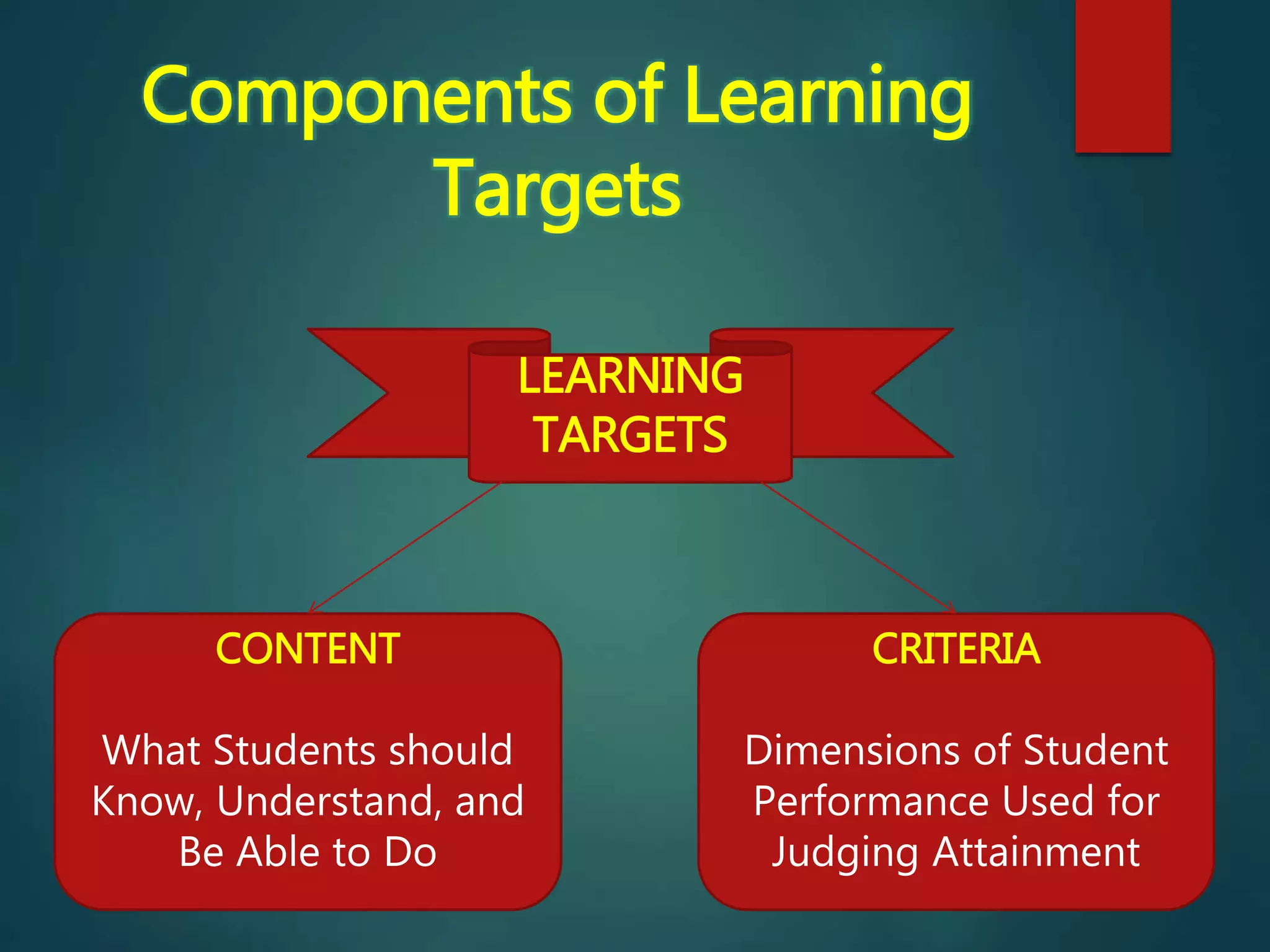
The document defines learning targets and their components. Learning targets are statements that describe what students should know and be able to do by the end of a unit of instruction. They include educational goals, which are general statements, and educational objectives, which are more specific statements of expected student performance. Highly precise performance objectives have four elements - performance, condition, criterion, and audience. The document also describes different types of learning targets, including knowledge, reasoning, skills, products, and dispositions. Finally, it outlines some common sources used to develop learning targets, such as Bloom's Taxonomy, professional experience, textbooks, and existing objective lists.