Embed presentation
Downloaded 15 times



An inverter is a static device that converts DC power from a source like batteries into AC power at a desired output voltage and frequency. There are different types of inverters classified by their commutation method, component connections, and the nature of the DC source. Voltage source inverters have a constant voltage input and output voltage does not depend on the load, while current source inverters have a constant current input and output voltage depends on the load. Common inverter configurations include single phase half and full bridge inverters, and three phase inverters that can operate in 180 or 120 degree modes.
Introduction to the presentation on Inverters by Mr. A. Johny Renoald.
Definition of an inverter as a device converting DC to AC power, with applications in various fields.
Inverters classified based on commutation, connections, and nature of DC source feeding.
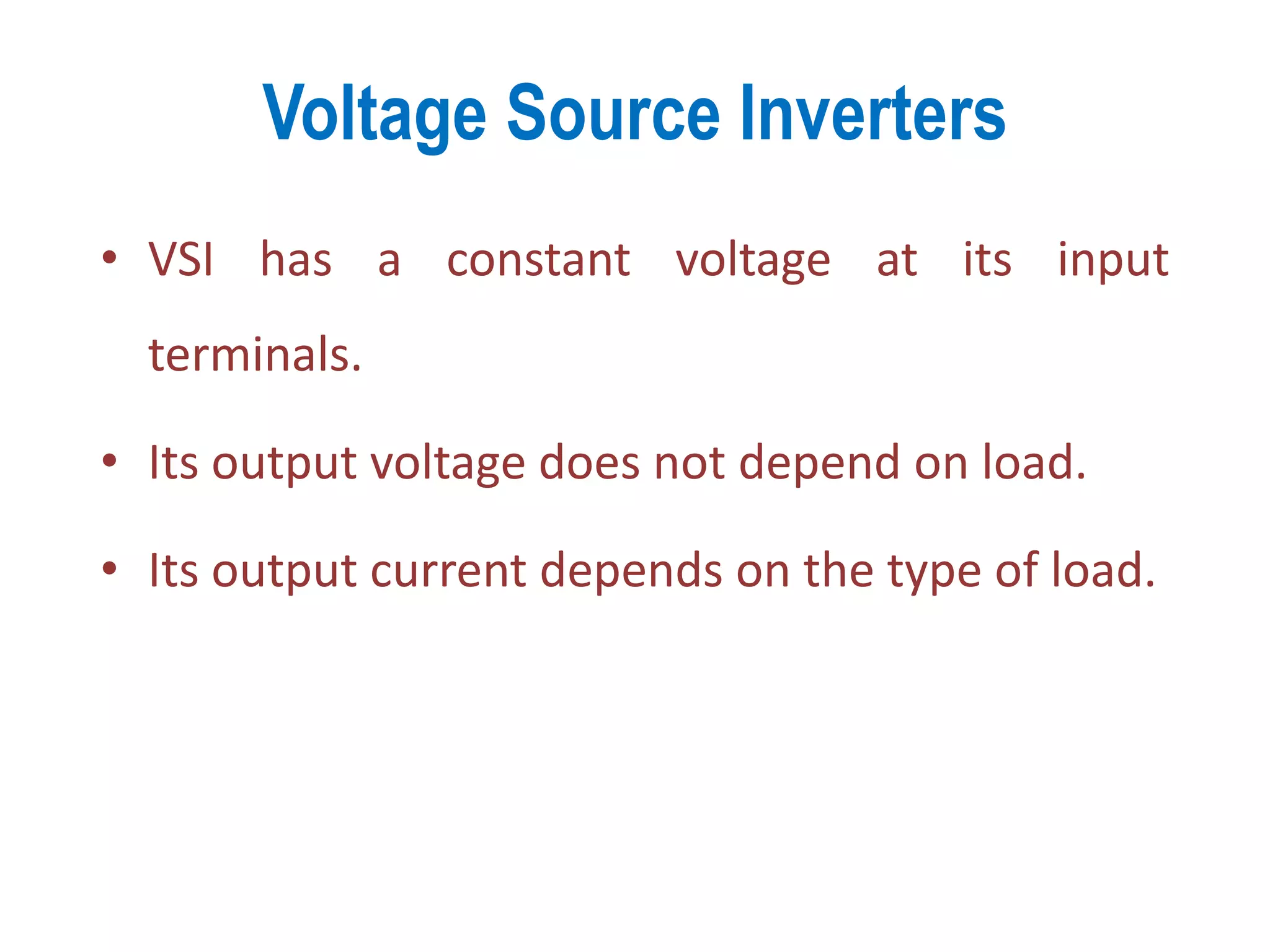
VSI features: constant input voltage, output voltage independent of load, and output current dependent on load type.
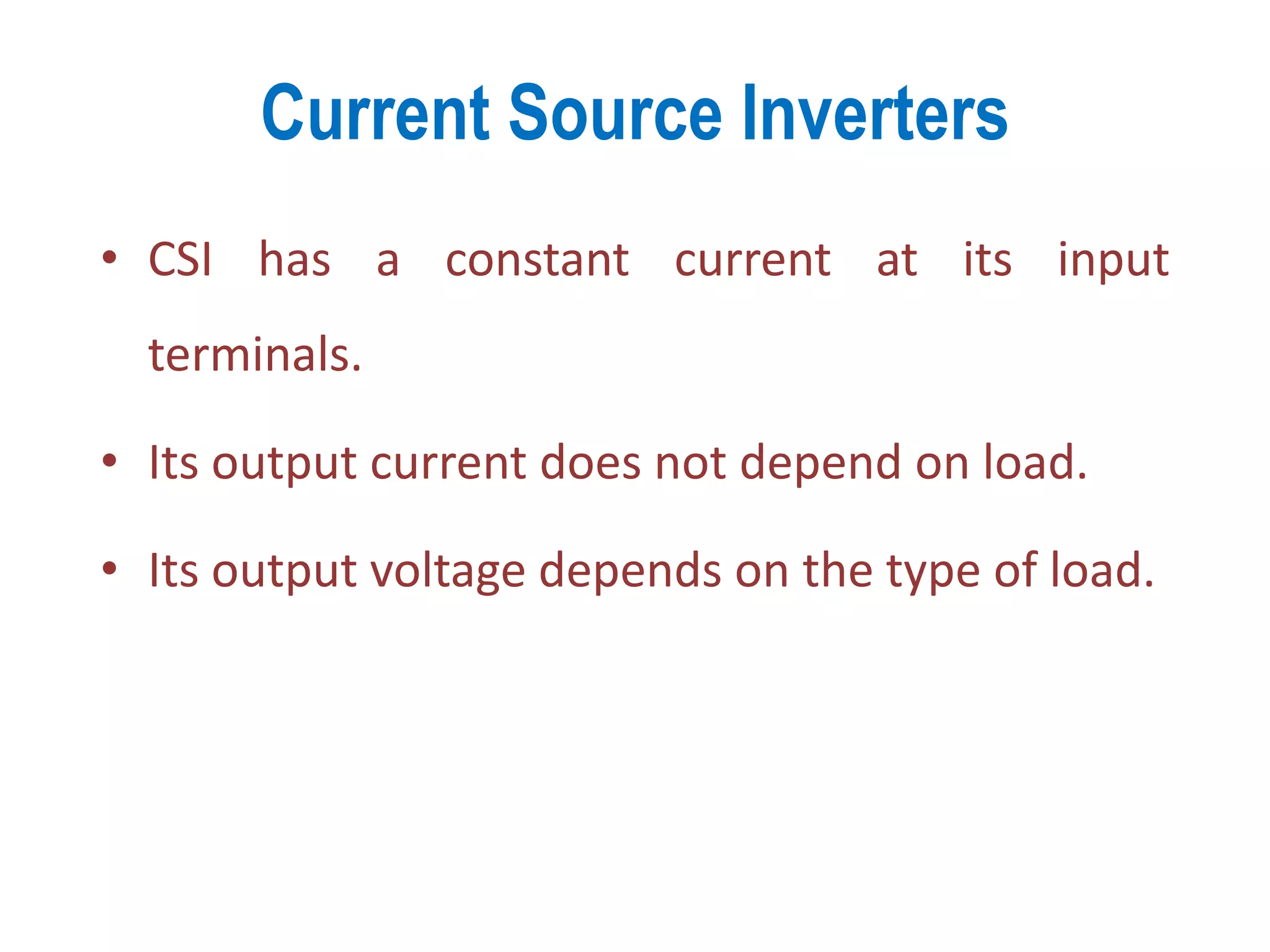
CSI characteristics: constant input current, output current independent of load, and output voltage depends on load.
Subcategories of VSI: single phase, half bridge, full bridge, and three phase variants.
