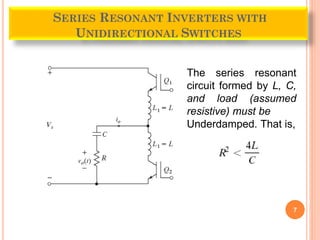
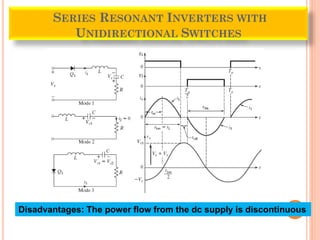
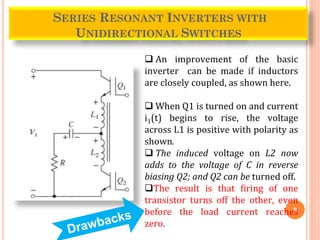
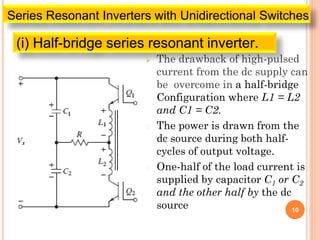
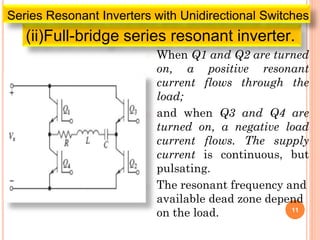
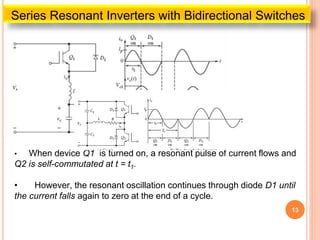
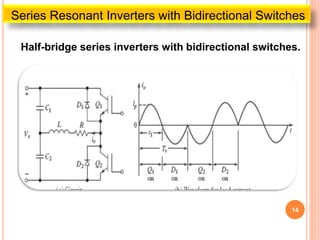
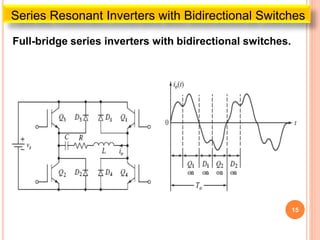
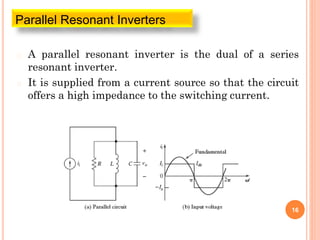
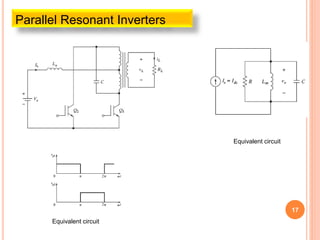
The document discusses different types of resonant pulse inverters. It begins by explaining the disadvantages of traditional pulse-width modulation controlled converters, such as high switching losses and electromagnetic interference. It then introduces resonant pulse converters which minimize these issues by forcing the voltage and current to zero during switching. The document outlines various resonant converter topologies, including series and parallel resonant inverters as well as classes of converters that achieve zero-voltage or zero-current switching. It provides examples of half-bridge and full-bridge configurations for series resonant inverters with both unidirectional and bidirectional switches. Finally, it briefly discusses the operation of parallel resonant inverters.