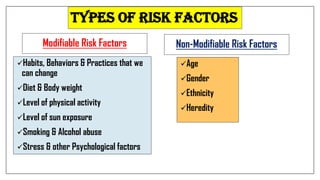
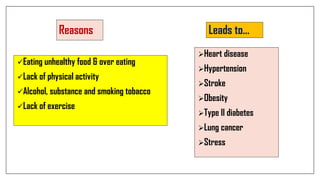
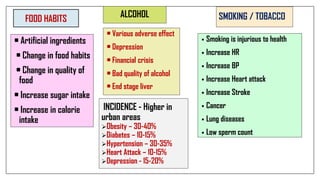
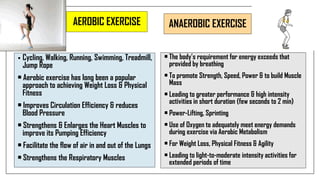
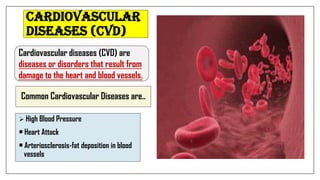
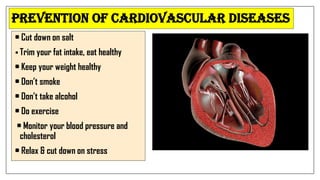
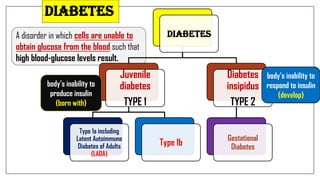
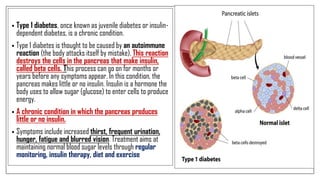
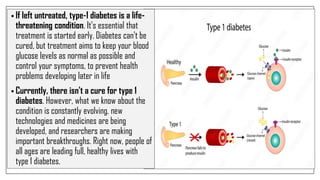
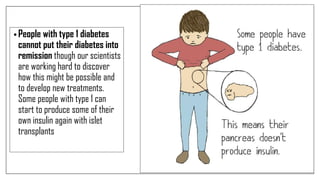
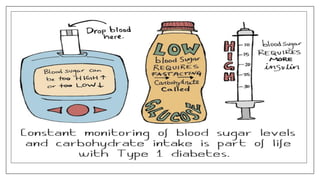
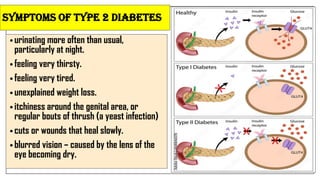
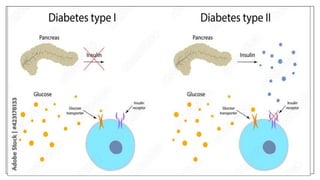
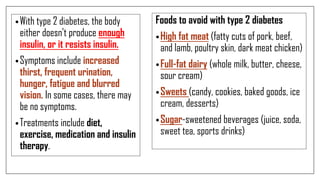
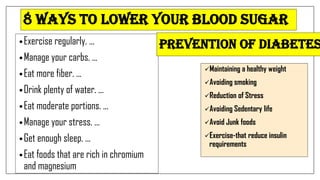
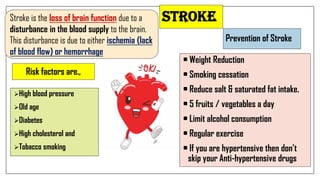
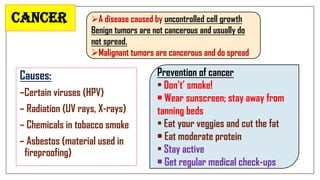
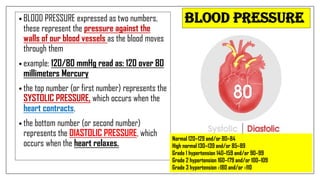
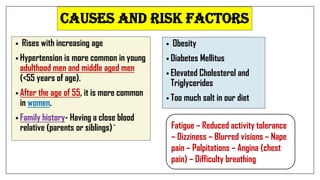
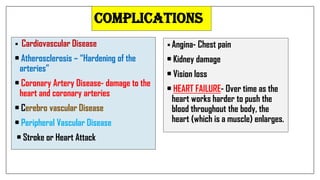
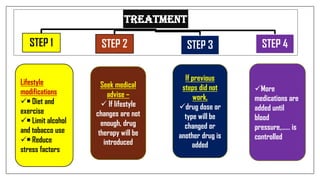
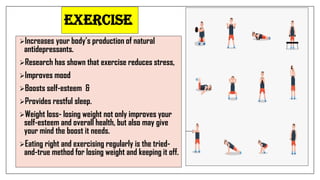
The document discusses lifestyle diseases, which are health issues primarily influenced by individual habits and routines. It outlines modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors, common diseases like cardiovascular conditions, diabetes, and cancer, as well as preventive measures including diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. Emphasis is placed on the importance of regular activity, healthy eating, and stress management to reduce the risk of chronic diseases.