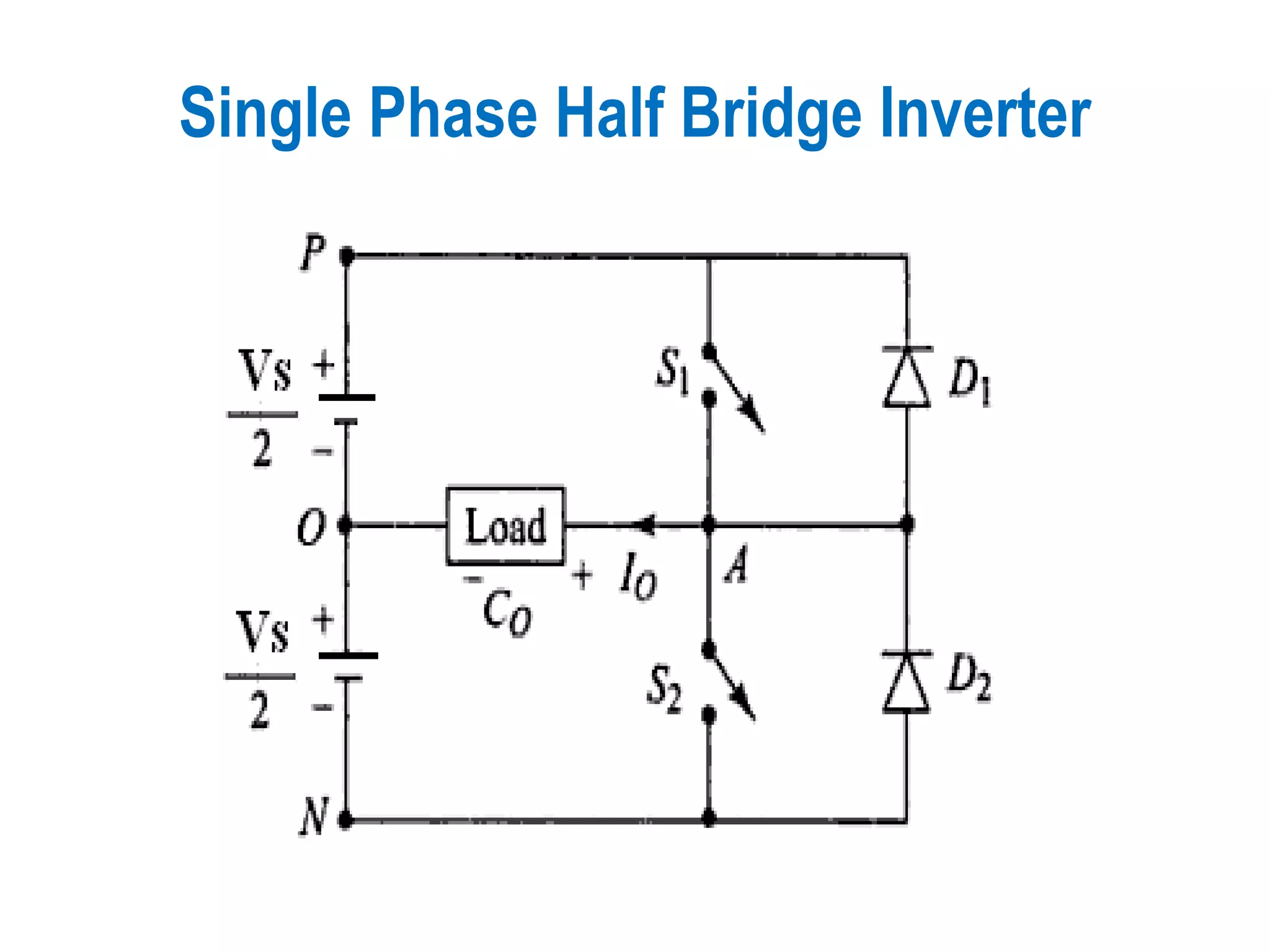
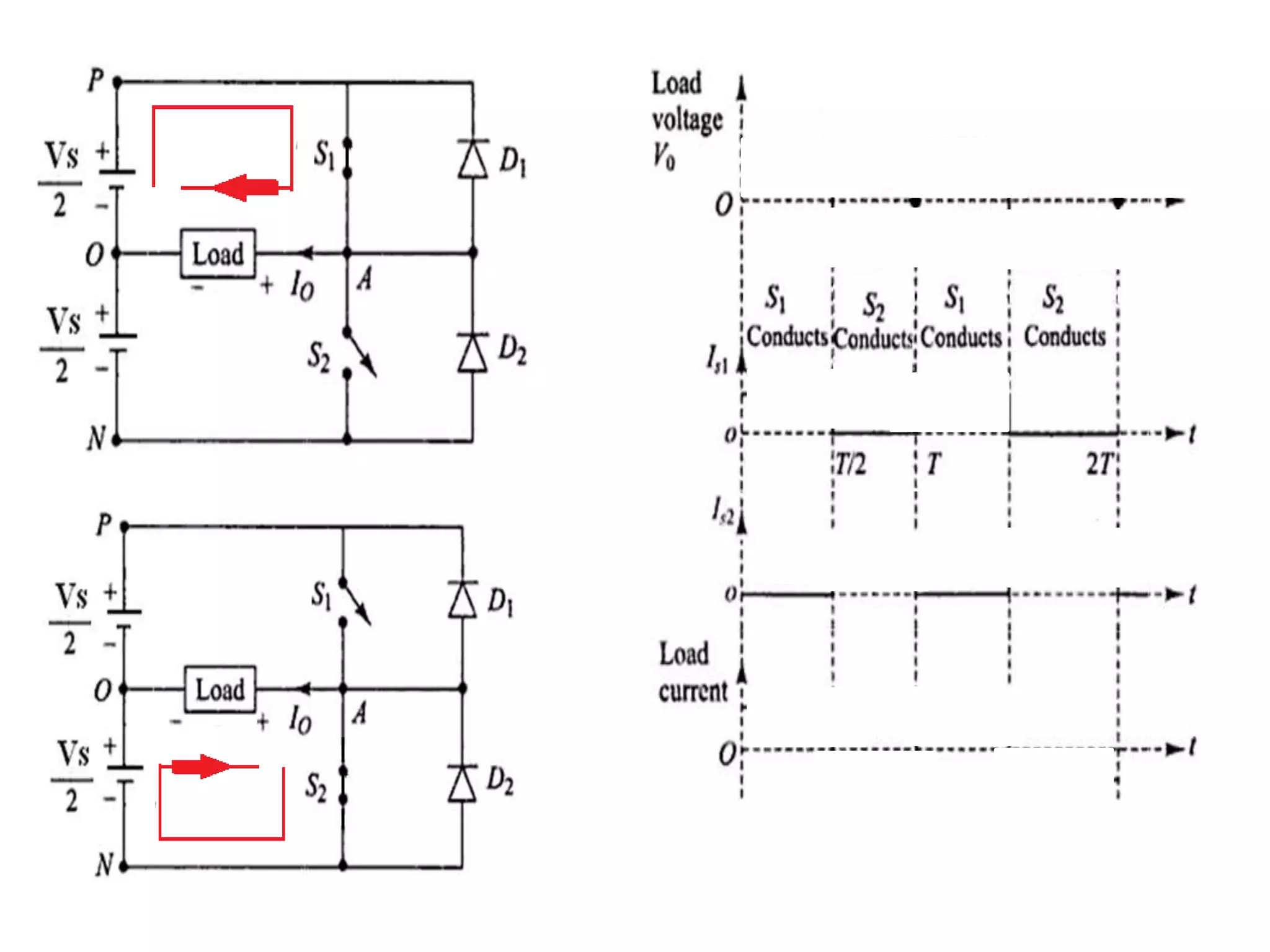
Focus on the design and characteristics of a Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter.
