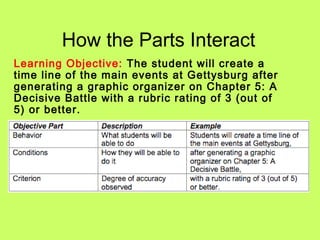
This document provides guidance on writing effective learning objectives. It explains that learning objectives should describe what students will be able to do after instruction using a measurable verb. Learning objectives have three parts - the description, condition, and criteria. The description is the skill or knowledge students will gain. The condition provides context for how the skill will be performed. The criteria establishes how well the skill must be demonstrated. Well-written learning objectives are aligned to curriculum standards and incorporate different levels of thinking based on Bloom's Taxonomy. The document provides examples to illustrate how to write learning objectives that meet these criteria.