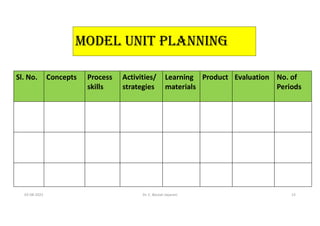
The document outlines the concept of unit planning in education, emphasizing its role in organizing instructional materials to enhance student learning experiences. It highlights the characteristics of effective units, necessary steps in unit planning, and the advantages of adopting a structured approach. Additionally, it underscores the importance of understanding student needs and applying pedagogical principles for successful implementation.