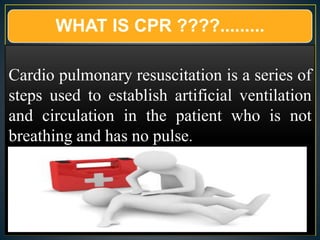
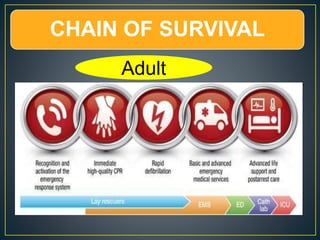
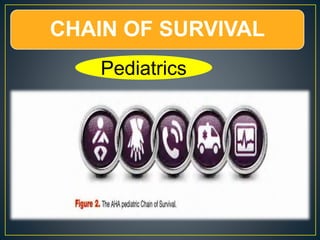
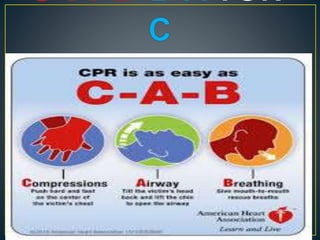
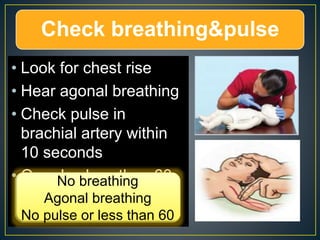
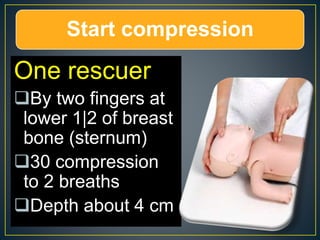
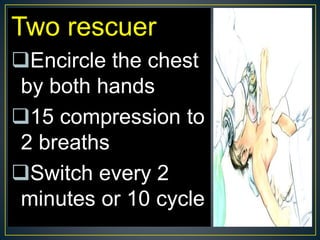
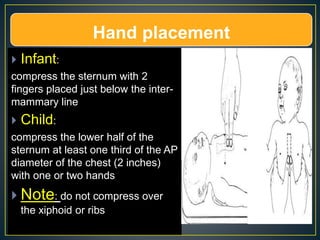
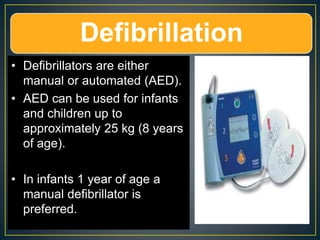
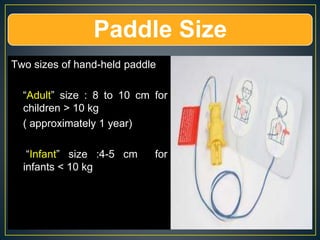
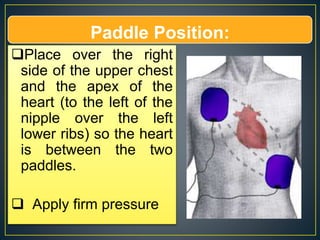
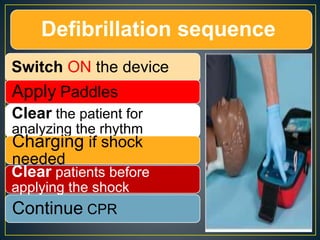
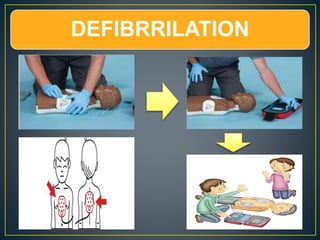
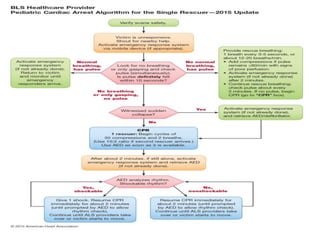
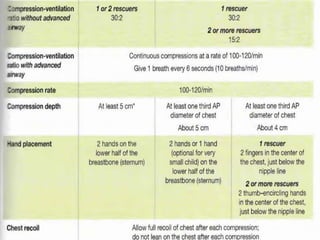
This document discusses recent changes to pediatric CPR guidelines. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) involves artificial ventilation and circulation for a patient not breathing and without a pulse. For infants and children, compressions involve either two fingers or encircling hands on the chest at a depth of 1/3 the chest diameter at a rate of 100-120 per minute. High quality CPR means starting compressions within 10 seconds without interruptions and effective breaths. Defibrillation uses either manual or automated external defibrillators, with smaller paddles for infants. The key takeaways are that pediatric CPR techniques differ from adults, compressions should not be delayed, high quality compressions are essential, and C