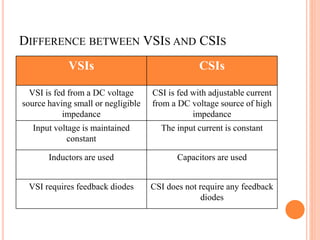
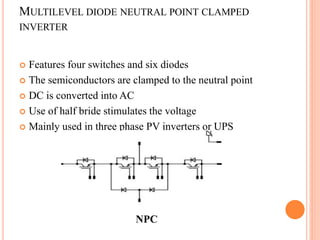
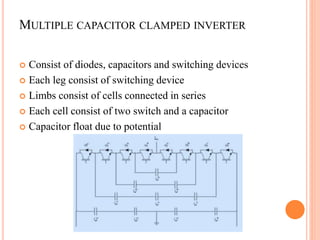
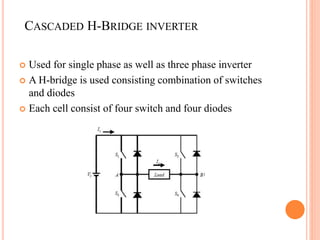
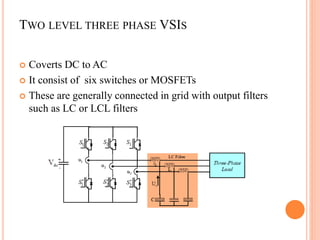
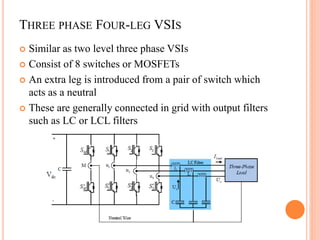
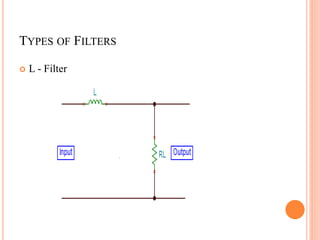
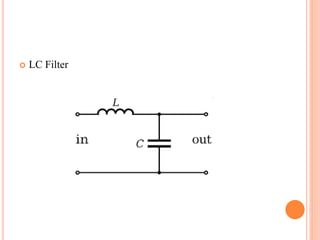
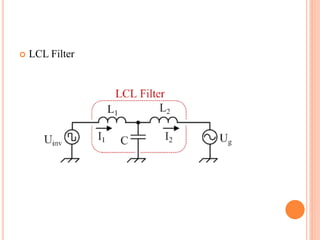
This document summarizes Preetam Jadhav's final seminar presentation on voltage source inverters. The presentation covers types of inverters including current source inverters and voltage source inverters. It then discusses different types of voltage source inverters such as multilevel diode neutral point clamped inverters and cascaded H-bridge inverters. The presentation also examines control systems, filter types, modulation schemes and excitation modes for voltage source inverters. Finally, it reviews conclusions and references presented in the seminar.