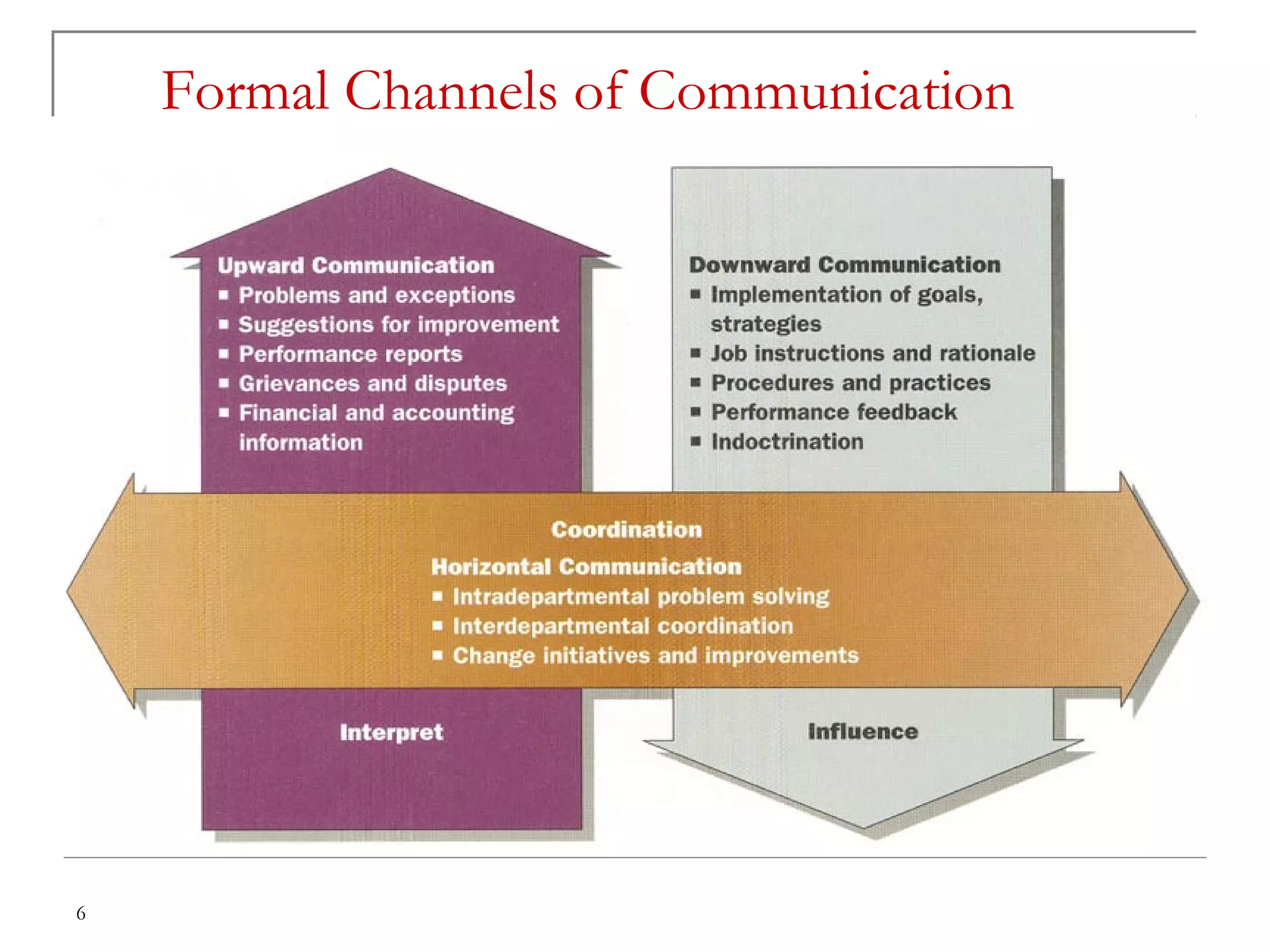
This document discusses communication skills and effective communication. It defines communication as a series of senses and describes the most common ways to communicate as speaking, writing, visuals, images, and body language. It then covers types of communication based on organization, flow, and expression. The document also discusses formal channels of communication like downward, upward, and horizontal communication. It identifies barriers to communication such as semantic, emotional, organizational, and personal barriers. Finally, it provides tips for developing good communication skills through exploring related skills, maintaining eye contact, using gestures, practicing, and ensuring communication is two-way, involves listening, utilizes feedback, and is clear and free of stress.