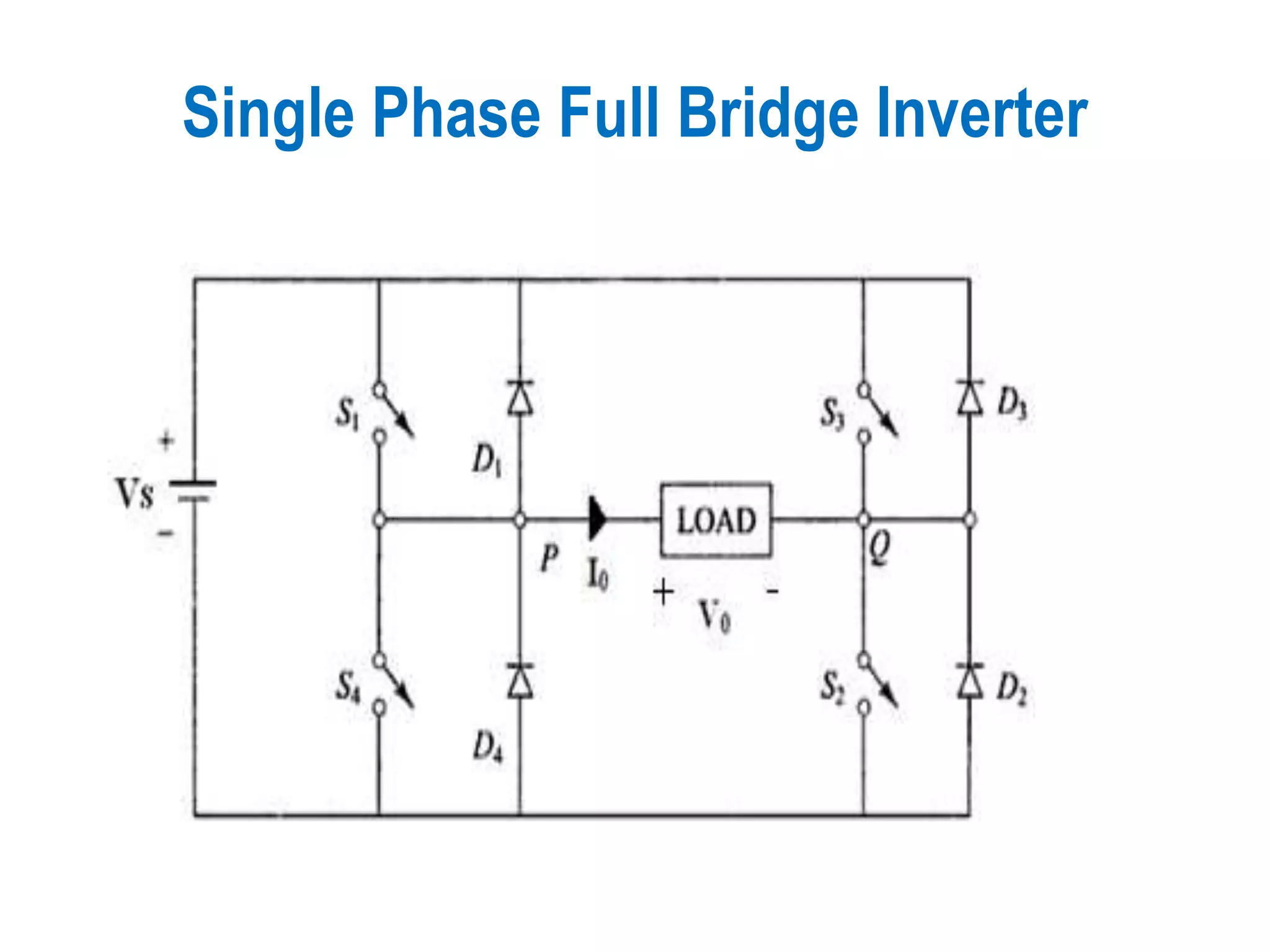
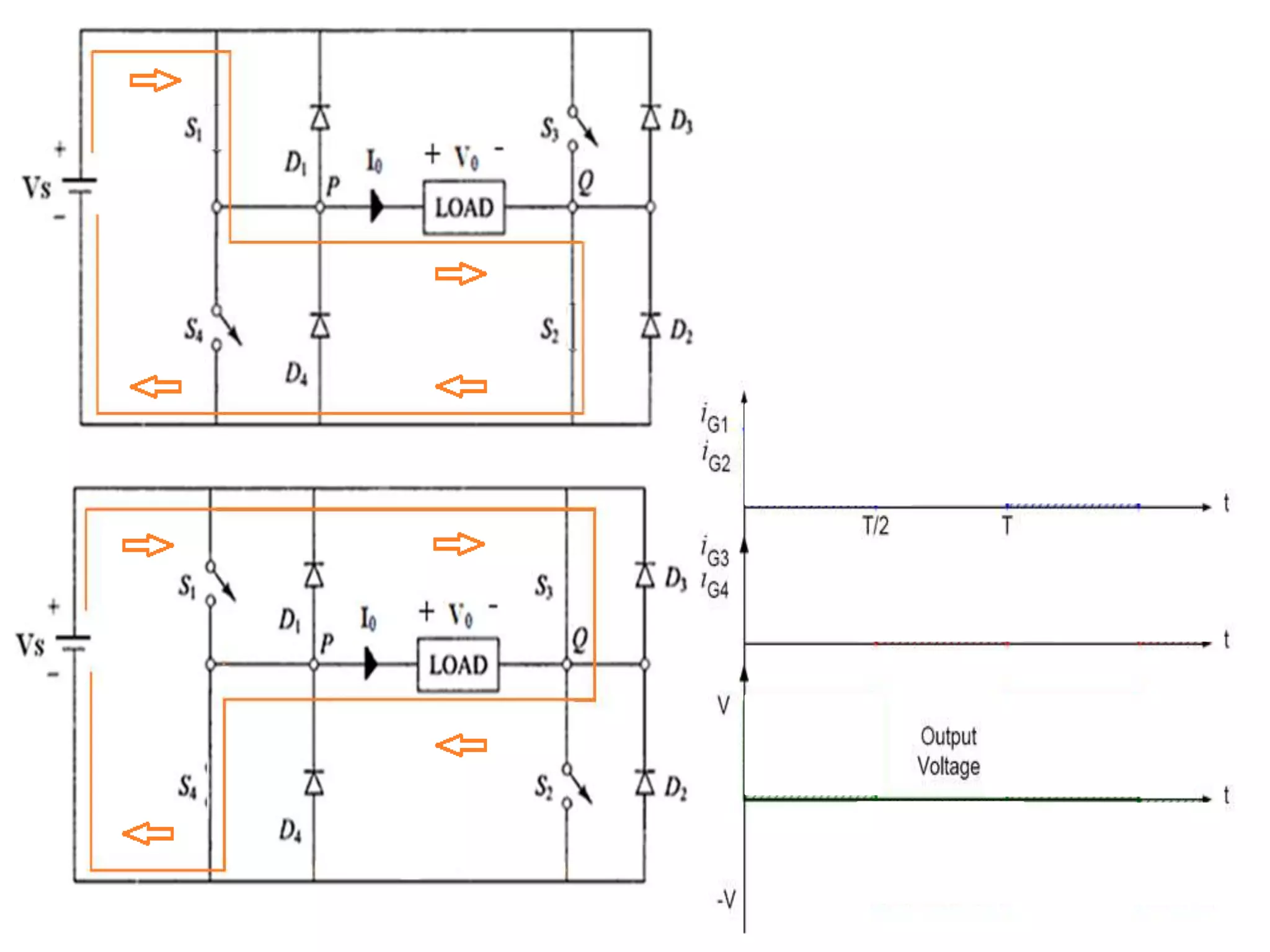
Details regarding the configuration and operation of a Single Phase Full Bridge Inverter.
