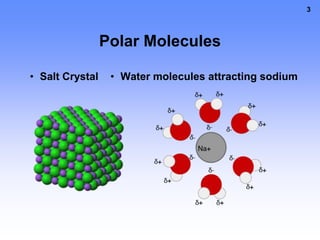
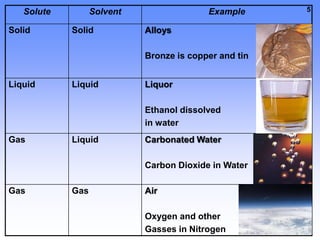
1. A solution is a mixture of two or more substances, where the substance that dissolves the others is the solvent and the substances that dissolve are solutes. For example, in salt water the solvent is water and the solute is salt.
2. Solubility is affected by temperature - more solute can dissolve in hot solvents than cool solvents. At saturation, cooling a solution can cause crystals to precipitate out.
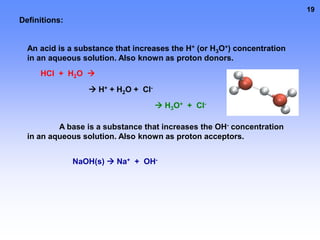
3. Electrolytes conduct electricity in solution due to dissociating into ions, while nonelectrolytes do not conduct electricity or dissociate. Electrolytes are important for functions like nerve signaling in the body.