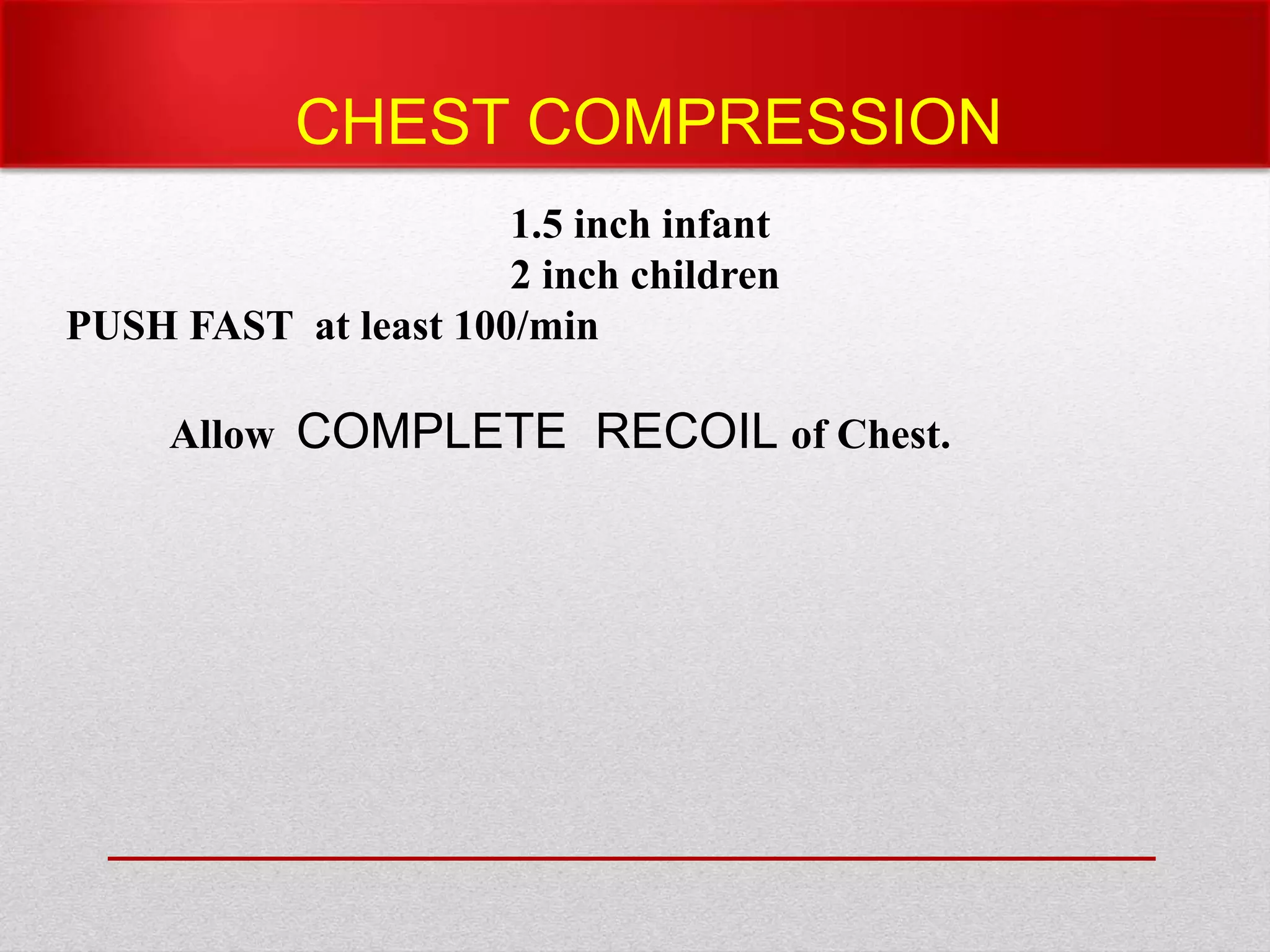
Paediatric basic life support (PBLS) involves resuscitation procedures to prevent anoxic brain damage and promote circulation and breathing in children. The key steps of PBLS are CAB - checking for circulation (C) by feeling for a pulse, opening the airway (A), and giving rescue breaths (B). For infants and children in cardiac arrest, high-quality chest compressions at least 100/min that depress the sternum 1/3 its depth are critical, along with proper head positioning and rescue breathing. PBLS should continue for 2 minutes in cycles of 30 compressions to 2 breaths before emergency help arrives or switching rescuers.