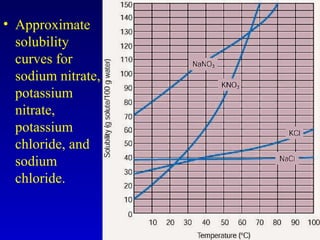
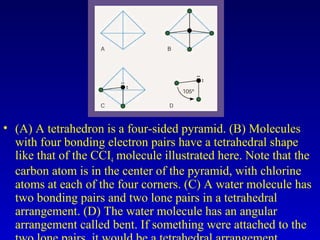
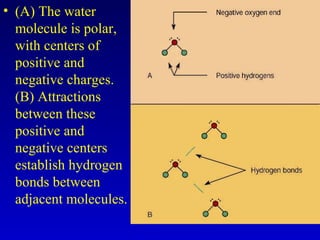
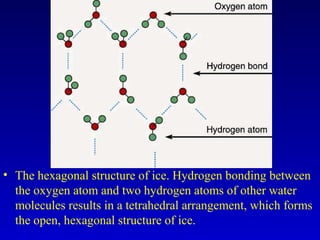
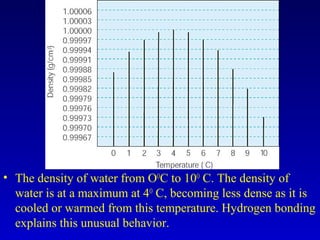
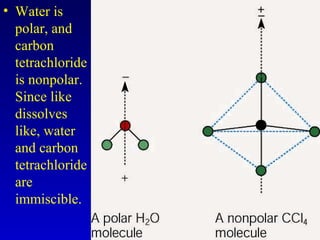
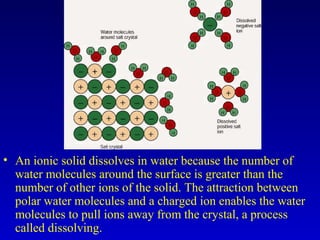
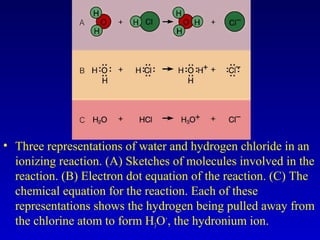
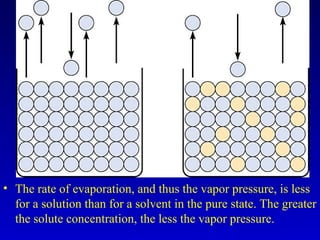
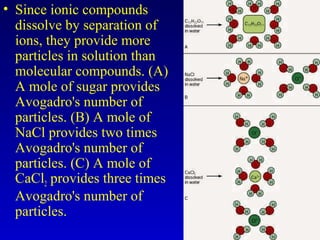
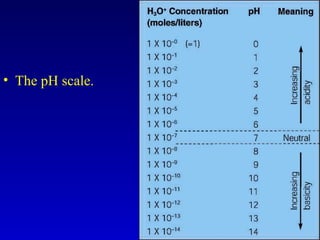
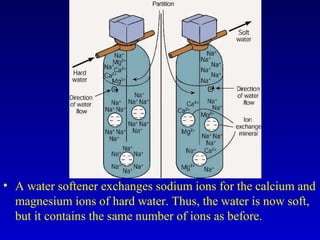
Water is a polar solvent that is able to dissolve many other polar substances through hydrogen bonding. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances, with water being the most common solvent. The concentration of a solution depends on the amount of solute dissolved and can be measured in various ways. Acids and bases are defined by whether they donate or accept protons in water, with pH used to measure their strength on a logarithmic scale. Salts are formed through neutralization of acids and bases. Buffers resist changes in pH through reactions between their components.