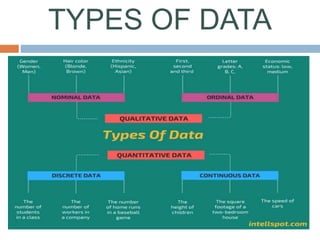
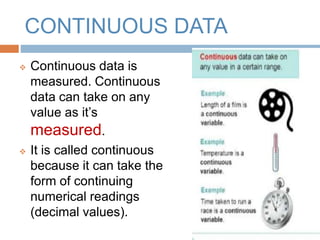
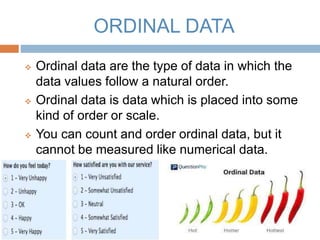
The document discusses the concept of data, defining it as collections of facts or information used for deriving conclusions. It categorizes data into quantitative and qualitative types, with quantitative data further divided into discrete and continuous data, and qualitative data into nominal and ordinal data. Each type of data is characterized by its nature, measurement, and organizational structure.