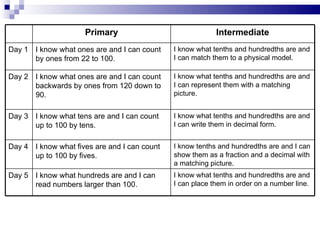
The document provides information on learning targets:
- Learning targets are specific goals that clearly state what students should know and understand, linked to adopted standards.
- Effective learning targets are measurable, specific to a lesson, written in student-friendly language, and shared with students.
- Research shows students perform better when learning targets are clear.
- Examples are given to distinguish learning targets from goals and standards.
- Guidance is provided on writing learning targets aligned to specific math standards.