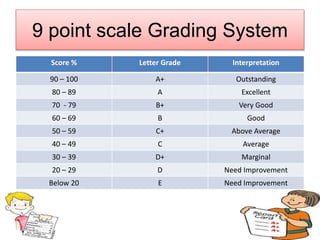
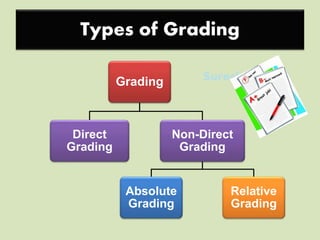
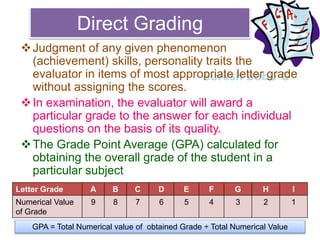
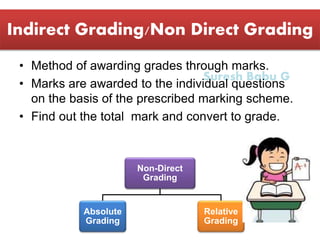
The document discusses different aspects of grading systems in education. It defines grading as a process of evaluating student performance on exams using scales with letters or numbers. There are different types of grading systems such as percentage grading from 0-100, letter grading from A-F, norm-referenced grading comparing students, and mastery grading based on attaining a specified level. Direct grading involves directly awarding letter grades without scores while indirect grading uses marks that are then converted to grades. Relative grading compares student performance within a group/class using statistical methods to determine grade ranges, while absolute grading is based on pre-specified standards for performance levels.