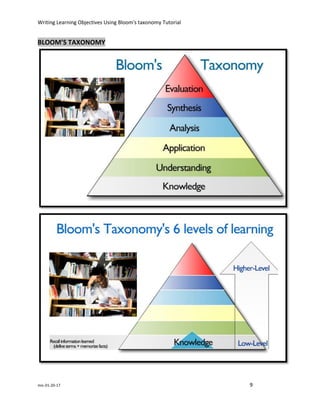
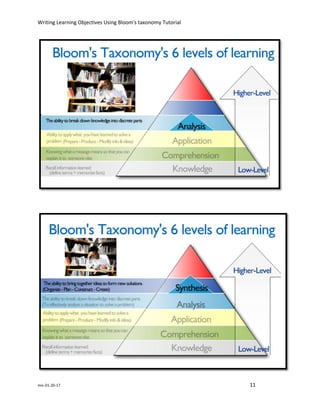
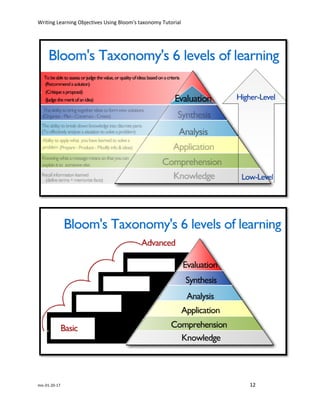
The document discusses how to write effective learning objectives using Bloom's taxonomy. It begins by defining learning objectives as statements that describe specific skills or knowledge students will demonstrate after a lesson. Common mistakes like using "understand" or "know" are avoided by focusing on observable and measurable actions. Bloom's taxonomy categorizes six levels of intellectual skills - from basic recall to advanced evaluation - that objectives can target. Using Bloom's levels helps write objectives that scaffold learning from fundamental to high-level knowledge.