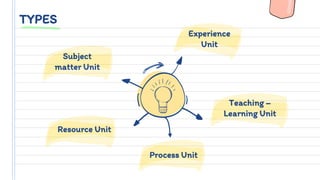
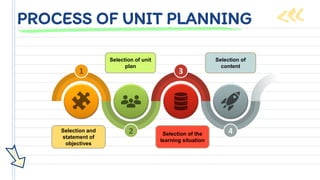
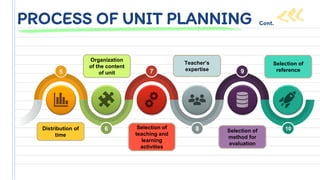
The document outlines a unit plan, detailing its objectives, criteria for a good unit, and the importance of unit planning in education. It explains types of unit planning and the process involved in creating a unit plan, including selecting objectives, content, teaching methods, and evaluation strategies. Additionally, it emphasizes the need to consider students' backgrounds, interests, and the various learning experiences necessary for effective teaching.