1. Basic life support for infants and children involves prompt cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), including chest compressions and breaths, which can significantly increase survival rates if provided before full cardiac arrest develops.
2. For infants, high-quality CPR involves two-finger chest compressions at a rate of 100 compressions per minute, with a compression depth of at least 1.5 inches, as well as breaths through a properly fitted face mask.
3. For older children, chest compressions are performed with one or two hands, depending on the number of rescuers, at a rate of 100 compressions per minute and a depth of at least 2 inches, along with breaths delivered through



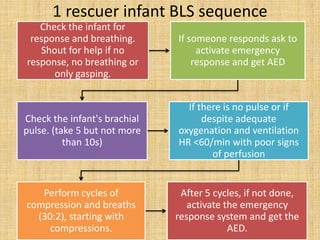







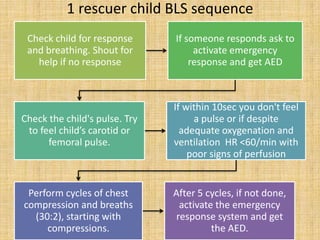


![High quality CPR improves chances of victim’s
survival-
Start compression within 10 sec of recognition of
cardiac arrest
Push hard push fast: Compress at a rate of at least
100/min with depth of approx. 2inches for children
and 11/2 inches for infants
Allow complete chest recoil after each compression
Minimize interruptions in compressions
Give effective breaths that make chest rise. [avoid
excessive ventilation]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bls-130321101436-phpapp01/85/BLS-and-CPR-15-320.jpg)
