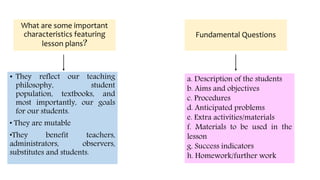
This document discusses unit and lesson planning for language teaching. It notes that unit plans are designed around a specific topic and help teachers integrate standards thematically while allowing them to reflect on learning goals. Well-designed unit plans stick to a timeline, consider student needs and interests, and include a variety of assessment tools. Lesson plans serve as a guide for teachers, help plan assessments, and provide a record of what was taught. They should reflect a teacher's philosophy and goals for students. Both unit and lesson plans are important planning tools for teachers.