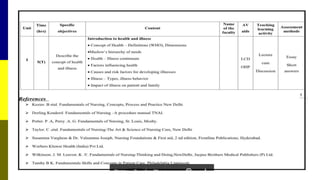
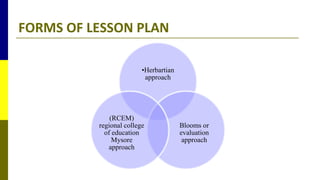
The document outlines the comprehensive processes of course, unit, and lesson planning in nursing education. It emphasizes the significance of structured planning for effective learning experiences, detailing criteria, characteristics, and essential steps for each type of planning. Additionally, the roles of teachers in facilitating this planning and the importance of clear objectives, resources, and evaluation methods are highlighted.