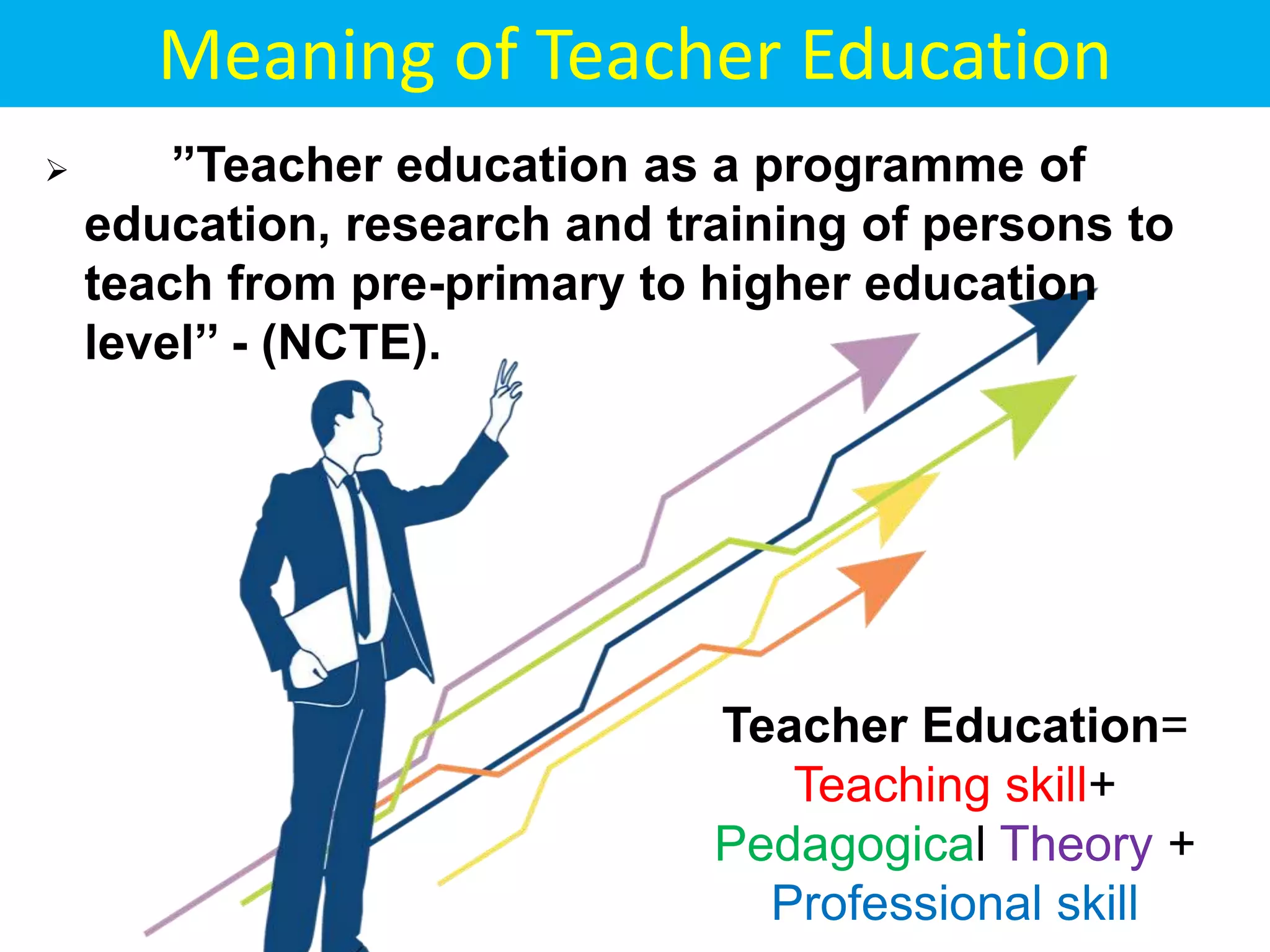
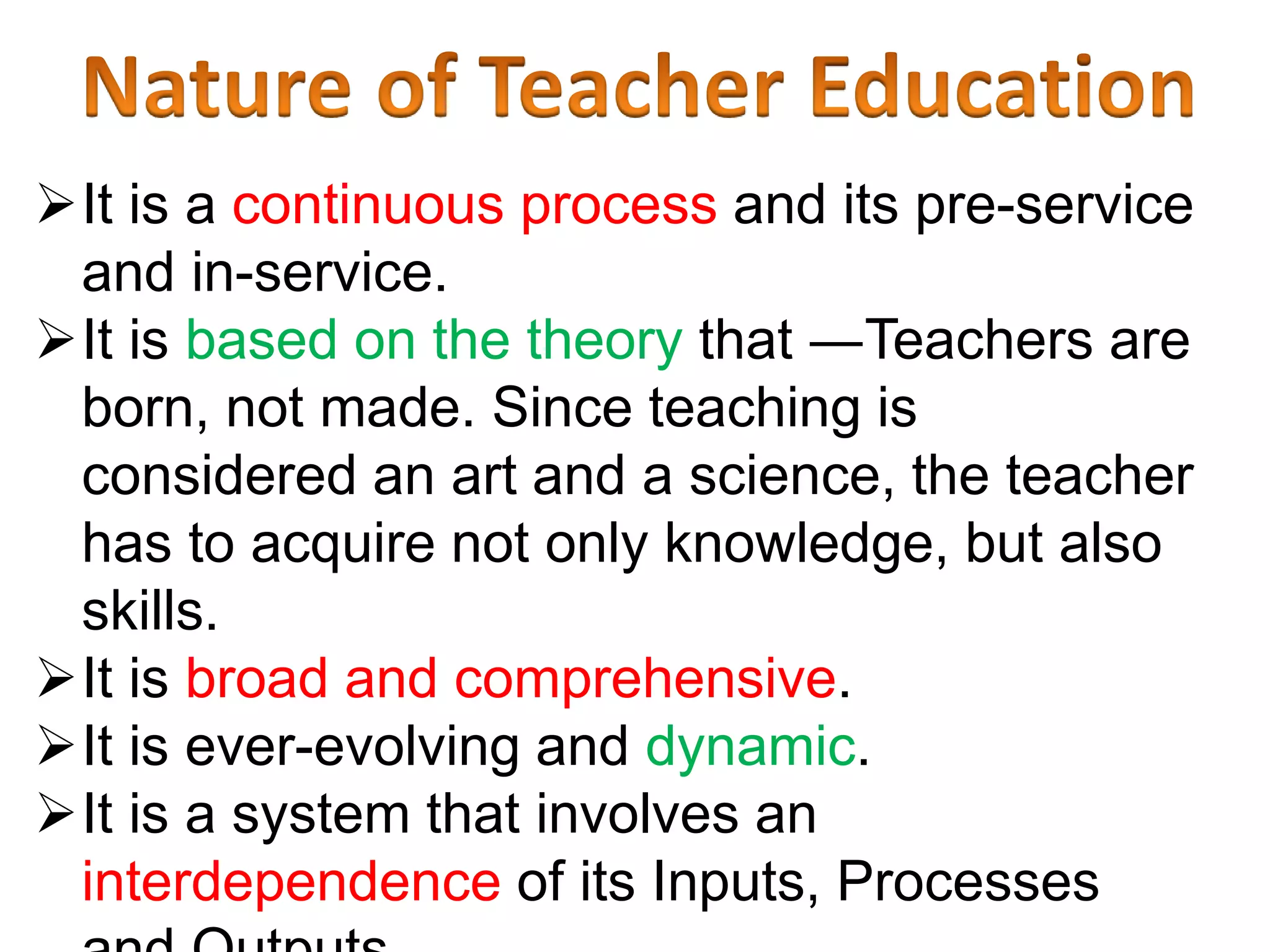
Education is a systematic process of acquiring knowledge, skills, values, and beliefs, particularly through teacher education which involves training for various educational levels. Teacher education encompasses teaching skills, pedagogical theory, and professional skills, and is a dynamic, continuous process tailored to meet the needs of pre-primary to tertiary education. It includes various training programs like Montessori, B.Ed, M.Ed, and vocational training for specialized subjects.