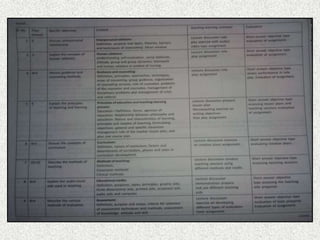
This document discusses course planning and unit planning for nursing programs. It defines course planning as organizing the content and learning experiences for a program leading to graduation. Unit planning involves dividing subject matter into large subdivisions. The key aspects of course and unit planning include:
1. Stating objectives and selecting appropriate content and resources
2. Organizing content and learning experiences in a logical sequence
3. Evaluating student learning through various assessment methods
The purpose is to ensure students learn essential information and skills through well-structured and coordinated programs and units. Teachers play an important role in effective planning at both the course and unit levels.