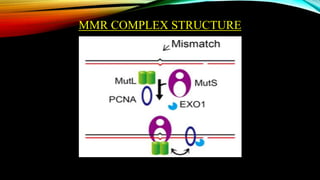
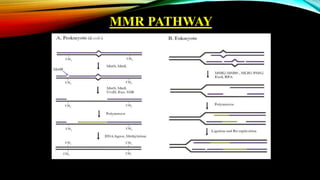
The document discusses mismatch repair (MMR), a critical DNA repair mechanism that fixes errors during DNA processing to maintain genomic stability and cellular homeostasis. It highlights the historical context of MMR's discovery by Tomas Lindahl, Paul Modrich, and Aziz Sancar, who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2015, and outlines the roles of various proteins involved in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic MMR systems. Additionally, the MMR pathway is emphasized for its importance in promoting apoptosis, genomic stability, and antibody diversity.






![BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE
It Promotes DNA Damage Induced Cell Cycle Arrest And Apoptosis.
It Promotes Genomic Stability.
It Increases “Antibody Diversity” By Promoting Immunoglobulin Class
Switching And Somatic Hypermutation.
It Promotes Trinucleotide Repeats (TNR) Expression [Under Research].
It Promotes Homologous Recombination.
It Promotes Interstrand Crosslink Repair Mechanisms.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mismatchrepair-210701112930/85/Mismatch-Repair-Mechanism-9-320.jpg)