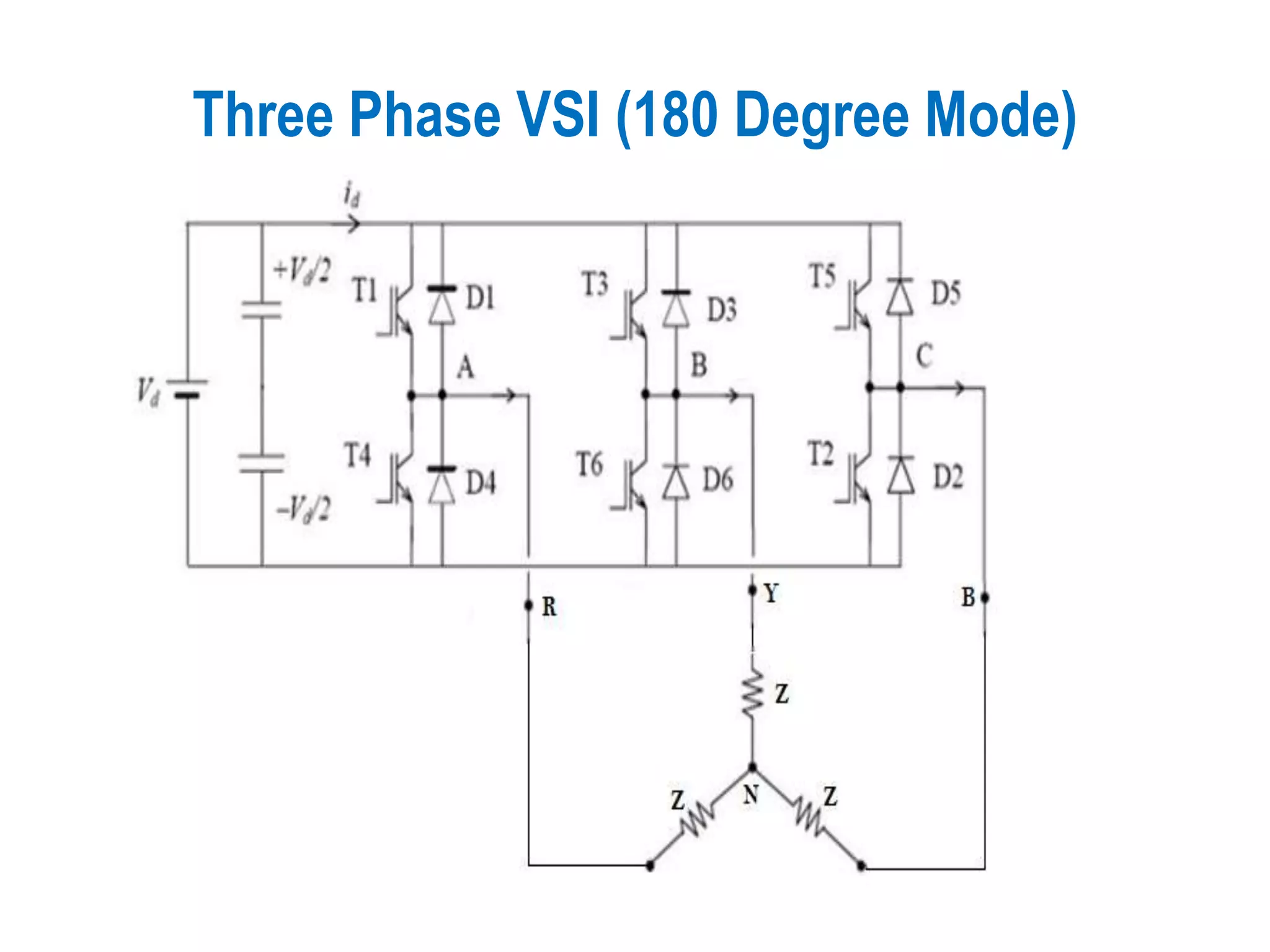
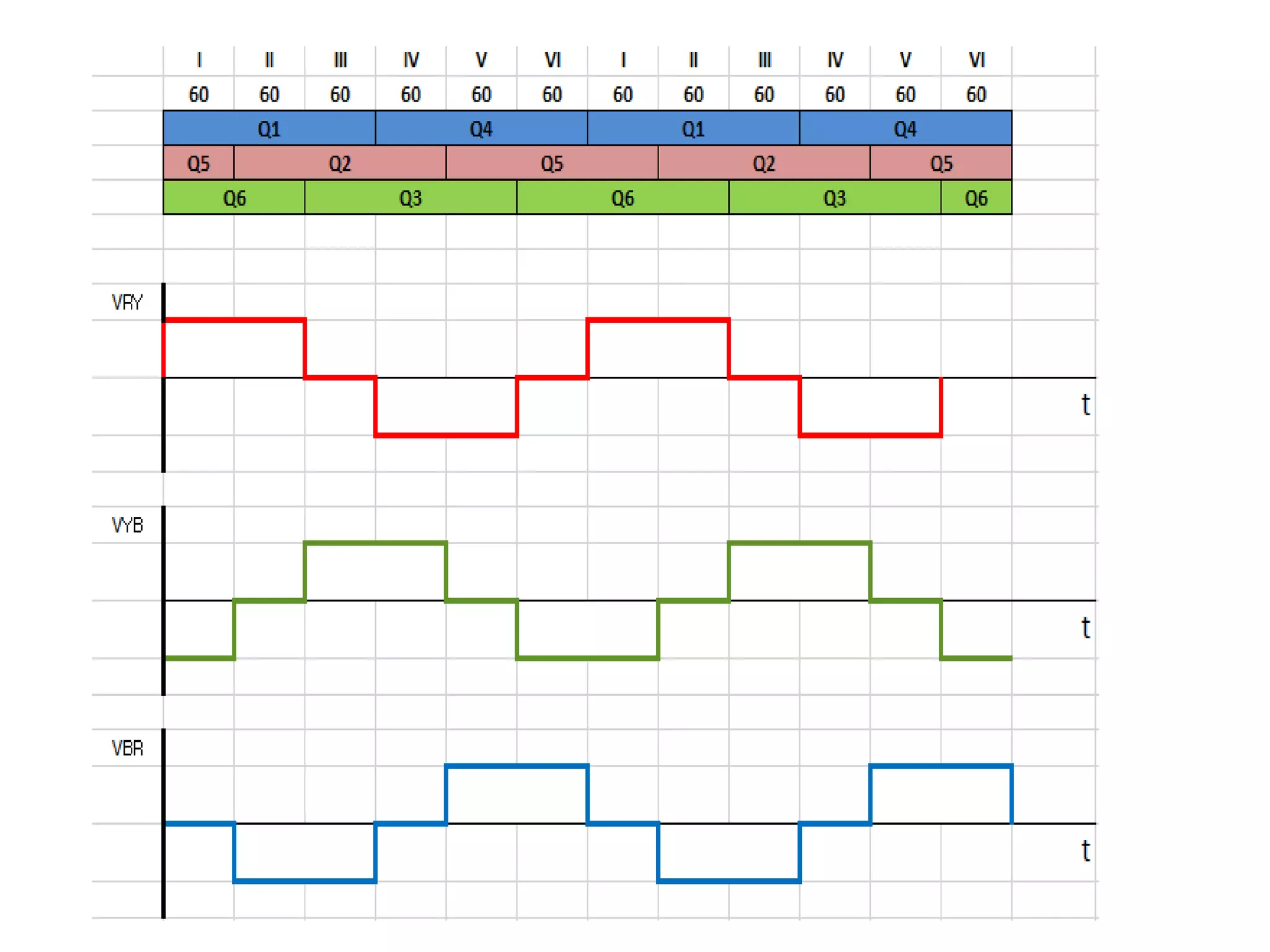
Exploration of the Three Phase VSI operating in the 180-degree mode.
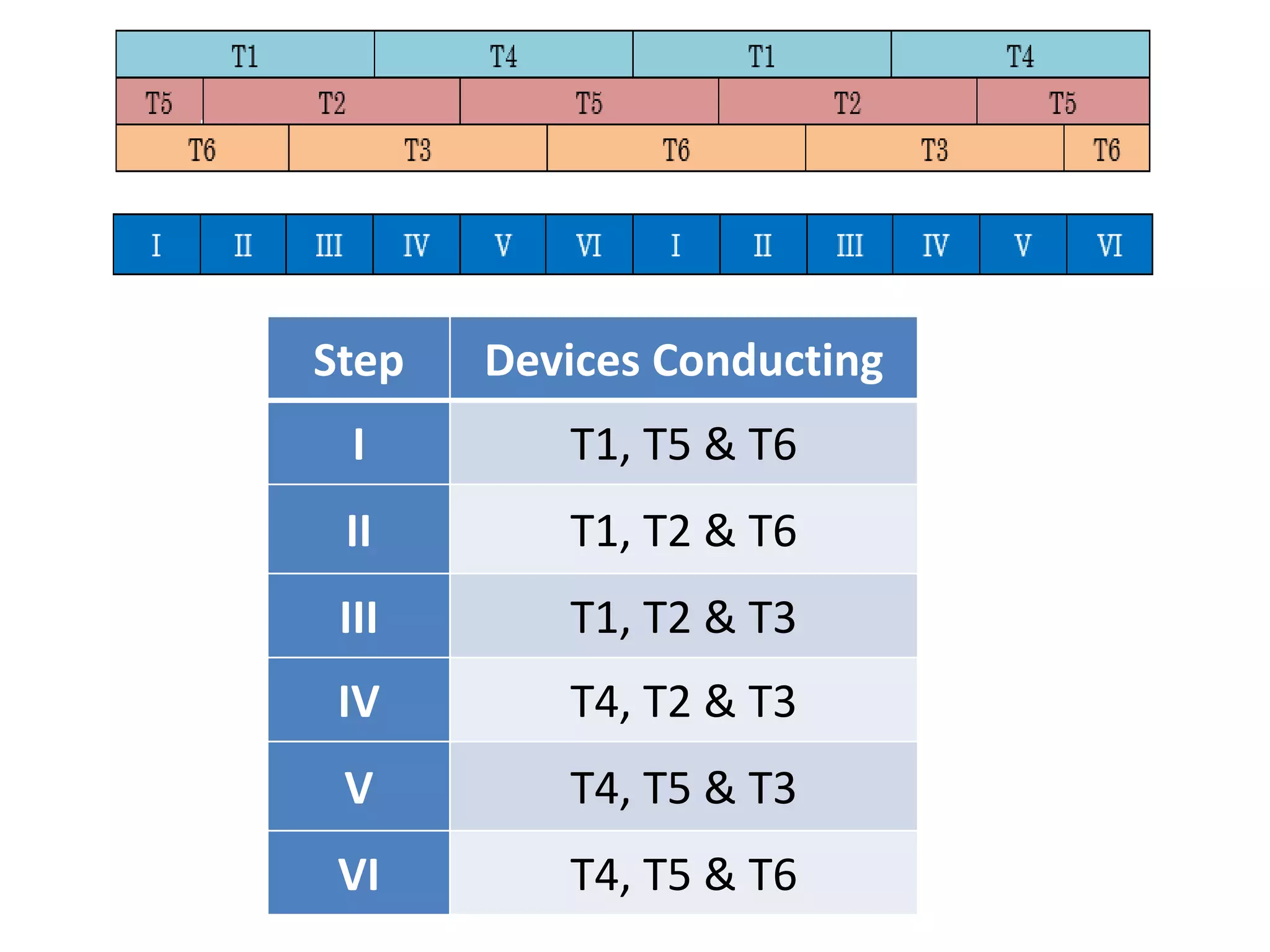
