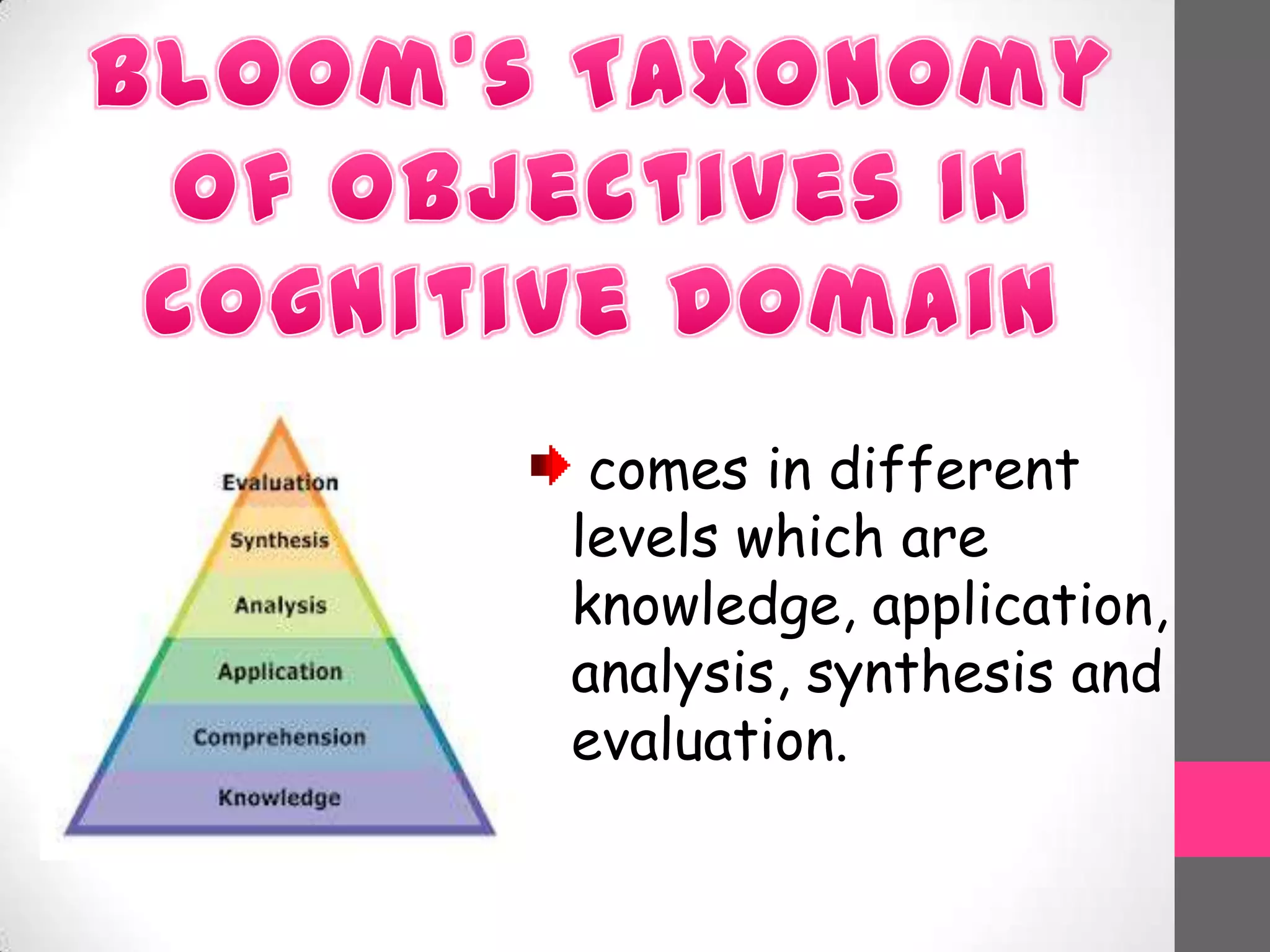
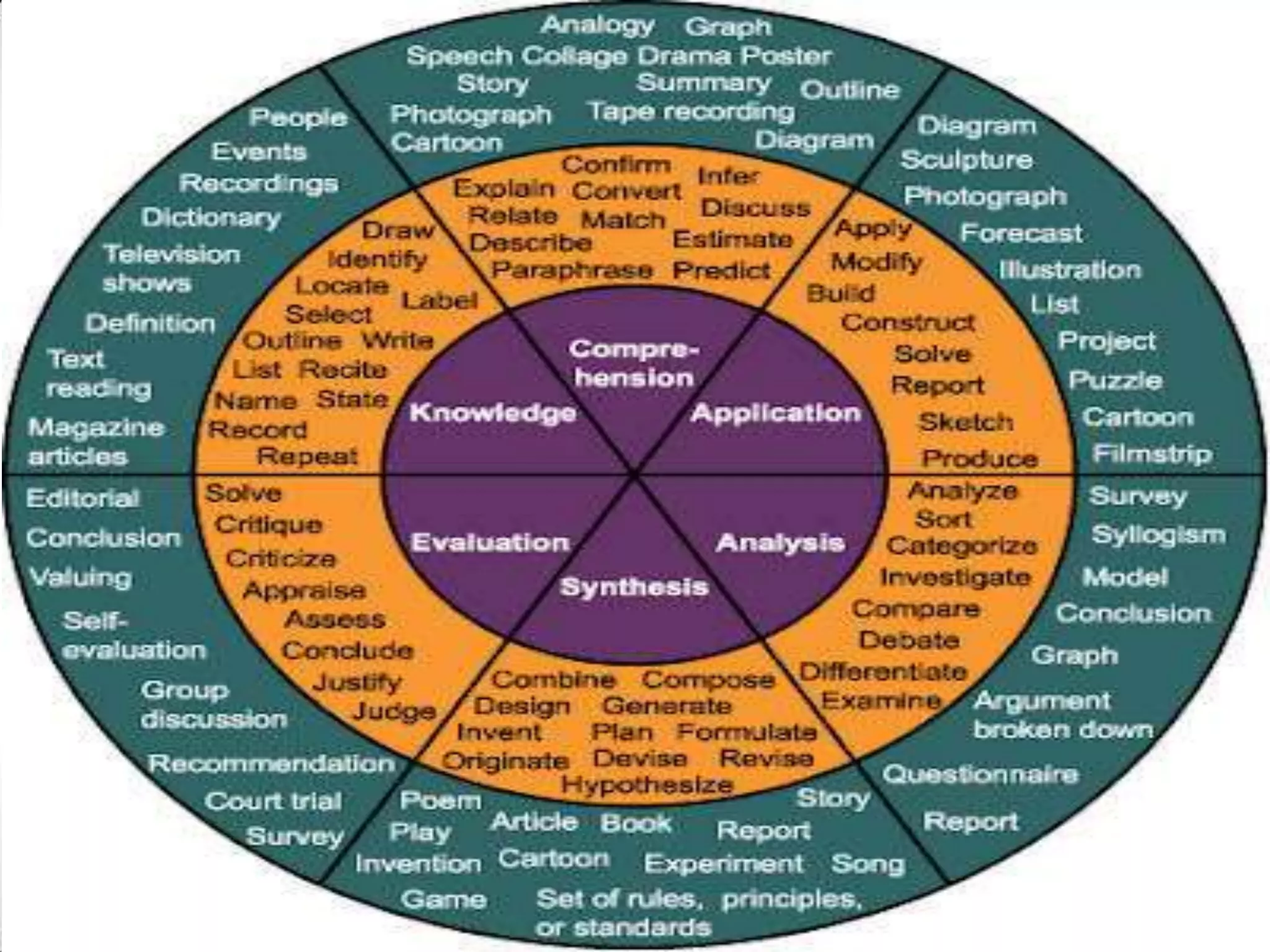
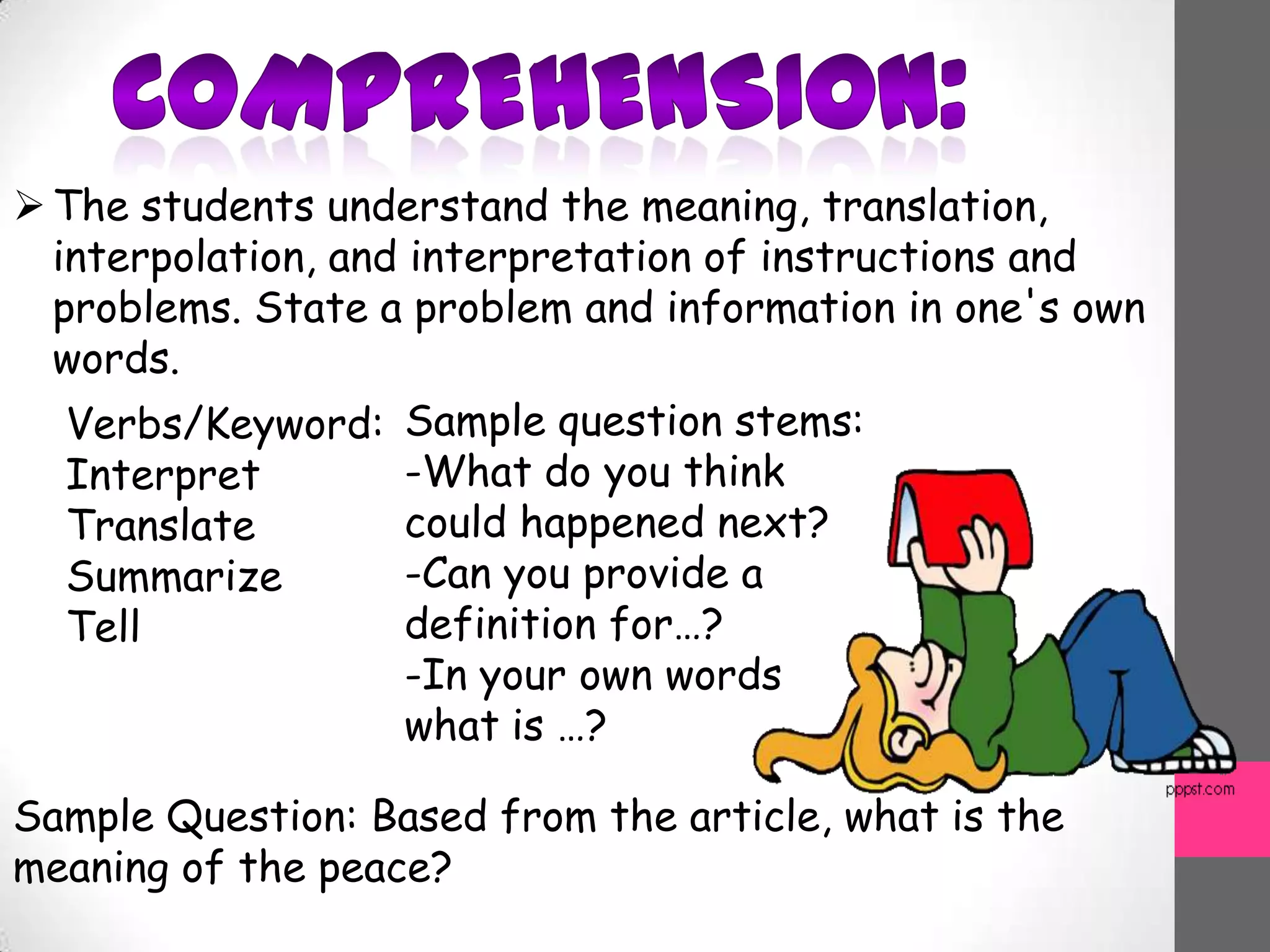
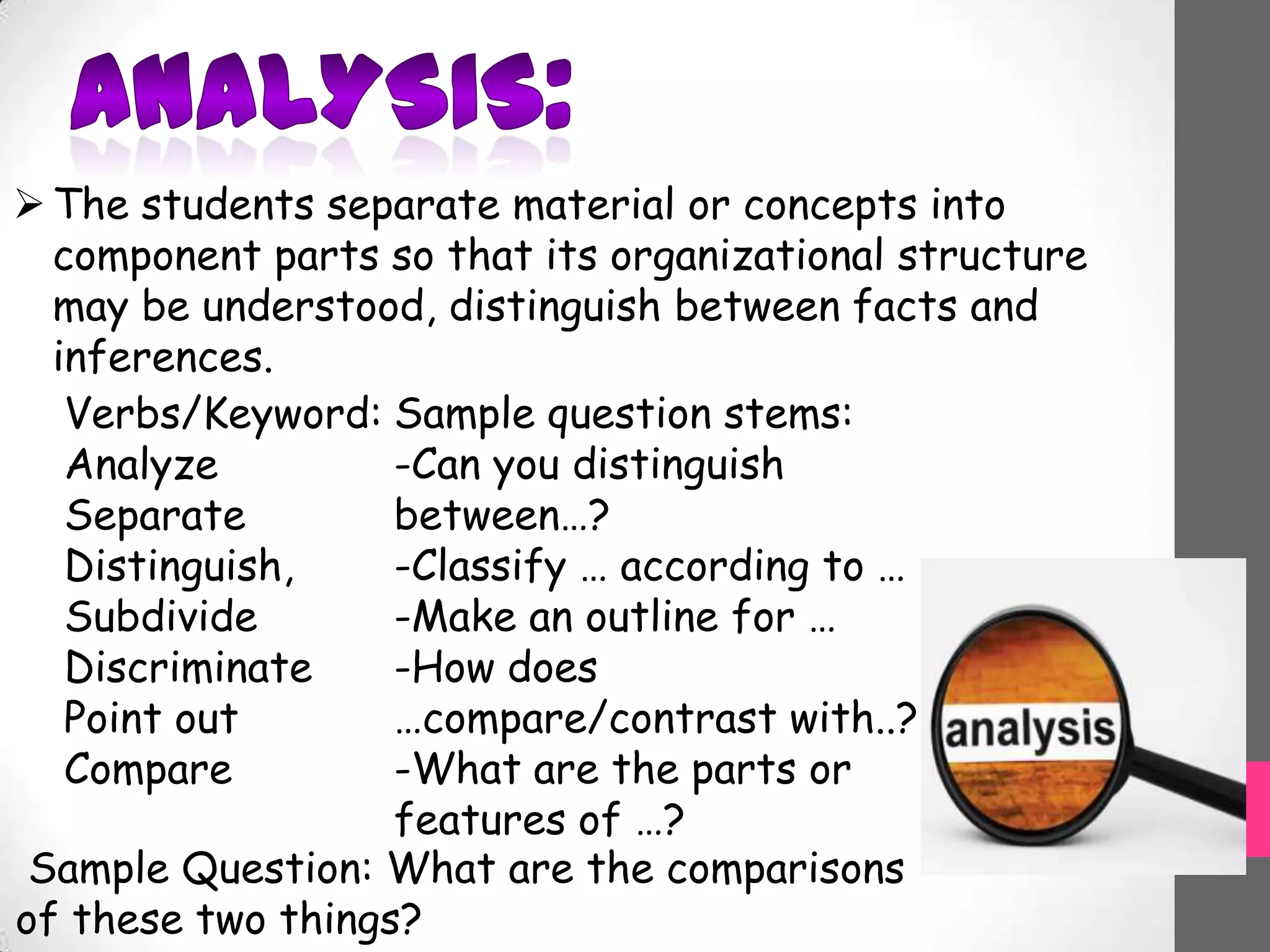
This document discusses Bloom's Taxonomy, a classification of learning objectives proposed in 1956 by Benjamin Bloom and a committee of educators. The taxonomy divides educational objectives into three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. The cognitive domain involves knowledge and intellectual skills and is broken down into six levels - remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. The document provides examples of questions and verbs for each level of Bloom's Taxonomy to illustrate how it can be used to promote higher-order thinking in education beyond just remembering facts.