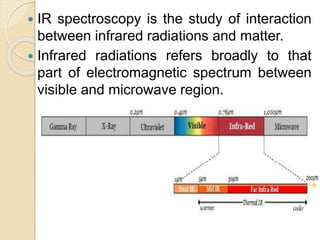
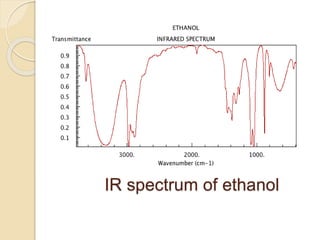
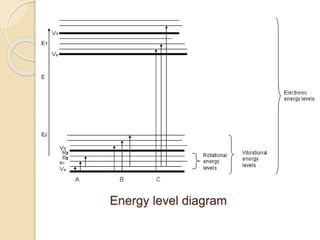
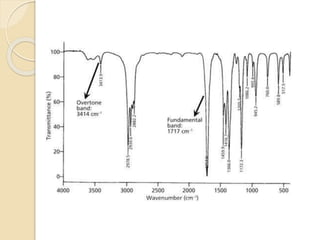
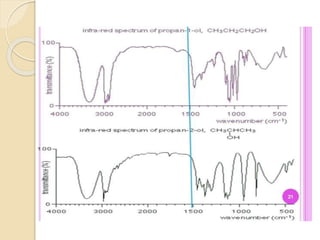
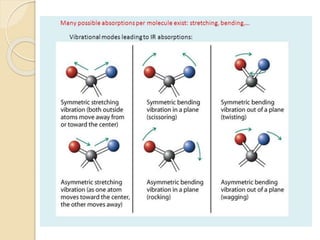
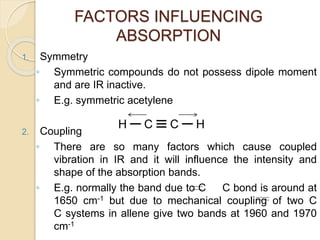
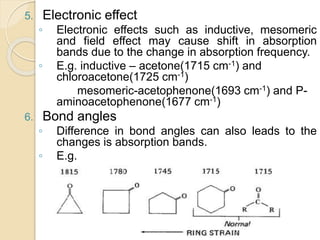
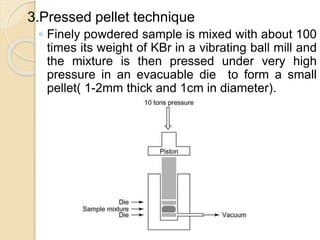
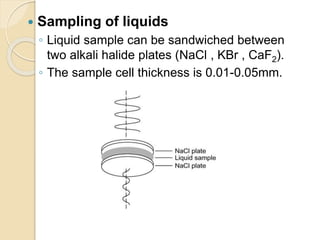
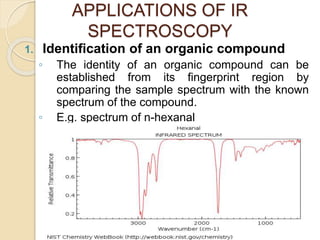
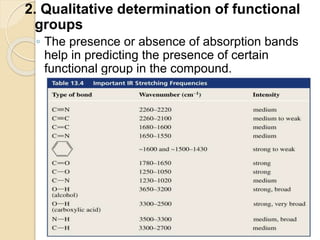
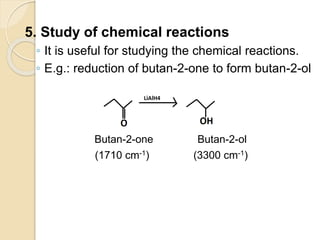
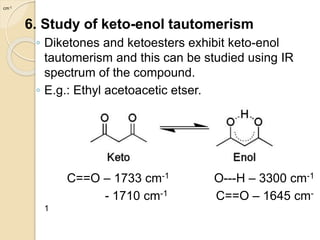
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy studies the interaction between infrared radiation and matter, focusing on vibrational and rotational energy changes in molecules. Key principles include the absorption of IR radiation by active transitions associated with dipole moment changes and the existence of unique IR spectra for different compounds. Applications range from identifying organic compounds to analyzing functional groups, bonding types, and even studying chemical reactions.