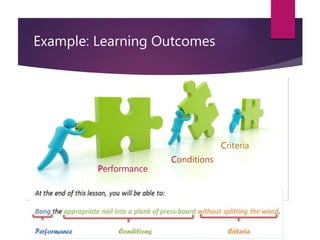
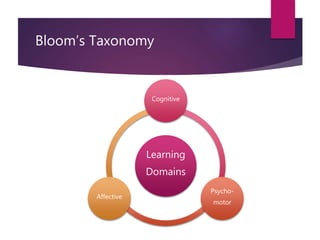
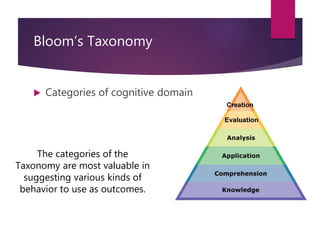
The document outlines the importance of writing effective learning outcomes that encompass performance, conditions, and criteria. It emphasizes their role in guiding both instructors and learners regarding expected knowledge, skills, and attitudes by the course's completion. Additionally, it highlights characteristics of effective learning outcomes and integrates Bloom's taxonomy to enhance outcome formulation.