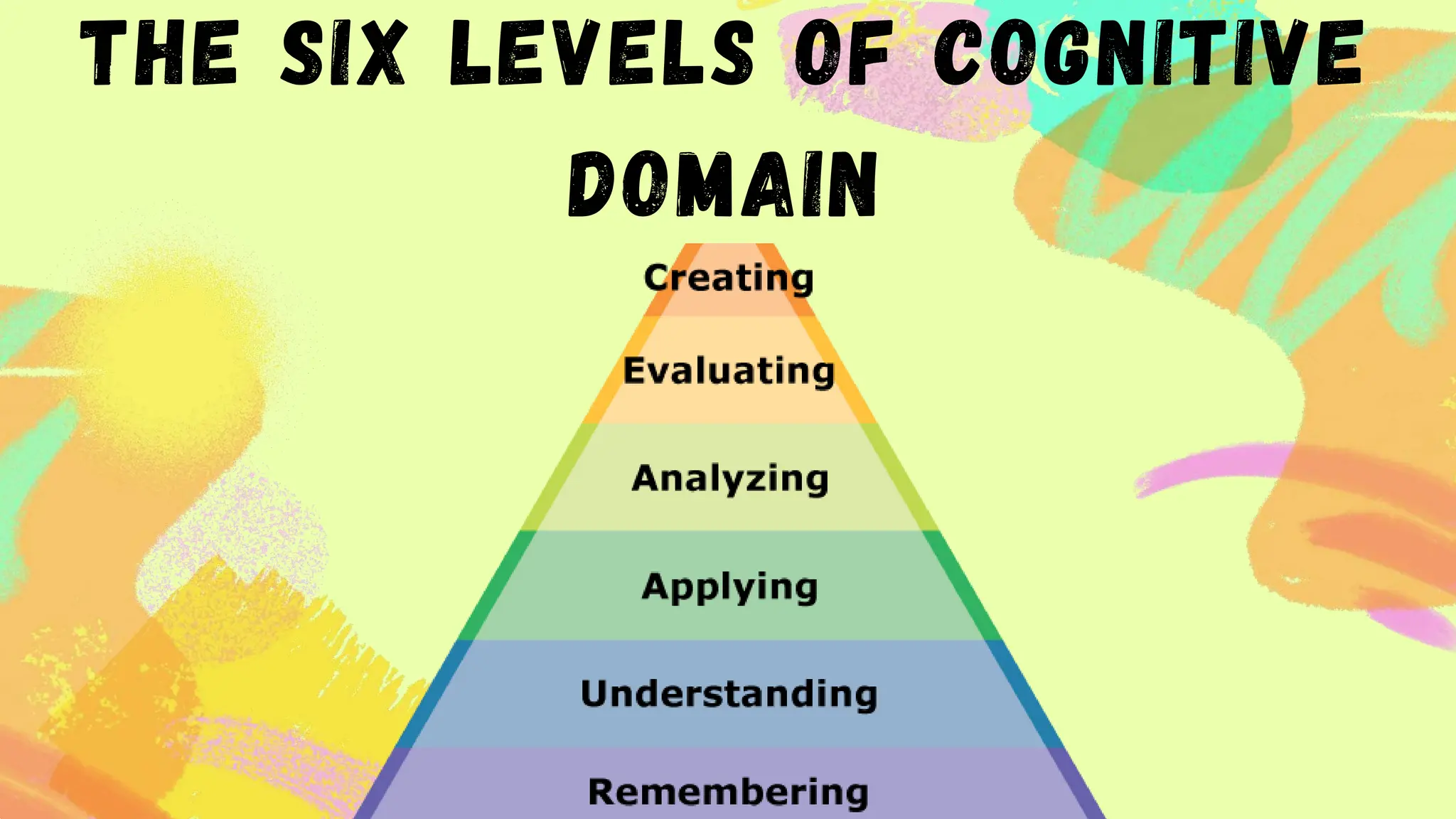
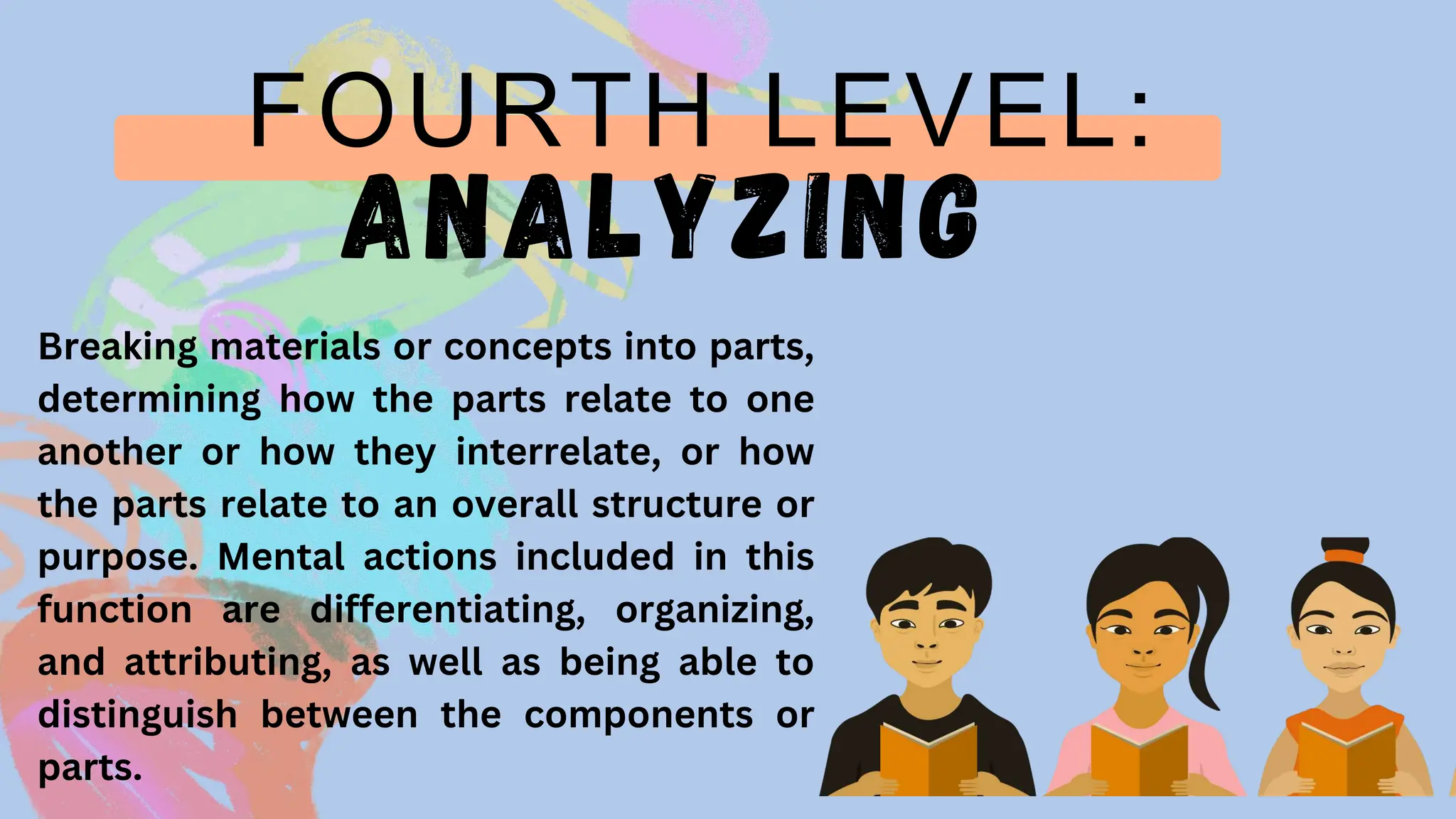
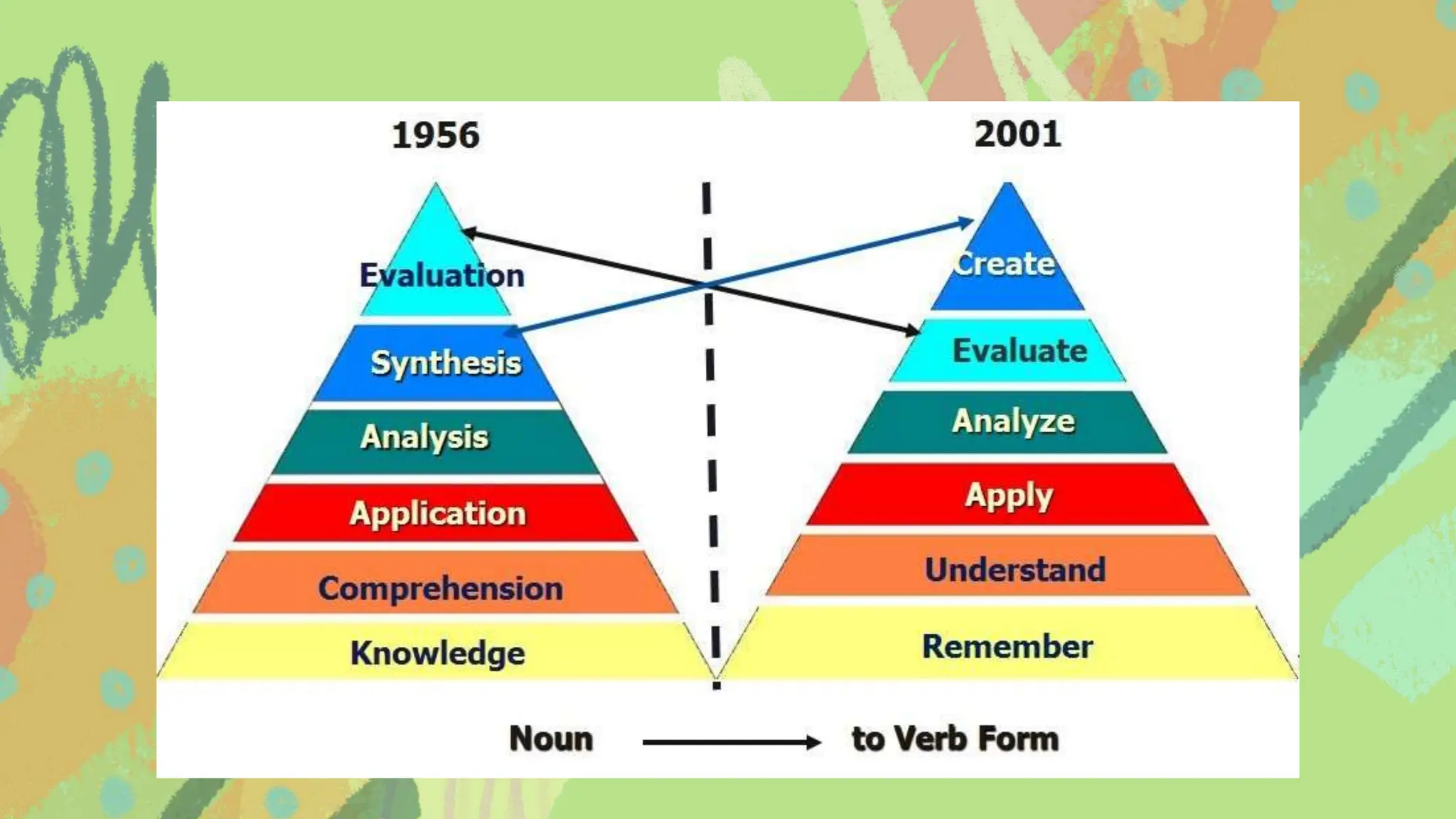
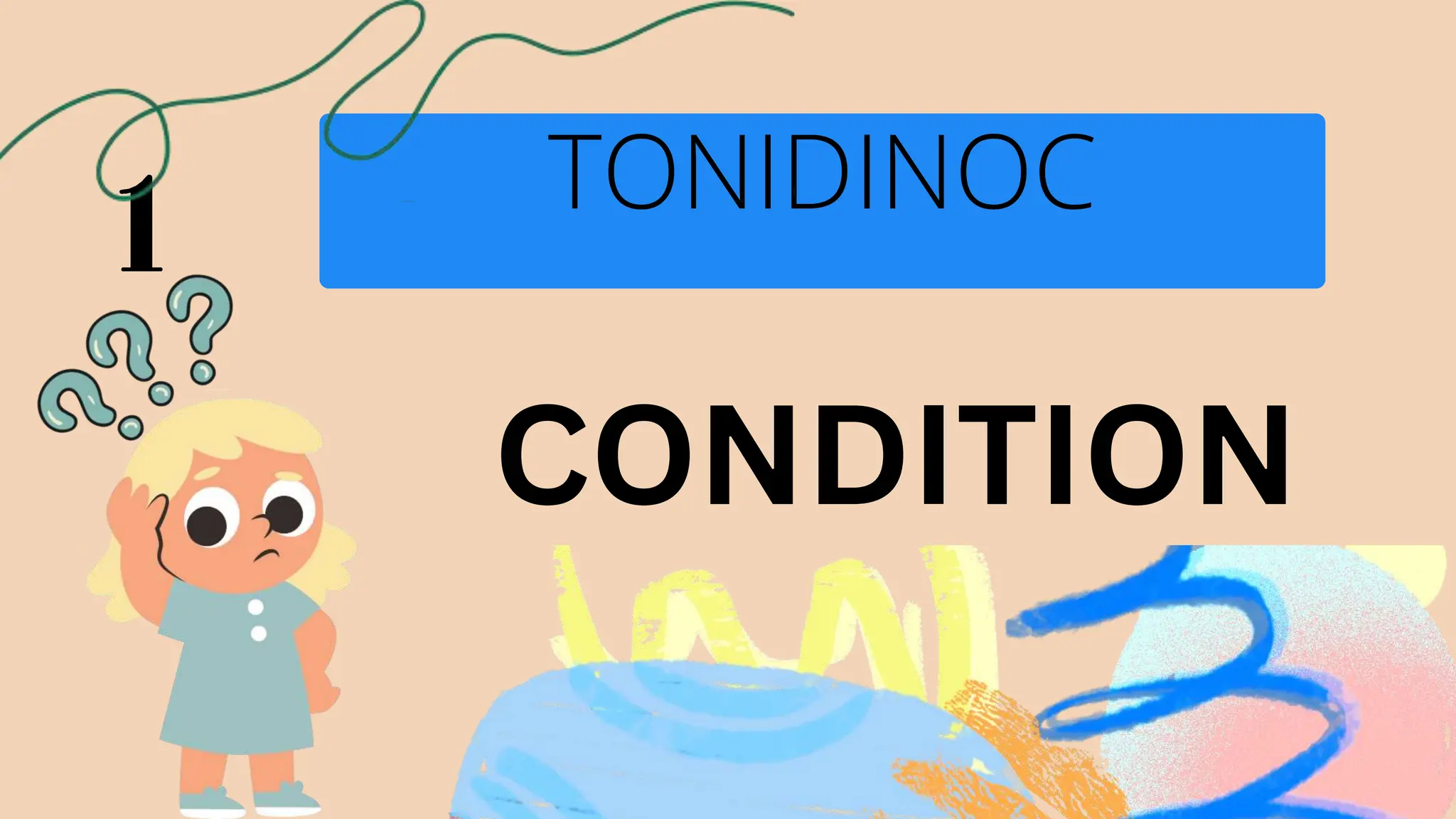
The document discusses learner-centered teaching, focusing on crafting goals, aims, objectives, and outcomes for educational purposes, including the importance of clear learning objectives. It explains the revised Bloom's taxonomy, detailing the six levels of cognitive processes and their relevance for educators in developing effective teaching strategies. Additionally, it outlines the structure of learning objectives using the ABCD method to ensure measurable outcomes and alignment with curricular standards.