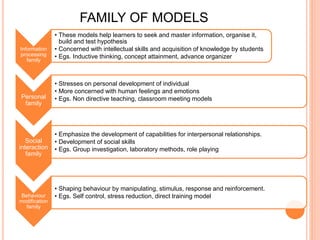
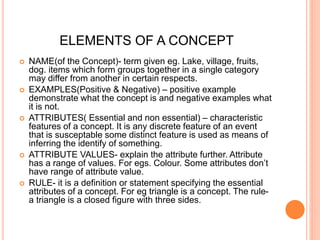
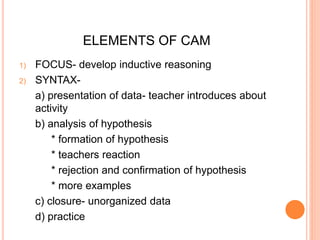
The document discusses models of teaching proposed by Bruce Joyce and Marsha Weil. It aims to provide different teaching strategies to match various learning styles. Joyce and Weil developed several teaching models consisting of guidelines for designing educational activities and environments to achieve learning goals. The models fall into four families - information processing, personal, social interaction, and behavior modification. Each model has elements like focus, syntax, social system, and principles of reaction. One example provided is the concept attainment model, which helps teach concepts by having students categorize examples and form hypotheses to understand attributes and rules.