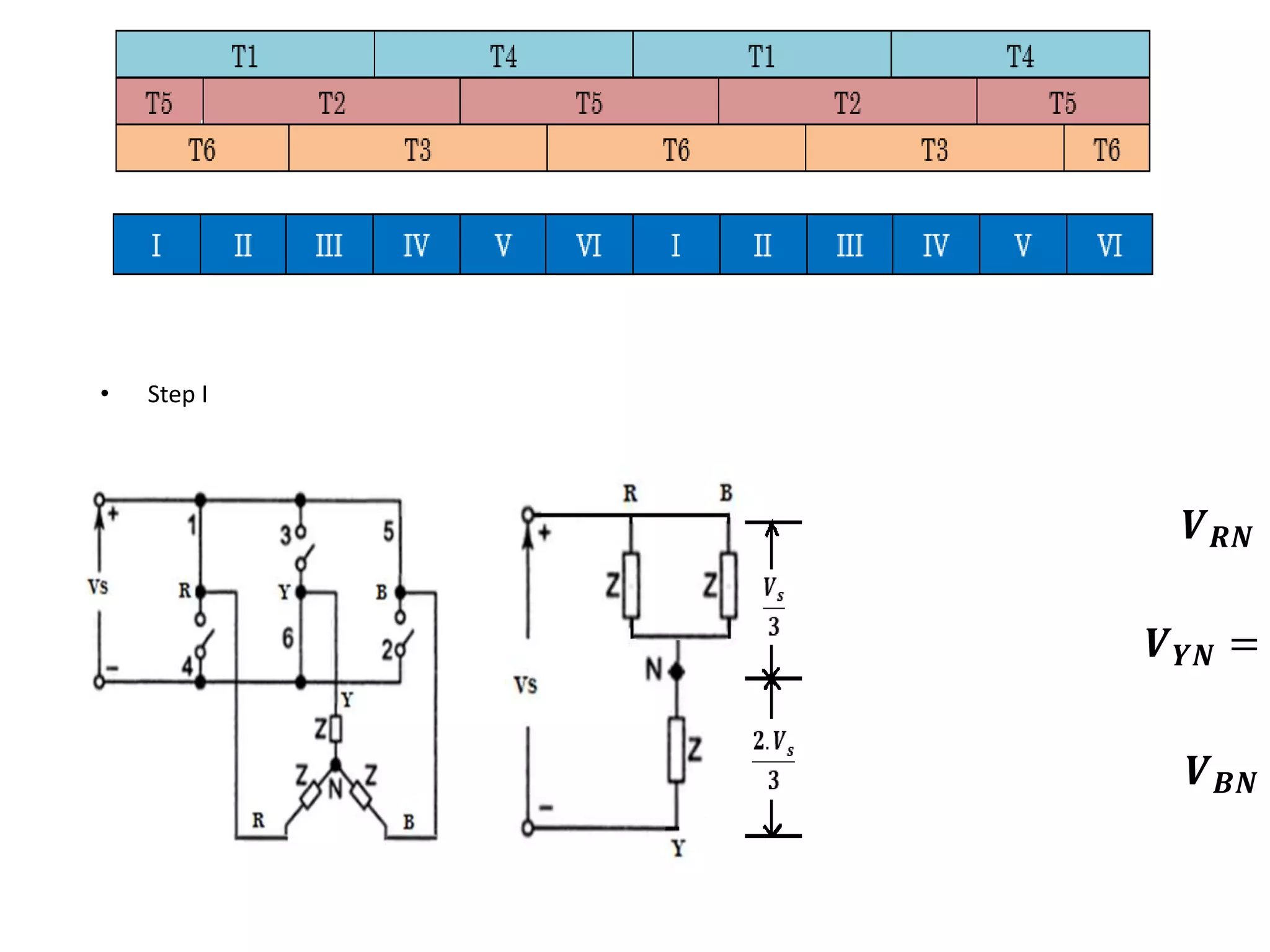
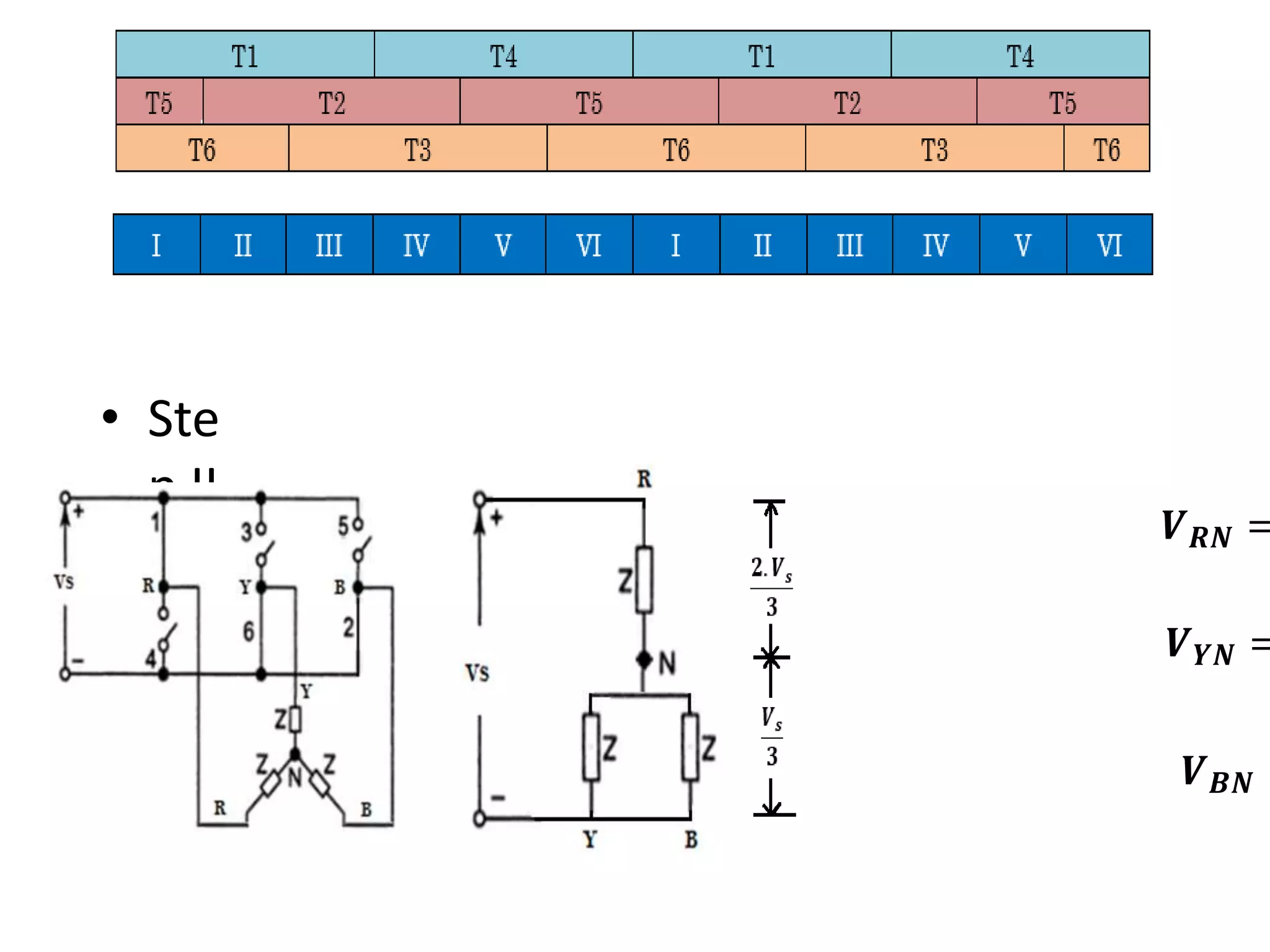
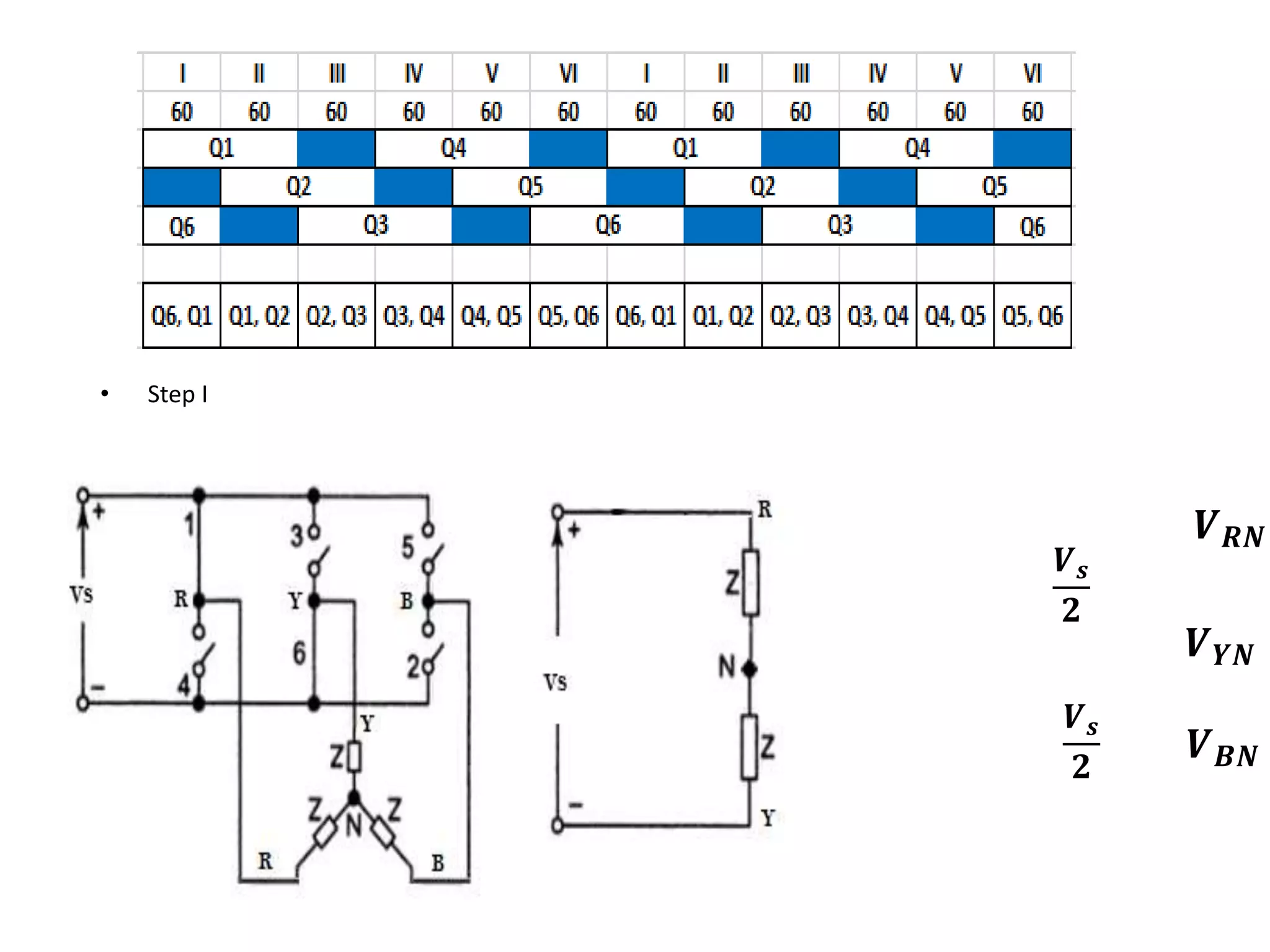
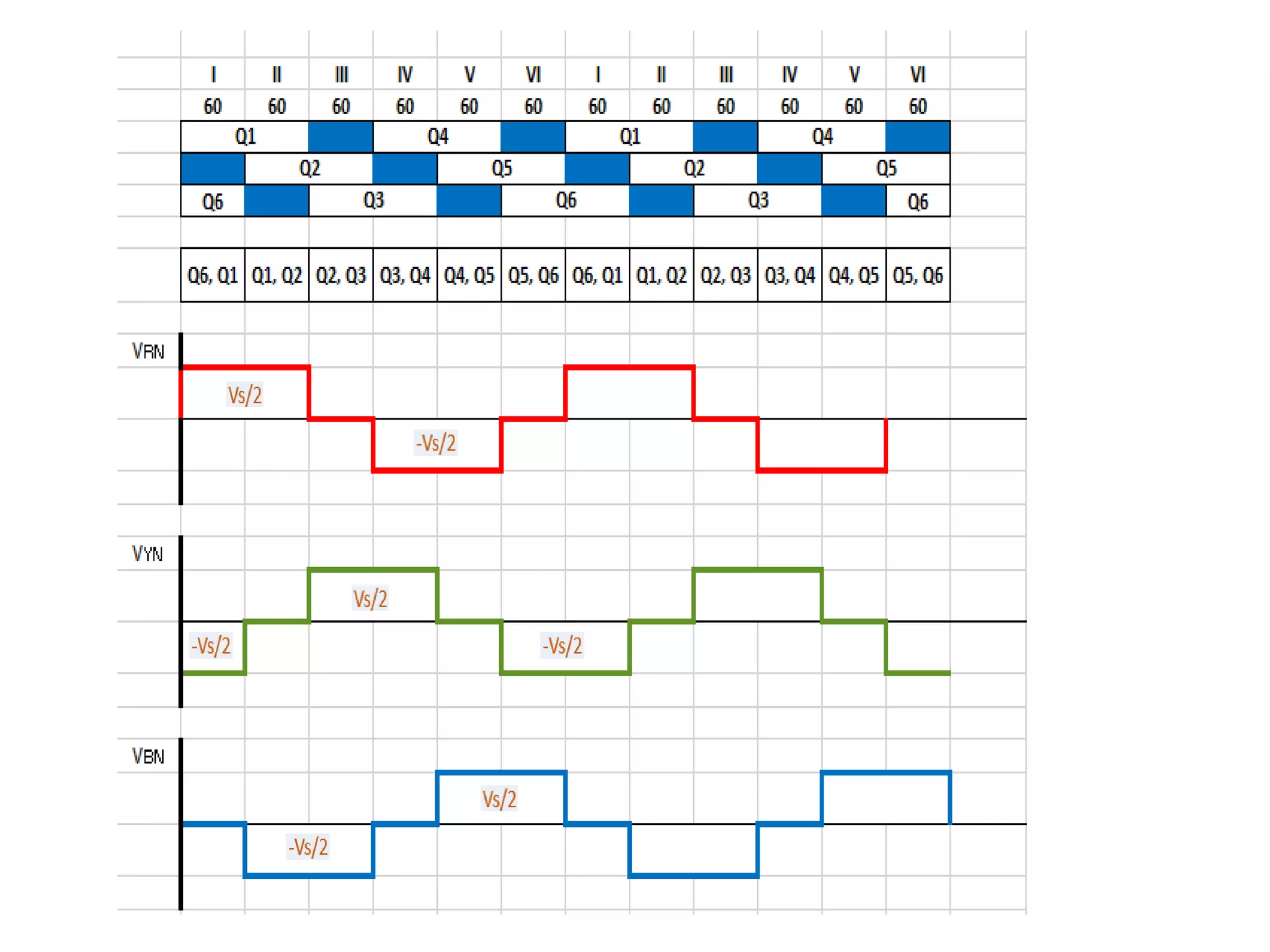
