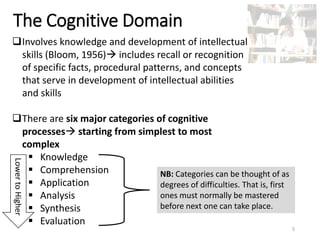
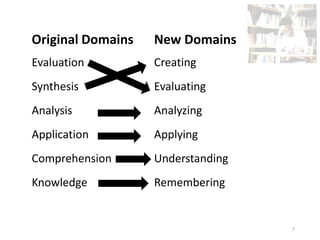
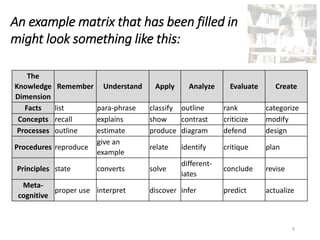
Bloom's Taxonomy was created in 1956 to promote higher-order thinking in education beyond memorization. It outlines three learning domains - cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. The cognitive domain involves intellectual skills and knowledge. It has six categories of cognitive processes ranging from simple to complex: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. In 2001, Anderson and Krathwohl revised Bloom's Taxonomy, changing the names of the categories to verb forms and rearranging their order. The revision also included a matrix to classify learning objectives based on knowledge and cognitive process.



![4
Instructional designers, trainers, and educators
refer to these three categories as KSA
Knowledge [cognitive],
Skills [psychomotor], and
Attitudes [affective])
Domains may be thought of
as categories](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/writingeffectivelearningobjectivesbloomstaxonomy-170120022532/85/Writing-Effective-Learning-Objectives-Using-Bloom-s-Taxonomy_Ppt-4-320.jpg)