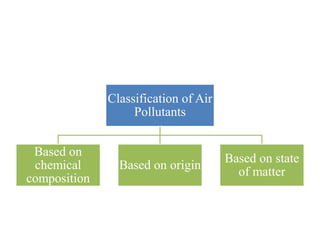
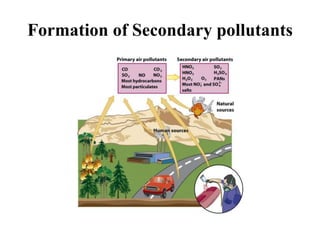
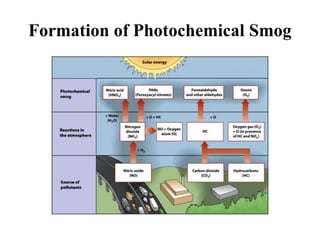
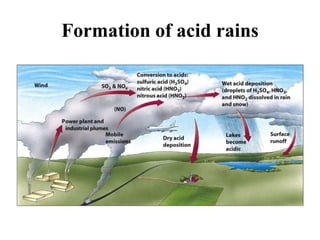
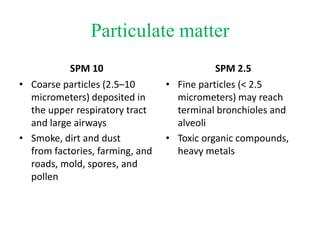
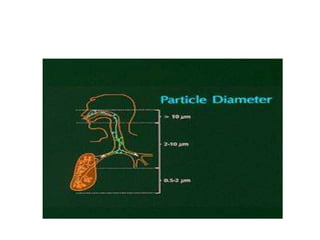
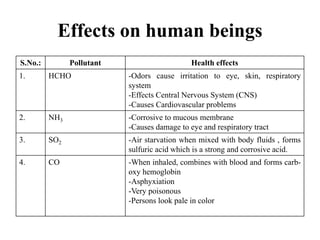
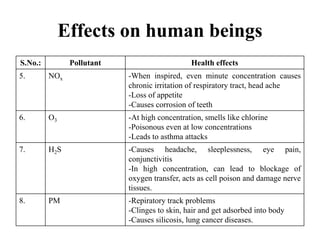
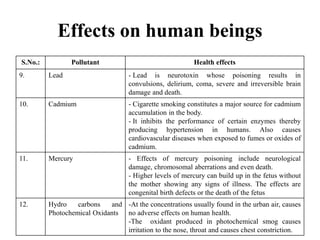
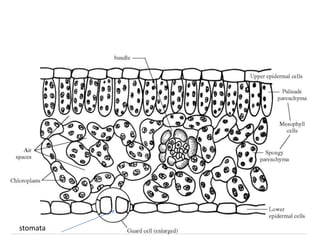
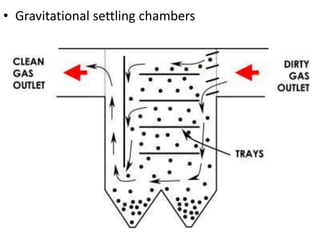
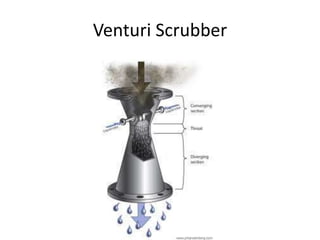
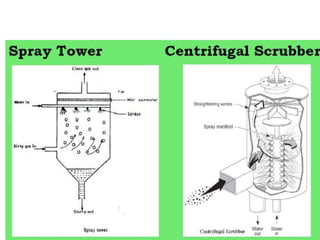
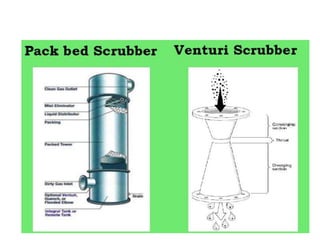
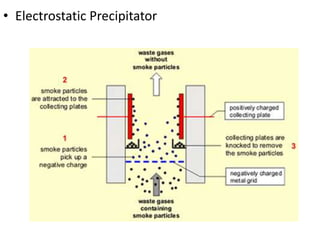
The document details the world's five major air pollution disasters, including the Bhopal Gas Tragedy and the Chernobyl Disaster, highlighting their causes, impacts, and long-term effects on the environment and human health. It further discusses types and classifications of air pollutants, their sources, and adverse effects on health and vegetation, along with methods for control and preventive measures for indoor air quality. Finally, an overview of the Air Quality Index (AQI) is provided, explaining its categories and health implications based on varying levels of air pollution.