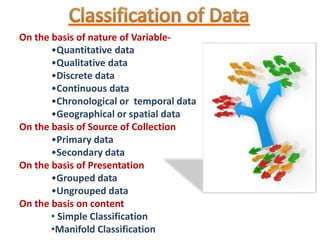
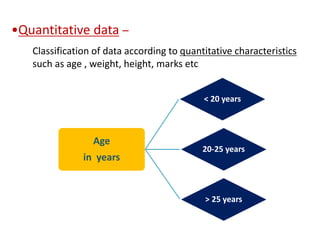
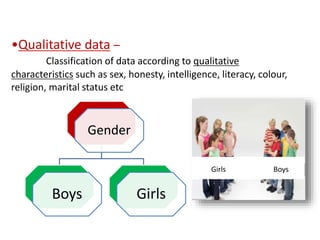
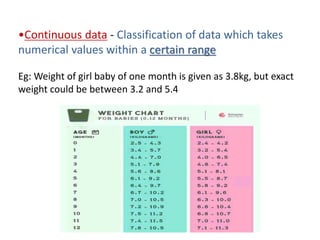
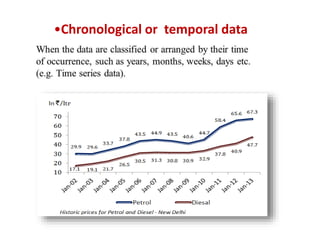
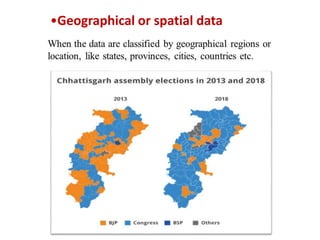
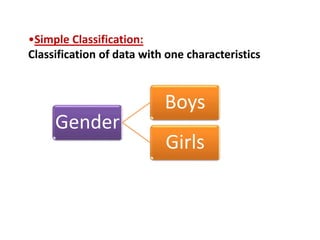
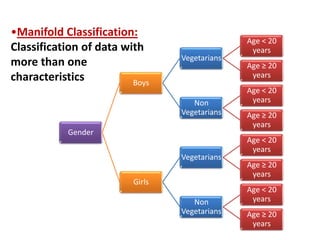
This document discusses different types of data classification. It defines classification as systematically grouping data based on common characteristics. There are several ways to classify data, including by the nature of the variable (e.g. quantitative, qualitative), source of collection (e.g. primary, secondary), presentation (e.g. grouped, ungrouped), and content (e.g. simple, manifold). Examples are provided for each type of classification.