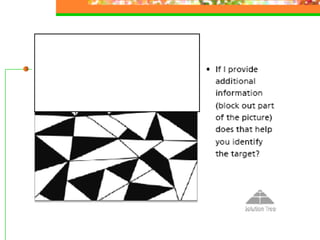
The document provides guidance on developing clear learning objectives from academic standards. It outlines a process for "deconstructing" standards by identifying verbs and nouns to create measurable learning objectives. Clear objectives stated in student-friendly language help focus learning, assessment, and feedback. Examples show how to transform broad standards into specific objectives students can understand and work towards. Overall the document emphasizes that clear objectives are necessary to effectively plan instruction and evaluate student learning.