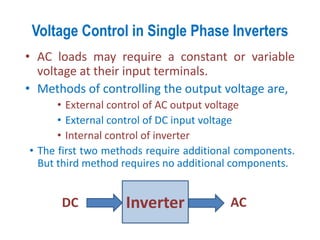
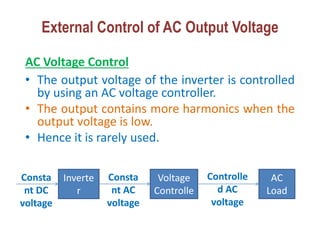
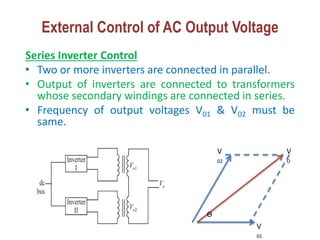
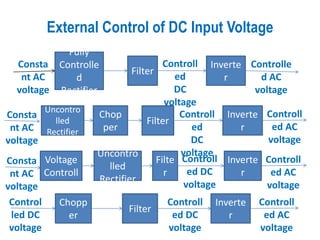
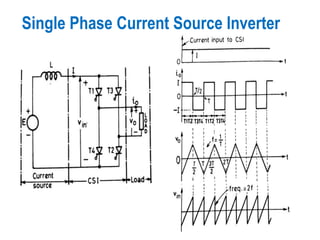
1) There are several methods to control the output voltage of single phase inverters including external control of AC output voltage, external control of DC input voltage, and internal control of the inverter.
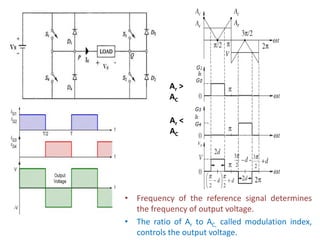
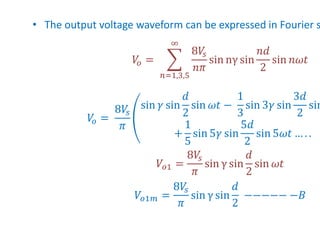
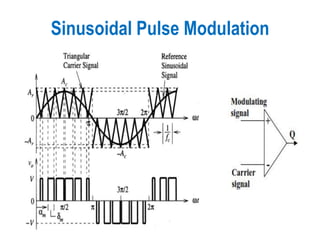
2) Internal control of the inverter through pulse width modulation is commonly used as it requires no additional components. Pulse width modulation controls the output voltage by adjusting the ON and OFF periods of the inverter components.
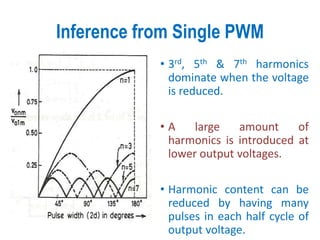
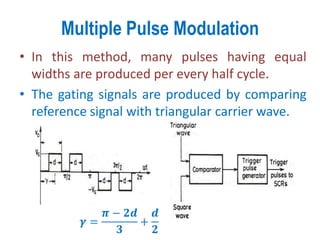
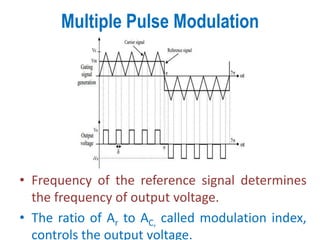
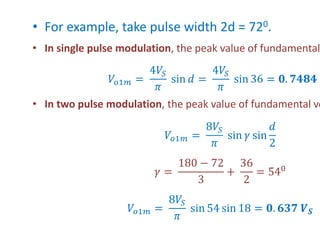
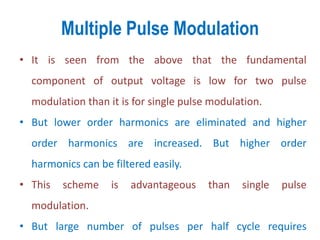
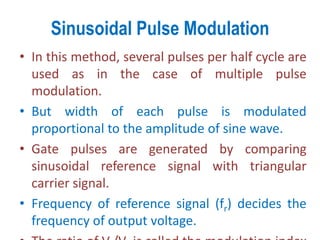
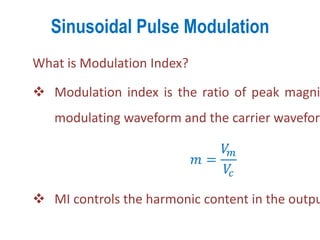
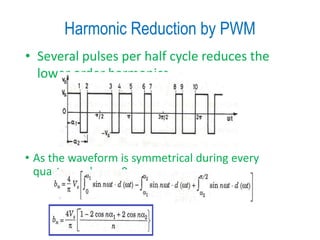
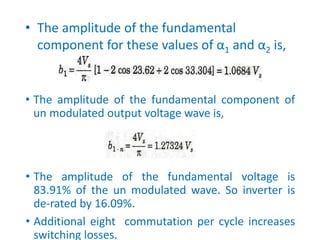
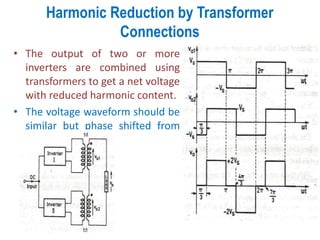
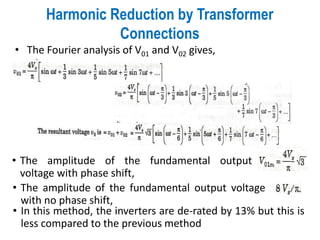
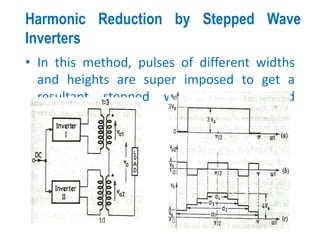
3) Harmonic reduction can be achieved through techniques like multiple pulse modulation, sinusoidal pulse modulation, and combining output voltages from multiple inverters with transformer connections. Internal control of the inverter through advanced PWM techniques is effective in minimizing harmonics in the output voltage.