Conducting steps for three-phase VSI involving switching devices in different combinations.
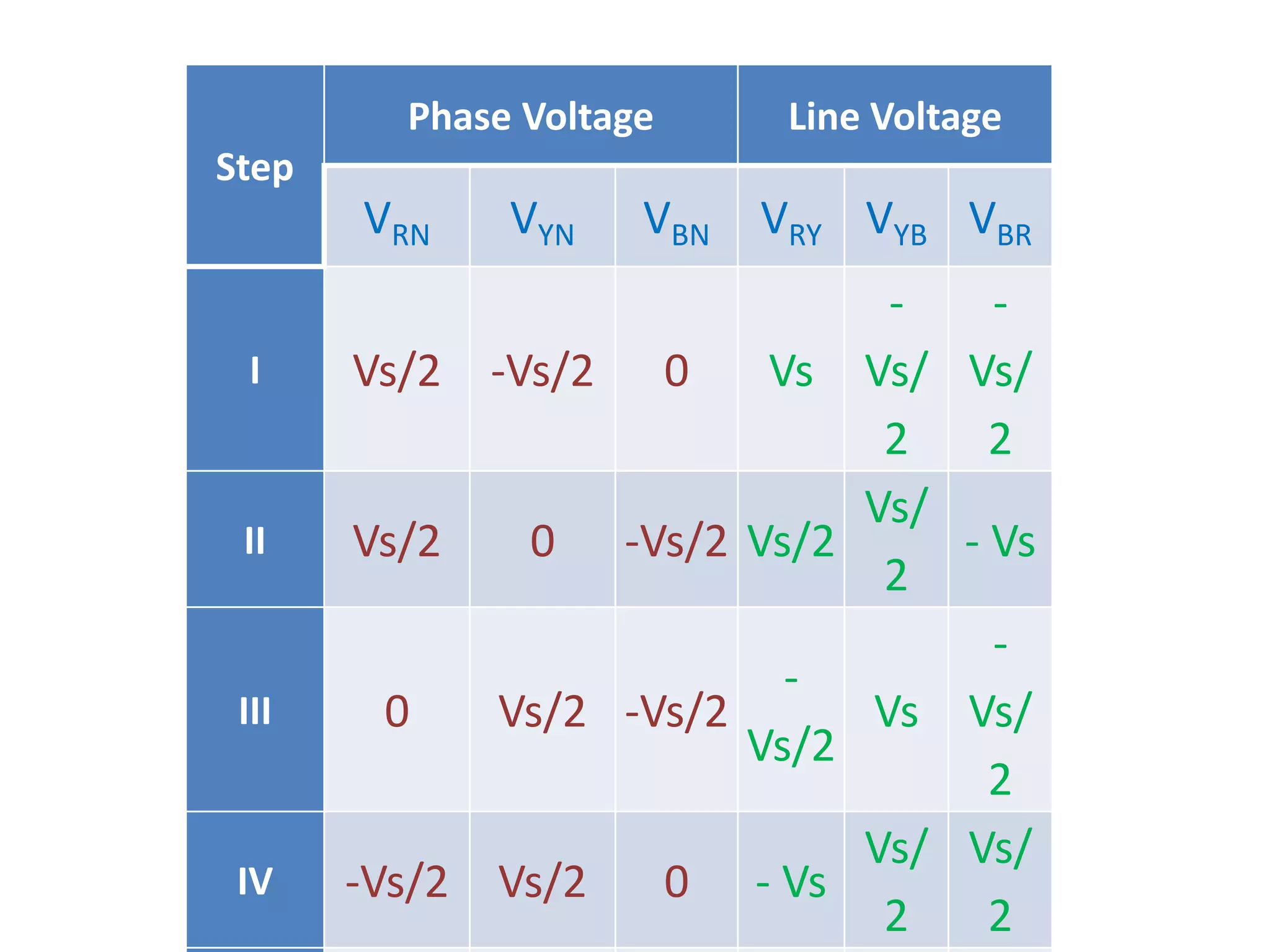
Calculation of phase and line voltages for Step I of the inverter operation.
