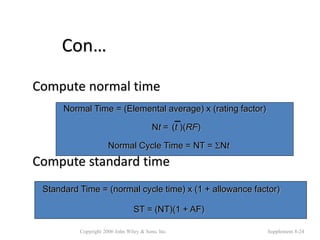
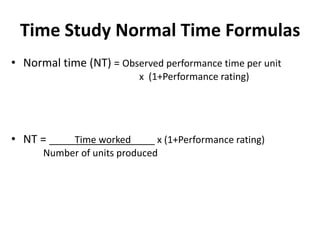
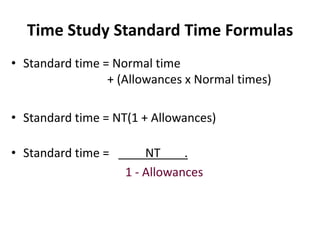
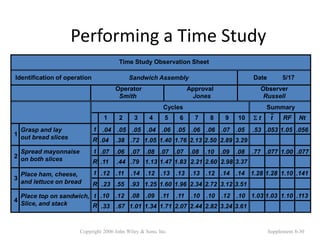
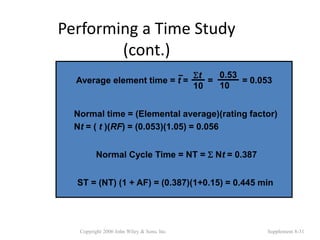
3. The document provides an example of performing a time study, including setting up an observation sheet and calculating normal time and standard time based on observed performance times. Formulas for determining the needed number of observations in a time study are also presented.