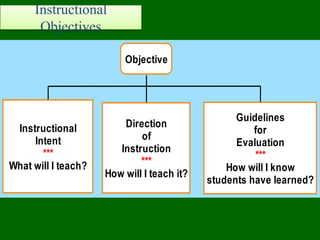
The document discusses the significance of instructional objectives in education, emphasizing measurable learning outcomes and their classification into cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. It outlines components for effective objectives using the ABCD model, which includes observable behavior, conditions for demonstration, and proficiency criteria. Additionally, it illustrates objectives with examples related to troubleshooting computer programs and applying Ohm's law.