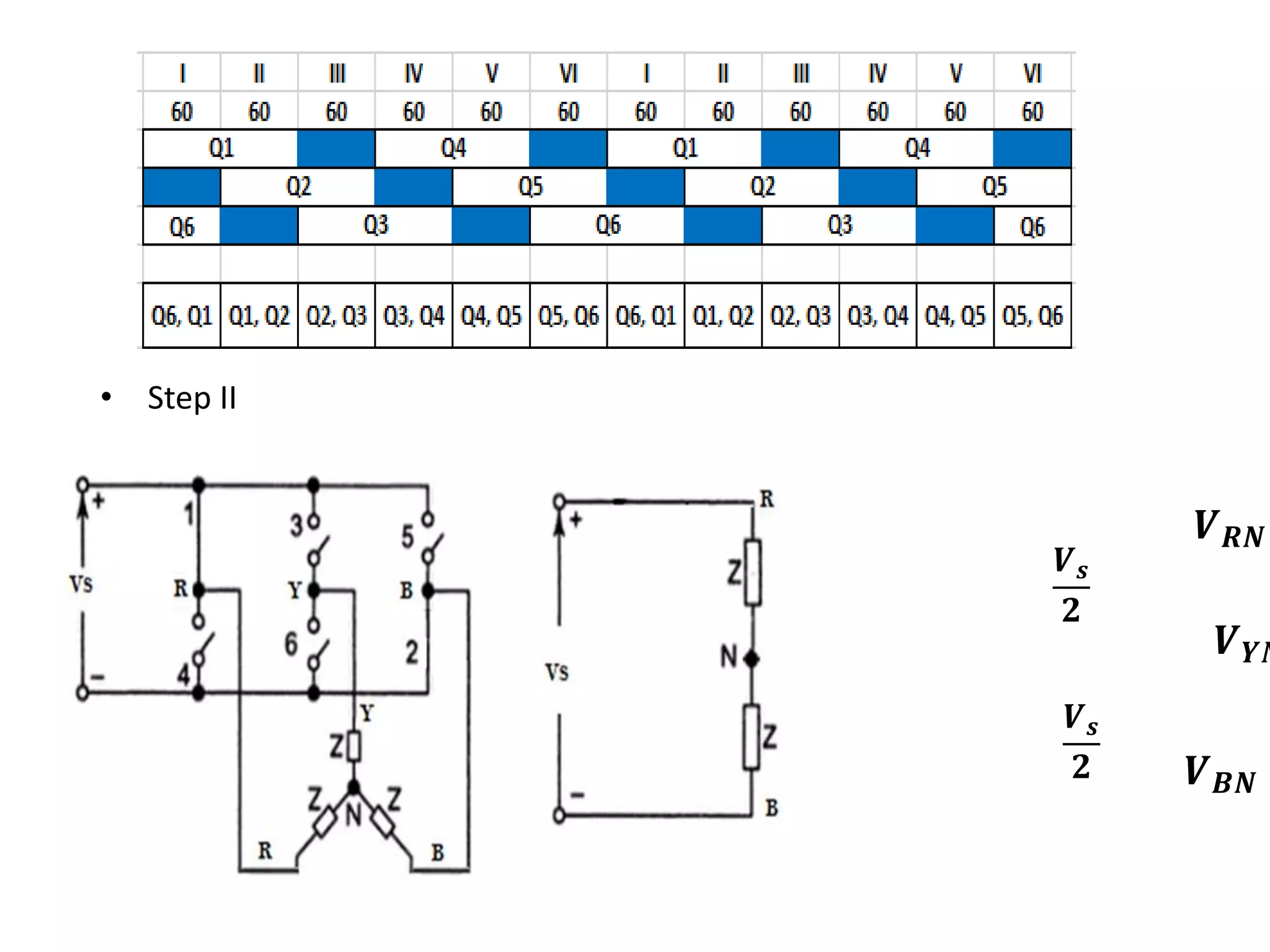
Voltage calculations for Step II, similar structure to Step I.
Detailed phase and line voltage calculations for Step III of the inverter operation.
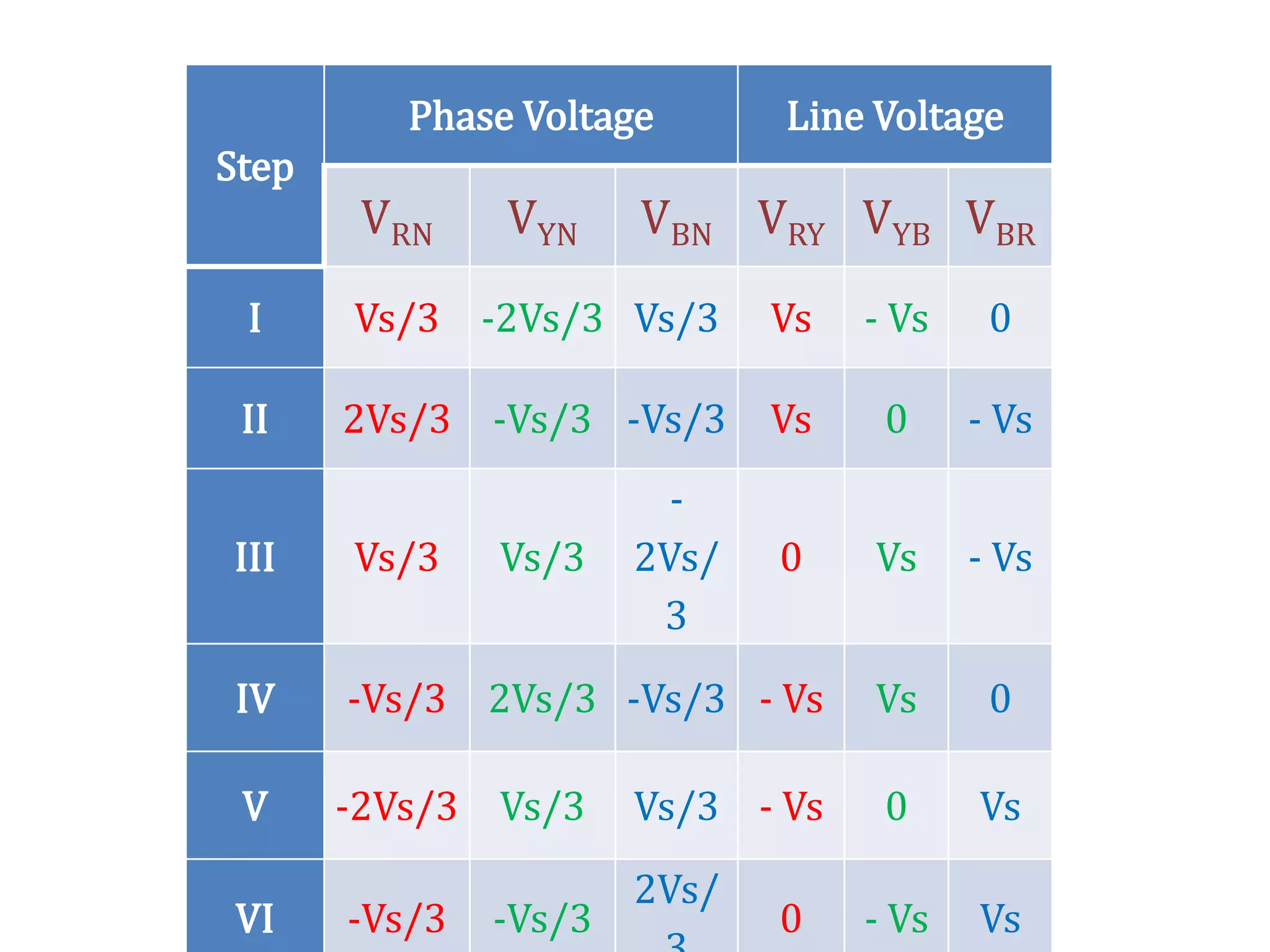
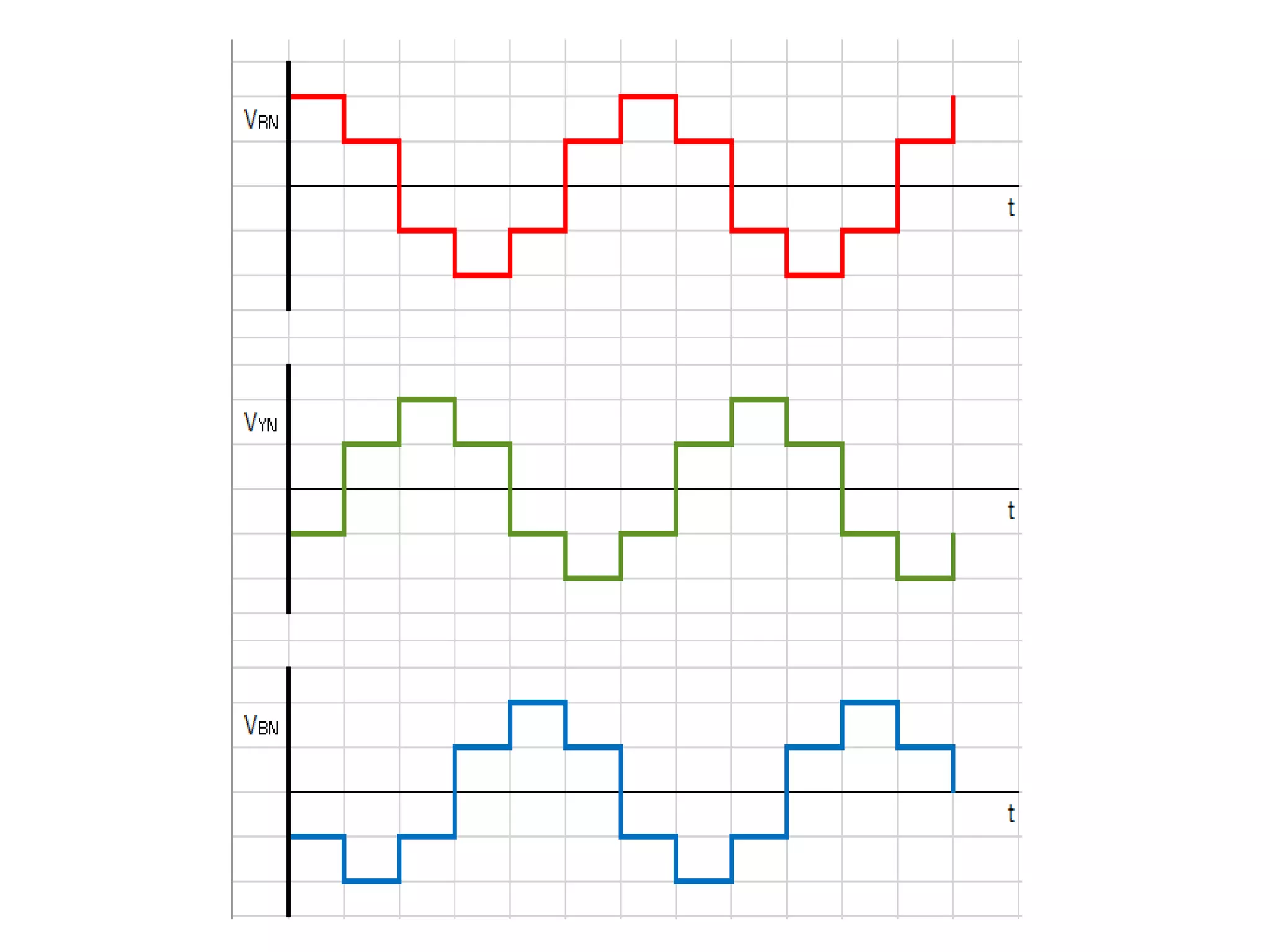
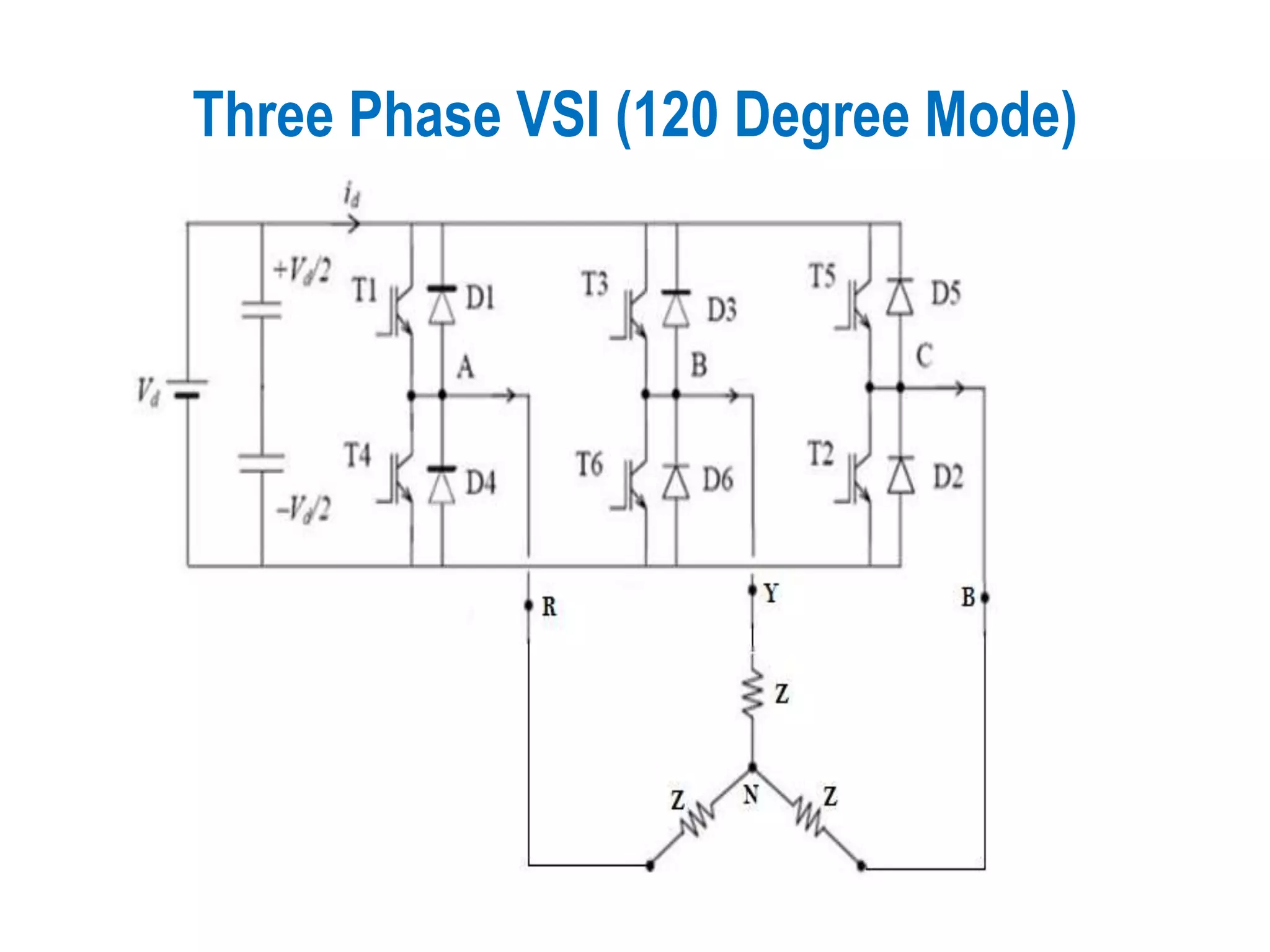
Overview of the Three Phase VSI operating in the 120-degree mode.
