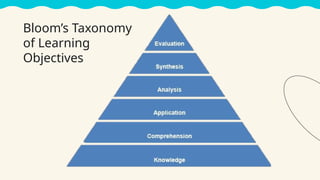
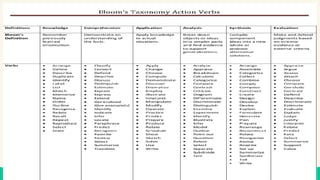
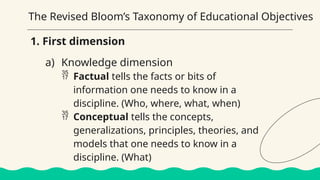
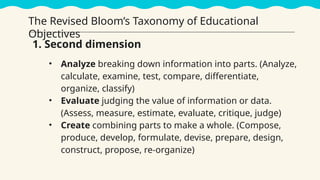
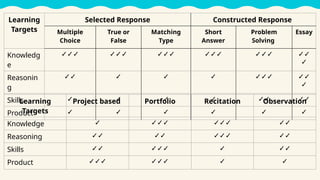
This lesson focuses on understanding the purposes of classroom assessment, formulating specific learning targets, and matching assessment methods to those targets. It outlines different types of classroom assessments and their roles in enhancing teaching and learning, while also discussing Bloom's taxonomy and its relevance in setting educational goals and objectives. Lastly, it highlights the importance of clear and achievable learning targets to guide the assessment process.