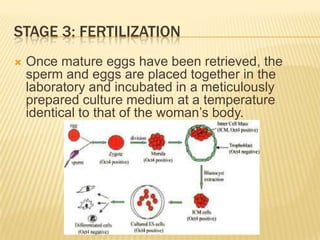
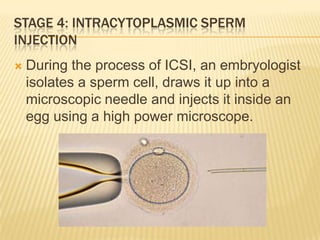
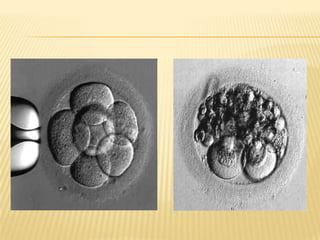
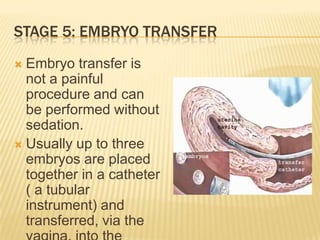
This document summarizes in vitro fertilization (IVF) and embryo transfer. [1] IVF involves removing eggs from a woman, fertilizing them with sperm in the lab, and then transferring the fertilized eggs (zygotes) into the uterus a few days later. [2] Reasons for IVF include infertility, which is increasingly prevalent worldwide. [3] The history, methodology, success rates, factors, and limitations of IVF are discussed over several stages: ovarian stimulation and monitoring, egg retrieval, fertilization, embryo transfer, and potential outcomes.