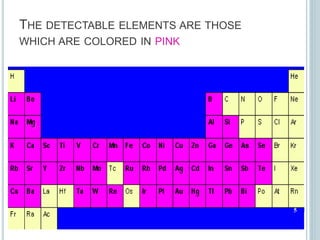
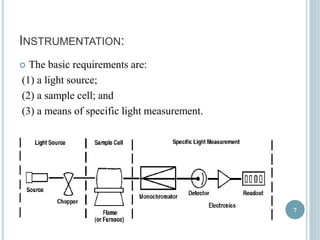
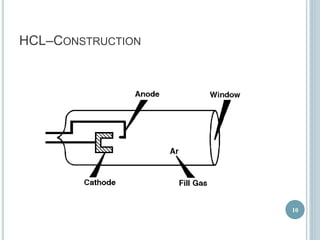
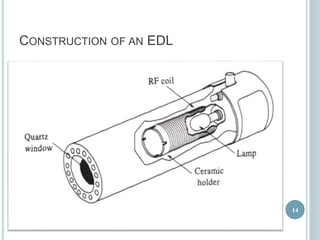
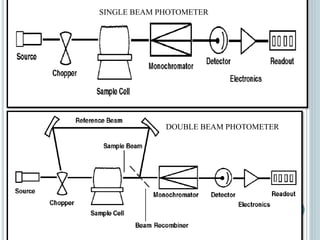
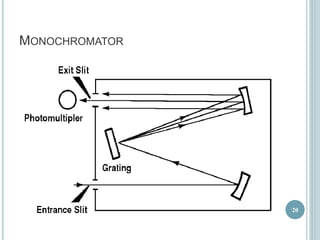
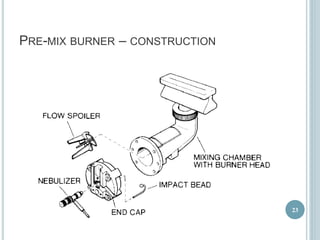
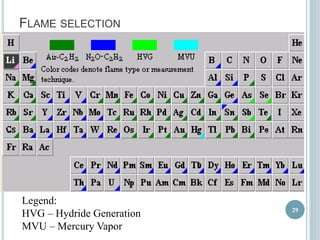
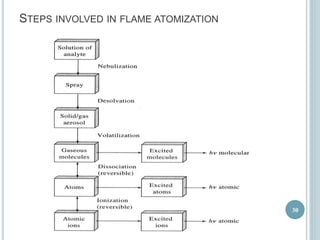
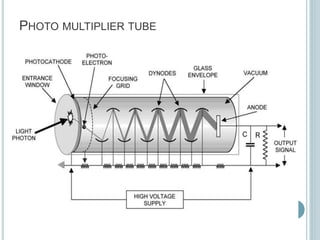
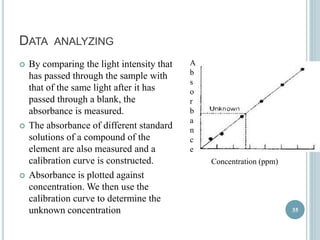
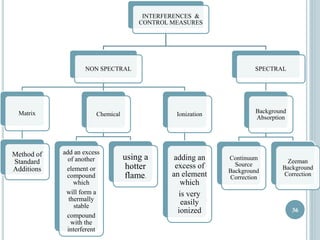
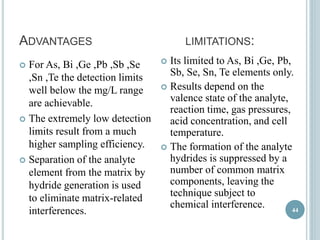
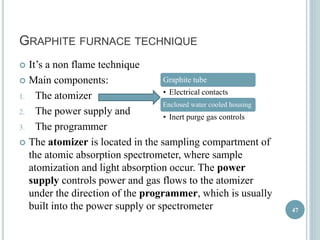
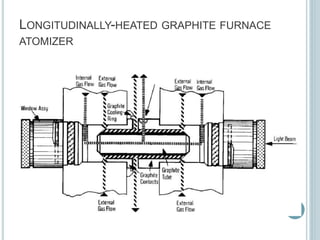
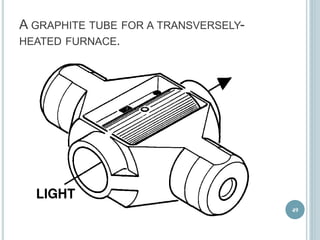
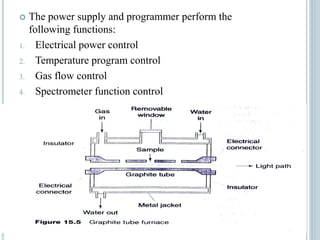
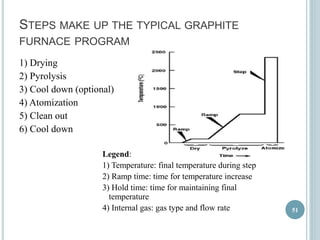
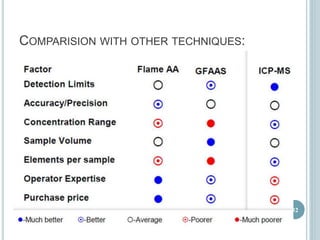
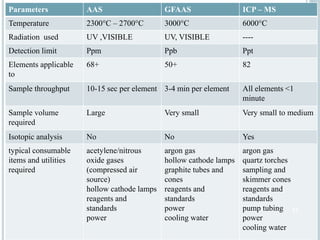
This document provides an overview of atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS). It discusses the history, principle, instrumentation, interferences and applications of AAS. The key components of an AAS include a light source such as a hollow cathode lamp, a sample atomizer like a flame, and a detector like a photomultiplier tube. AAS can be used to quantitatively analyze over 60 elements in solution by measuring the absorption of ground state atoms. Sensitivity can be improved using techniques like graphite furnace atomic absorption or hydride generation.