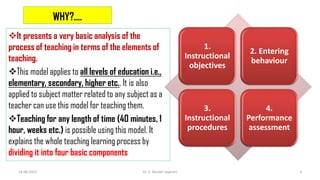
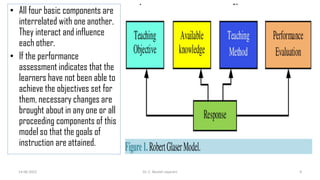
Glaser's Basic Teaching Model is a psychological model of teaching developed by Robert Glaser in 1962. It explains the relationship between teaching and learning through four basic components: (1) instructional objectives, (2) entering behaviors of students, (3) instructional procedures used by the teacher, and (4) performance assessments to evaluate student learning. The model assumes students have prior knowledge and the teacher guides students from their entering behaviors to achieving the instructional objectives through various teaching methods and strategies. It can be applied to any subject or grade level to systematically structure the teaching and learning process.