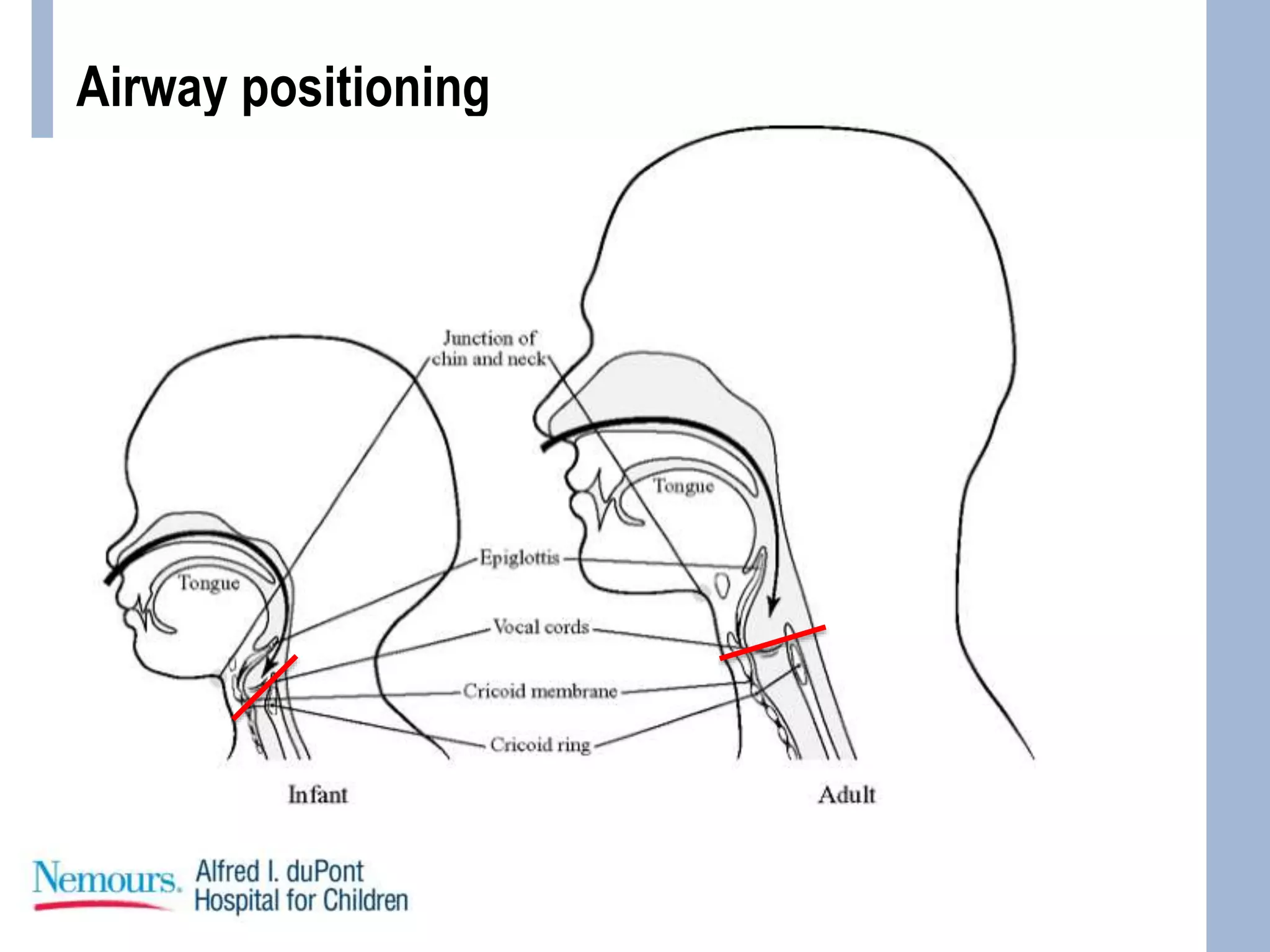
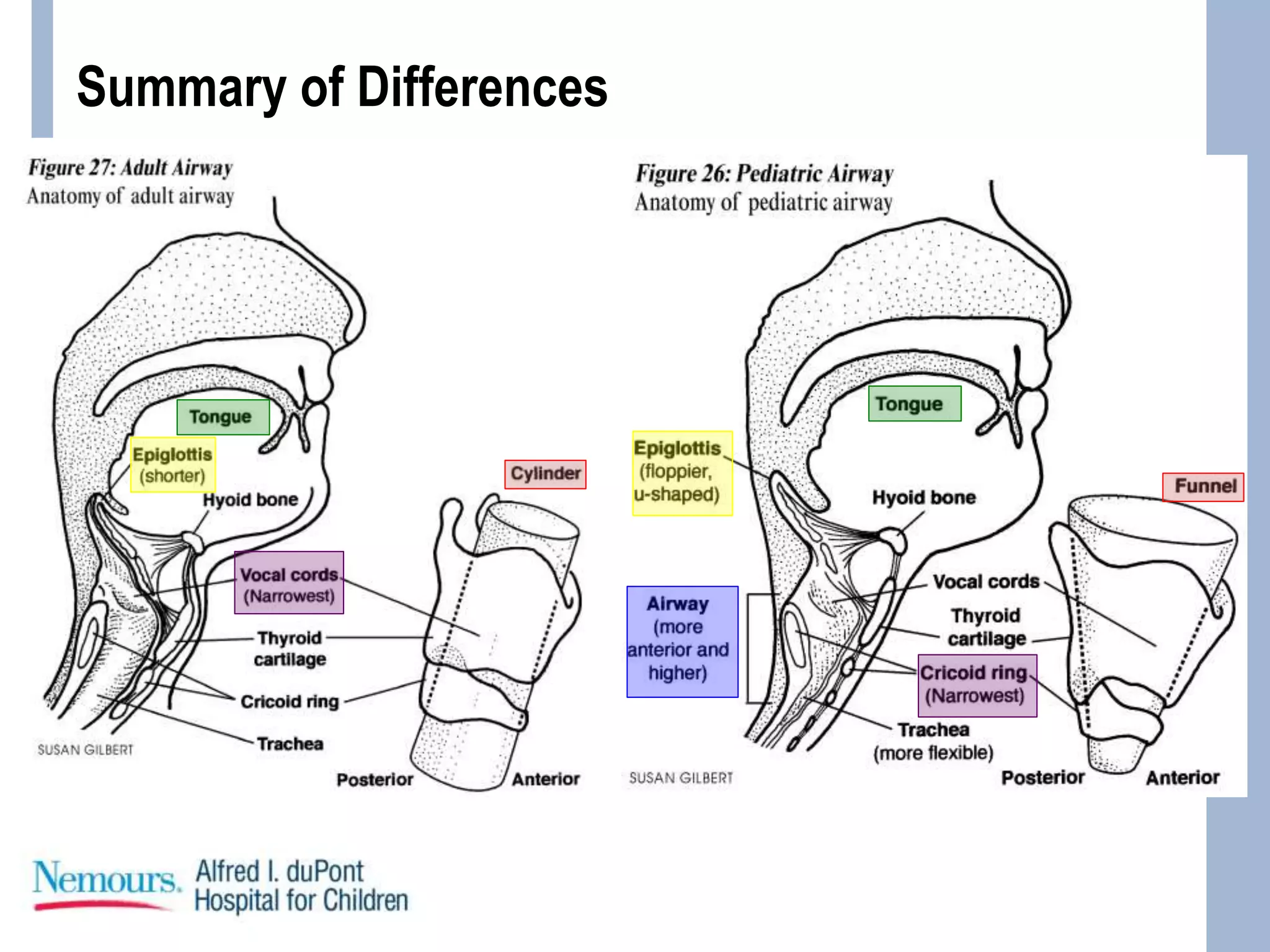
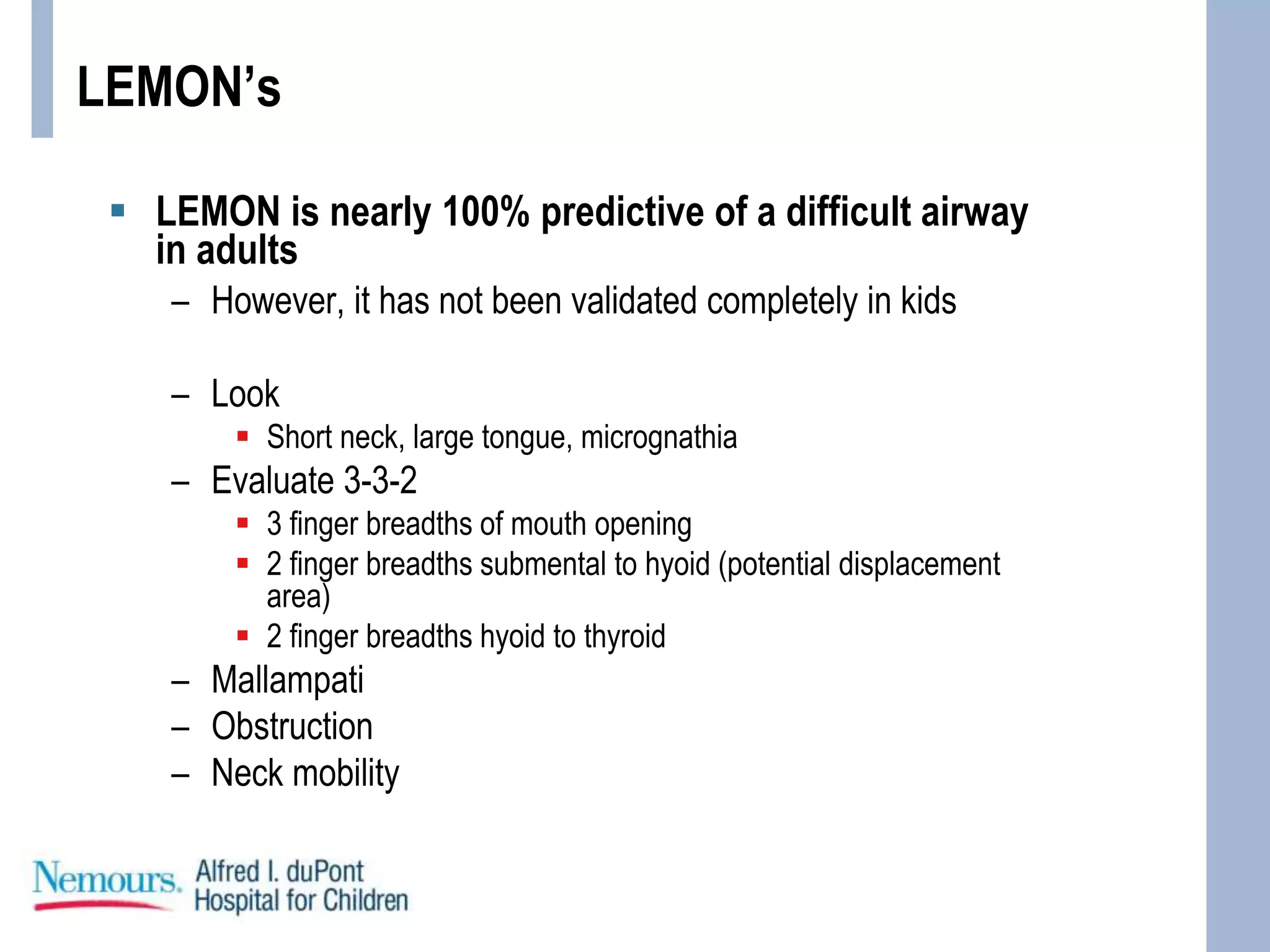
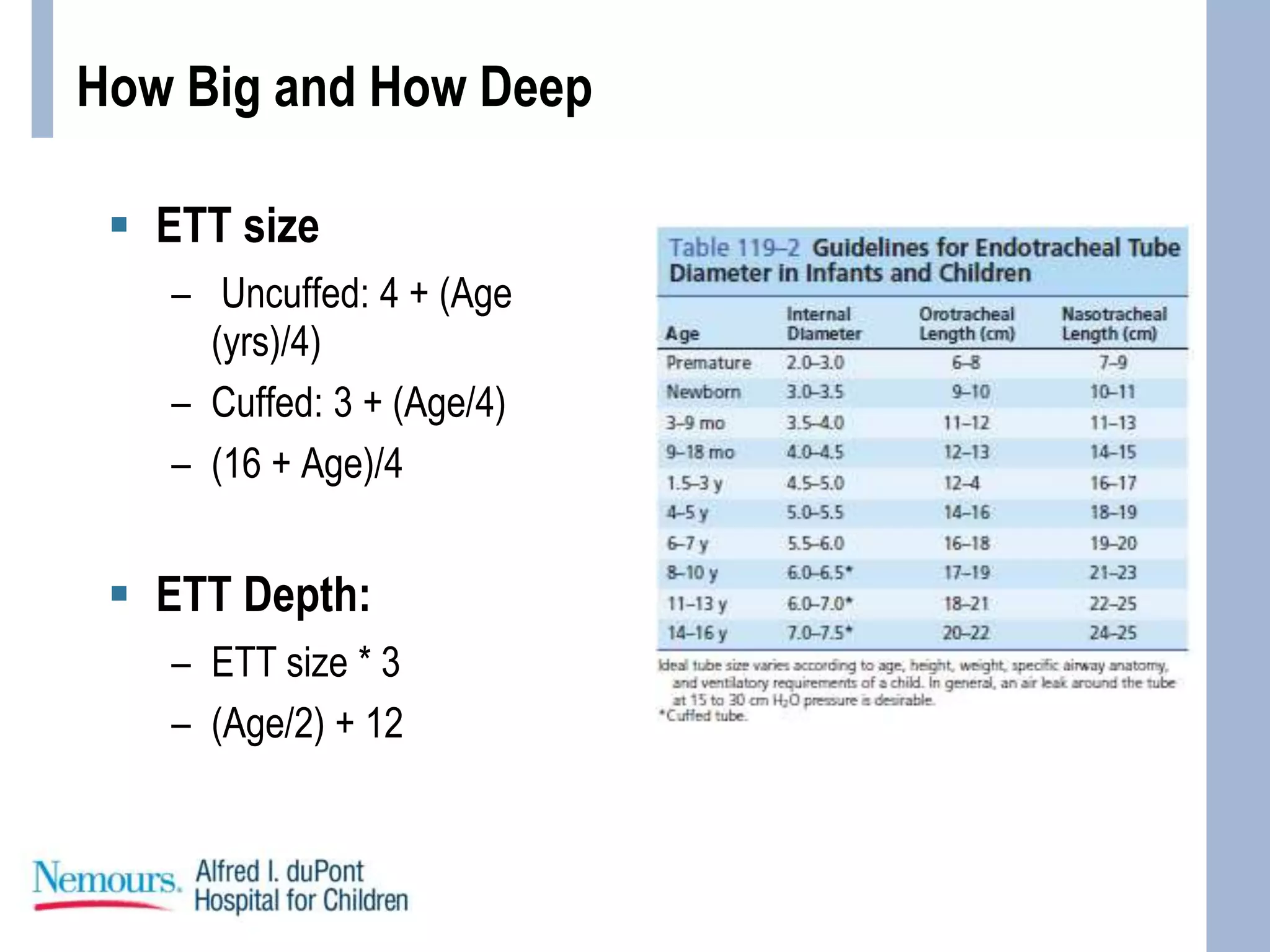
This document provides guidance on pediatric intubation. It discusses indications for intubation in pediatric patients, how pediatric airways differ from adults, important considerations before intubation, equipment and medications needed, and techniques for performing intubation. Key differences in pediatric airways include a larger tongue, angled vocal cords, differently shaped epiglottis, and a funnel-shaped larynx. Important assessments before intubation include evaluating mouth opening, neck mobility, and airway anatomy. Common induction agents described are etomidate, propofol, ketamine, and fentanyl/versed. Succinylcholine, rocuronium, and cisatracurium are paralytic options. Case examples are provided