Phase and line voltage calculations for Step I in 120-degree mode.
Voltage calculations for Step II in 120-degree mode. Similar to Step I.
Detailed calculations for Step III, presenting phase and line voltages for the inverter.
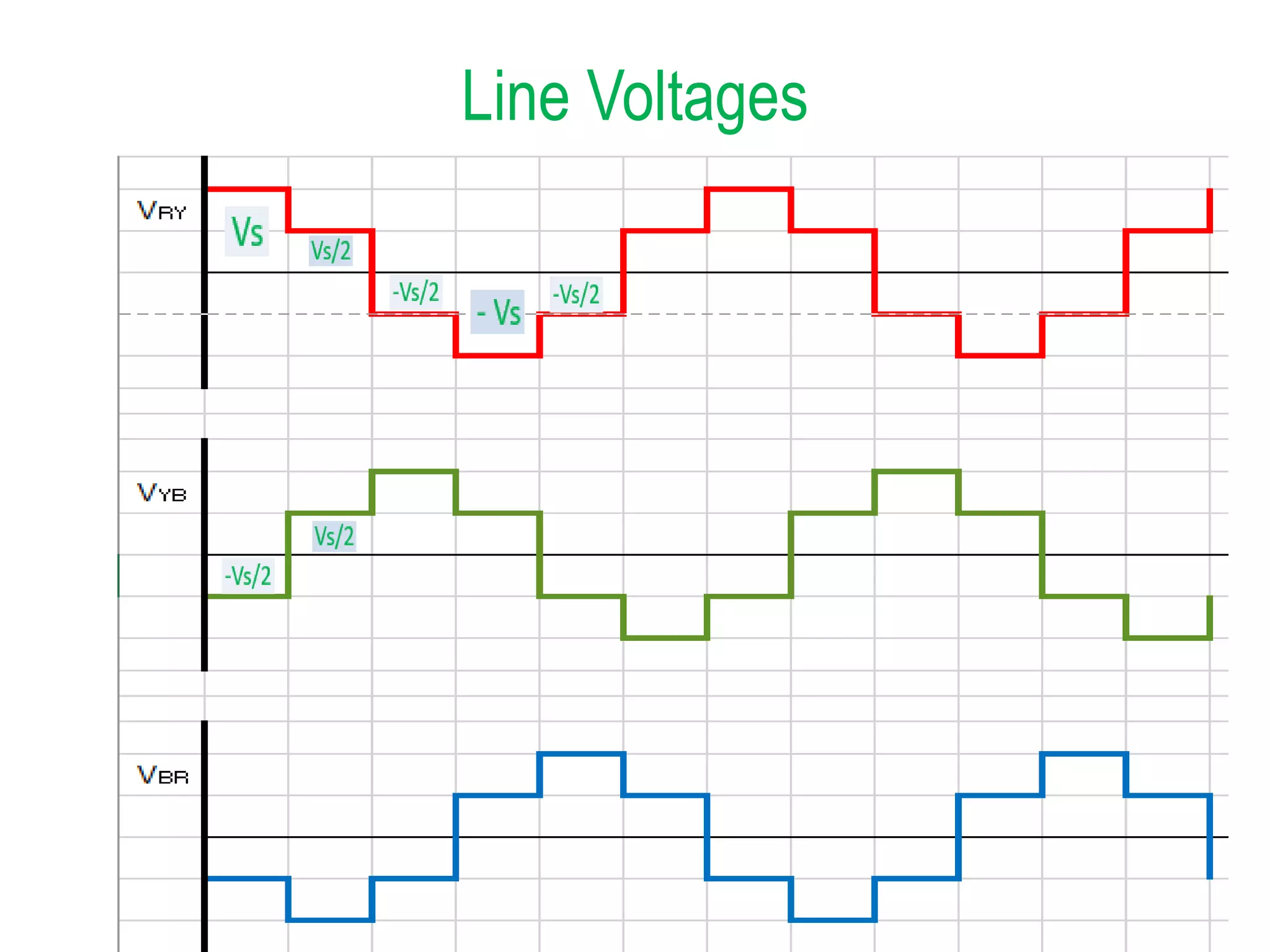
Summary of line voltage outputs for the discussed inverter configurations.






















