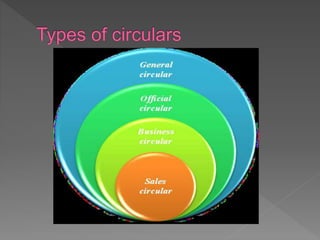
An e-mail is an informal method of communication between colleagues or fellow students. An agenda outlines the contents of an upcoming meeting and is sent with the meeting notice. Minutes are the official record of a meeting's proceedings and decisions, serving as a permanent reference. A circular letter is distributed to multiple customers at once without individual addresses. A bio-data, resume, and CV provide personal and professional details about a person, with the resume focused on qualifications for a specific job application.